Motor skills development Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 6-9
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child’s motor skills while mastering addition and subtraction with our engaging worksheets designed for ages 6-9. These specially crafted activities foster fine motor development through exciting exercises, such as tracing, drawing, and interactive problem-solving. Our worksheets are a perfect blend of fun and functionality, encouraging kids to strengthen their hand-eye coordination while gaining confidence in math fundamentals. Each sheet is designed to make learning enjoyable, ensuring that children develop essential skills that will benefit their overall academic journey. Explore our diverse collection of motor skills development worksheets today and watch your child excel in math with ease!
Motor skills development is crucial for children aged 6-9, as it lays the foundation for their overall learning and well-being. During this critical stage, children refine both fine and gross motor skills, which are essential for everyday activities and academic tasks. Parents and teachers should recognize that motor skills directly impact a child's ability to write, manipulate tools, and engage in physical activities—all of which are tied to their confidence and success in school.
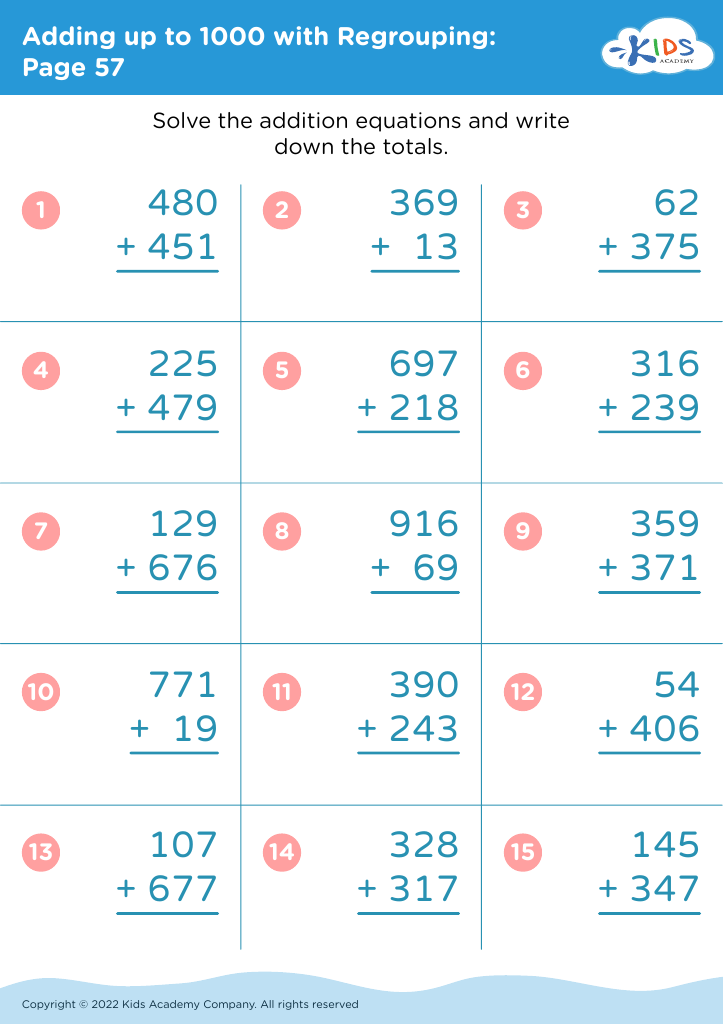
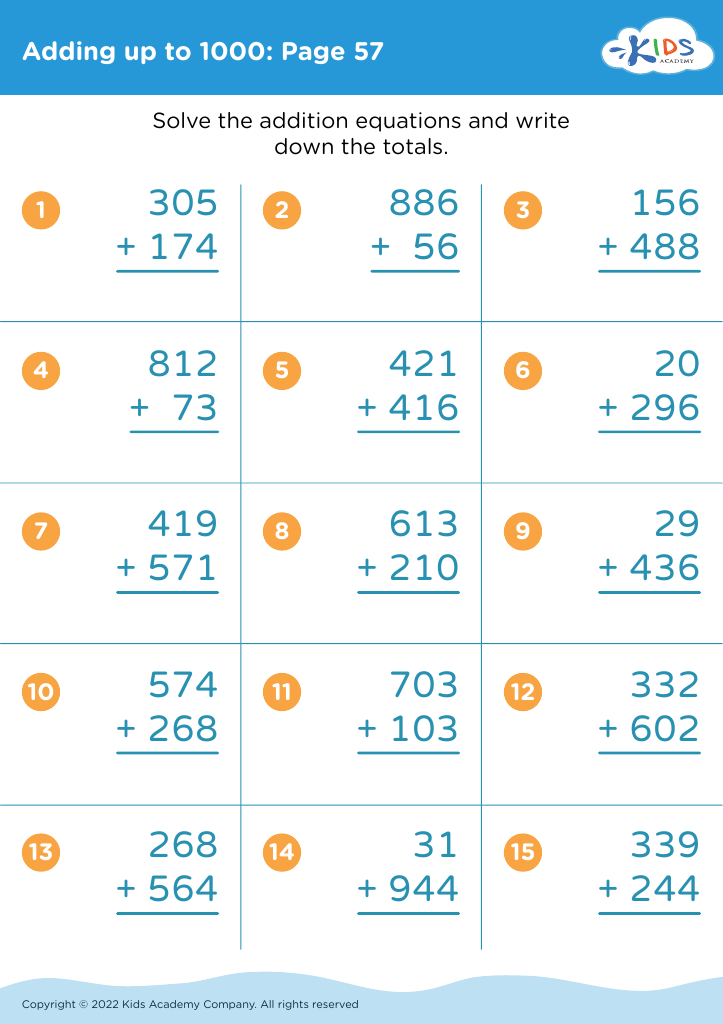
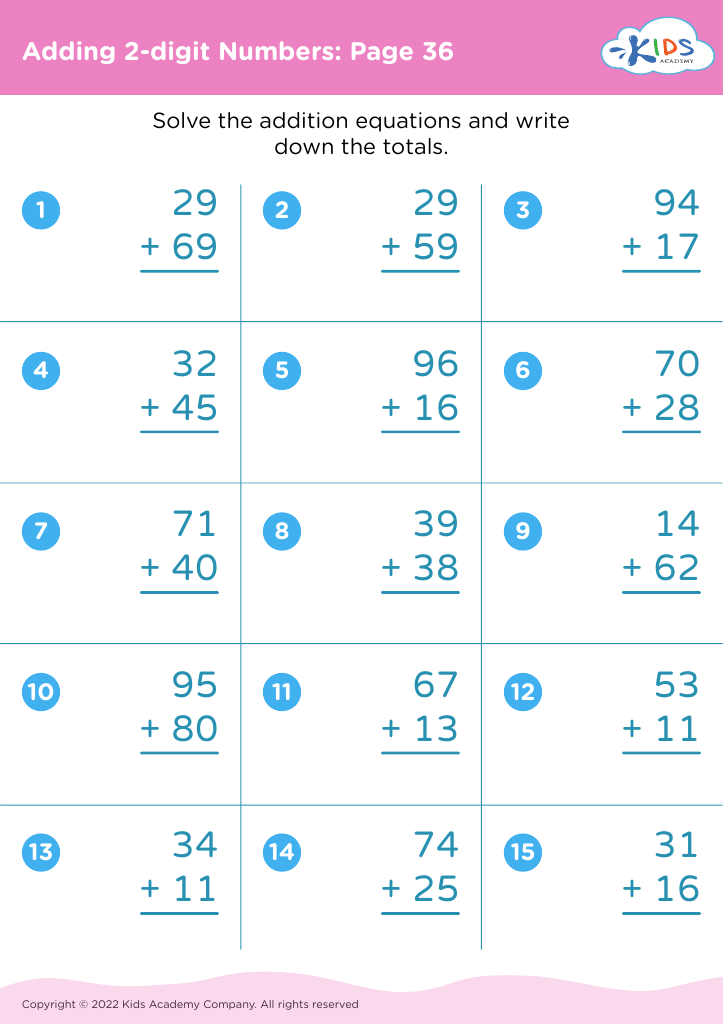
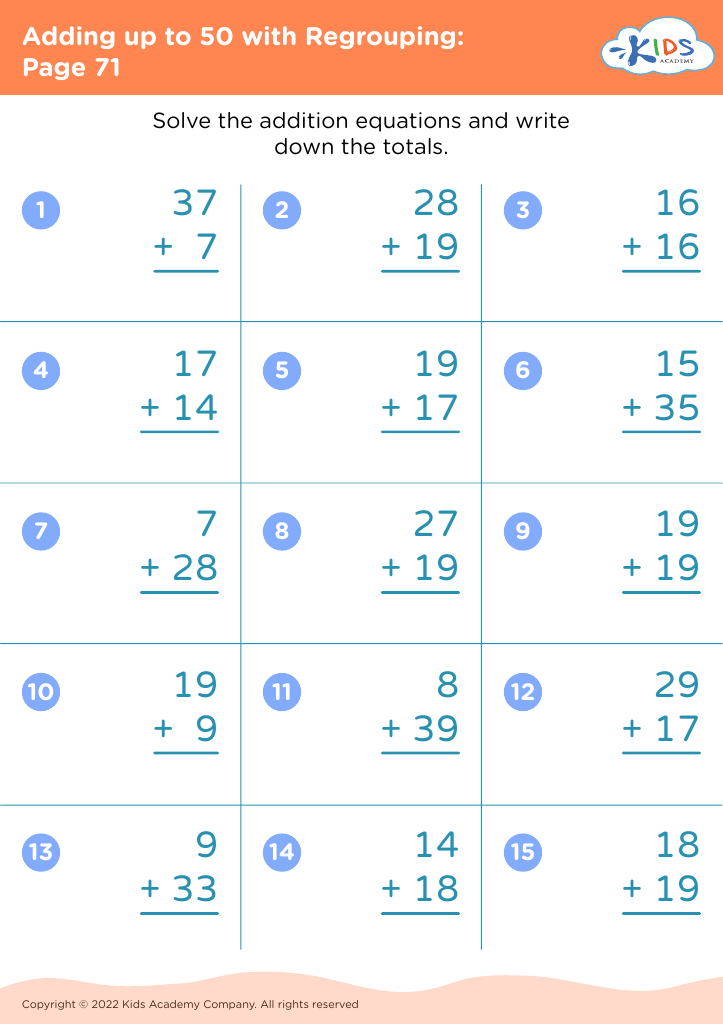
Additionally, when teaching addition and subtraction in this age group, incorporating physical activities that promote motor skills, such as using counters or drawing number lines, helps children grasp mathematical concepts more effectively. This kinesthetic approach makes learning more engaging and aids in memory retention.
When children have well-developed motor skills, they are more likely to participate actively in classroom activities, leading to enhanced collaboration and social skills. Parents and teachers, therefore, should prioritize motor skill development alongside math competencies. By fostering both skills, they equip children not just for academic success, but also for greater independence and confidence in their daily lives, setting them up for a positive future in both education and social interactions.