Visual discrimination Normal Geometry Worksheets for Ages 3-4
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Introduce your little one to the world of shapes and angles with our Visual Discrimination Normal Geometry Worksheets for Ages 3-4. Specially designed to develop young minds, these worksheets focus on honing visual discrimination skills. By engaging with simple geometric shapes and patterns, children enhance their ability to distinguish subtle differences, a key foundation for reading and math development. Each colorful and fun activity provides a stepping-stone in preschool education, fostering both cognitive skills and creativity. Ensure your child gains an early edge in learning through these expertly crafted, age-appropriate resources. Discover the excitement of geometric exploration today!

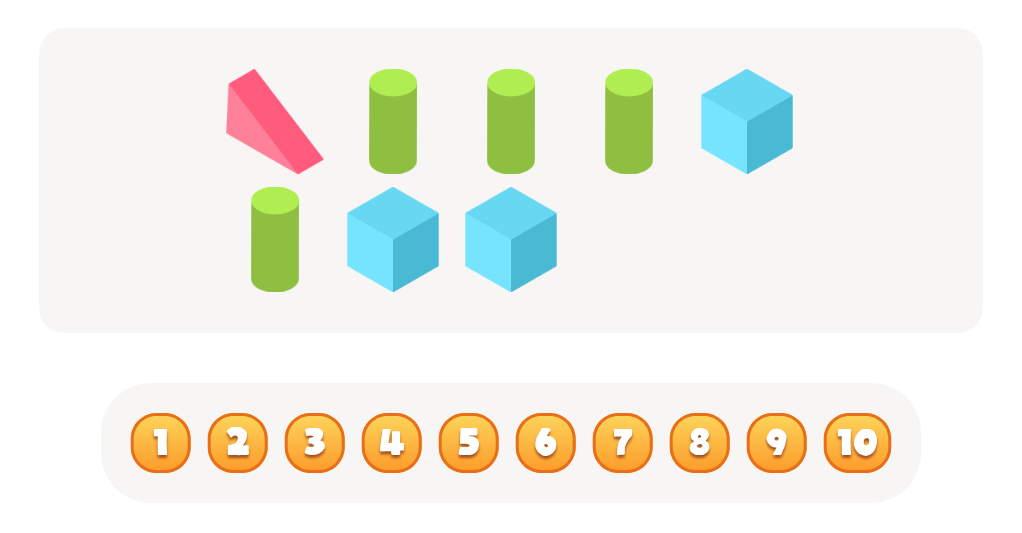
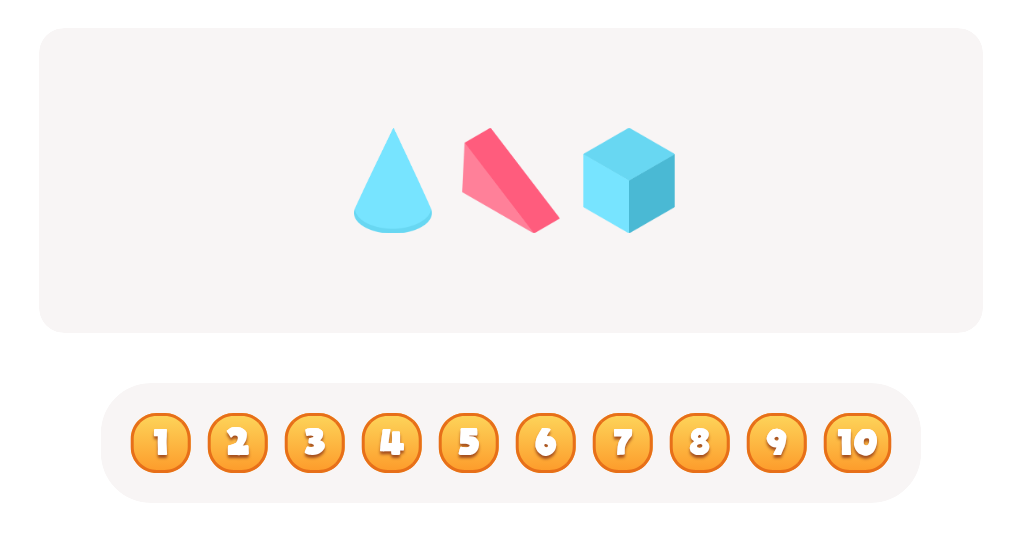
Practice Drawing Hexahedrons And a Rhombus Worksheet

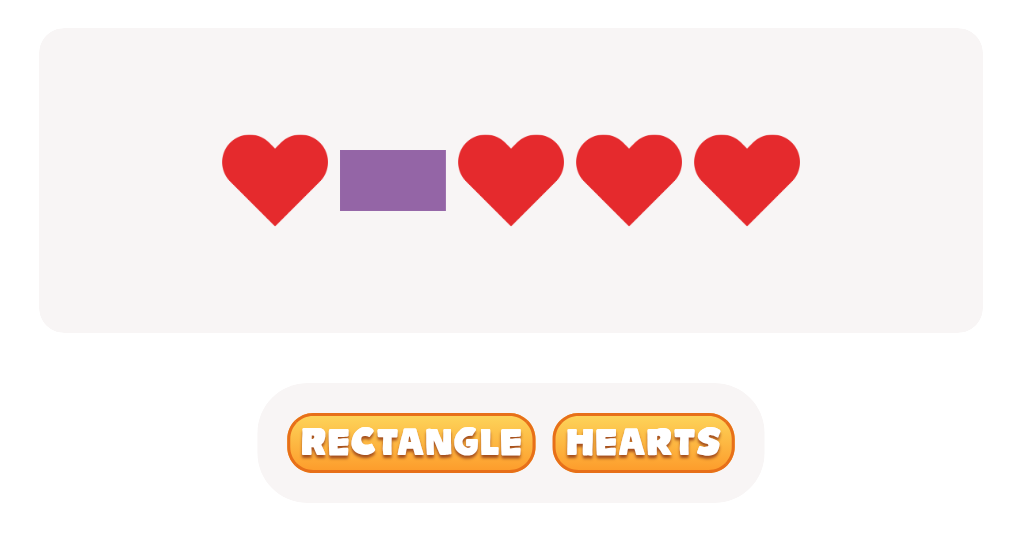
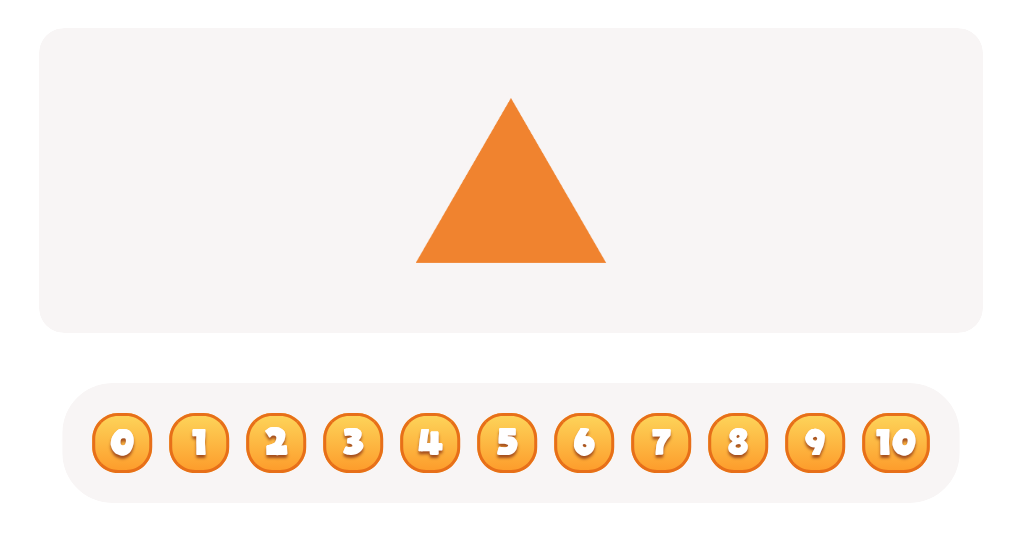
Comparing Triangles Squares Worksheet


Food Match Up Worksheet
Visual discrimination is a crucial preschool skill that pertains to a child's ability to recognize differences and similarities between objects, shapes, and patterns. At ages 3-4, this skill plays a vital role in a child’s cognitive development and paves the way for future learning.
Firstly, identifying shapes is foundational for both reading and mathematics. Visual discrimination helps children notice differences in letters, which is essential when learning to read. For example, distinguishing between "b" and "d" or "p" and "q" is easier when children have strong visual discrimination skills. This prevents confusion and aids in efficient reading and writing progress.
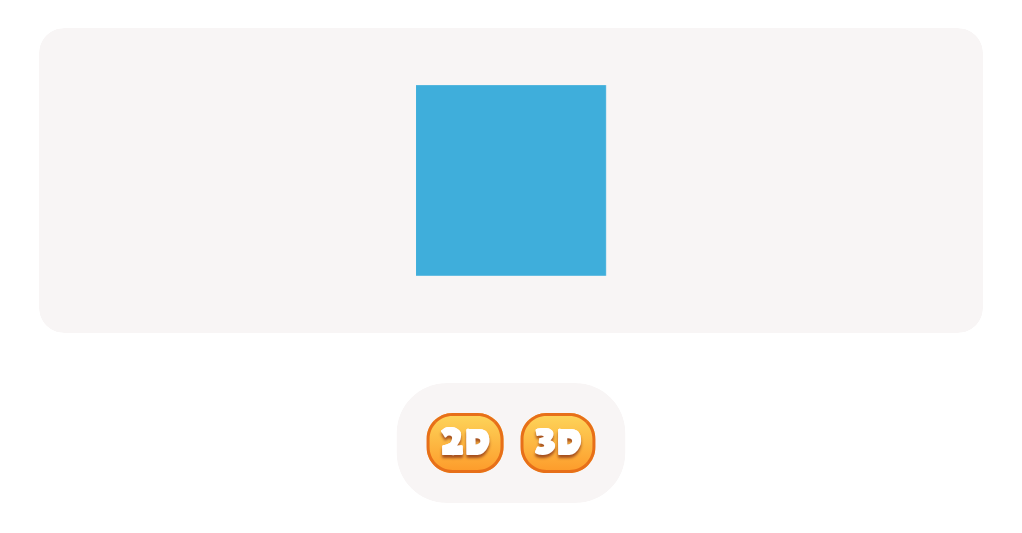
Secondly, recognizing and categorizing shapes is integral to early geometry. When children can sort and classify objects based on their shapes, they're practicing critical thinking and order, fundamentals in math. Understanding geometrical shapes—like circles, squares, and triangles—sets the stage for grasping more complex mathematical concepts later.
In addition, visual discrimination strengthens problem-solving and fine motor skills. Puzzles, shape-sorting activities, and drawing involve picking out differences and executing precise movements to match shapes or create patterns. These activities develop a young child’s coordination and analytical thinking.
Ultimately, fostering visual discrimination from a young age lays the groundwork for academic success, stimulating cognitive abilities that affect multiple areas of learning. Parents and teachers who prioritize activities enhancing this skill contribute positively to children's overall educational growth.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students