Fine Motor Skills Normal Worksheets for Ages 3-6 - Page 3
124 filtered results
-
From - To


Letter G Tracing Page

Easter Holiday Printable


Letter C Coloring Sheet

Counting Eggs Worksheet

First Words: Let's Trace Lines Worksheet


Preschool Geometry Match Up Worksheet


Find Uppercase Letters A, B, and C Worksheet
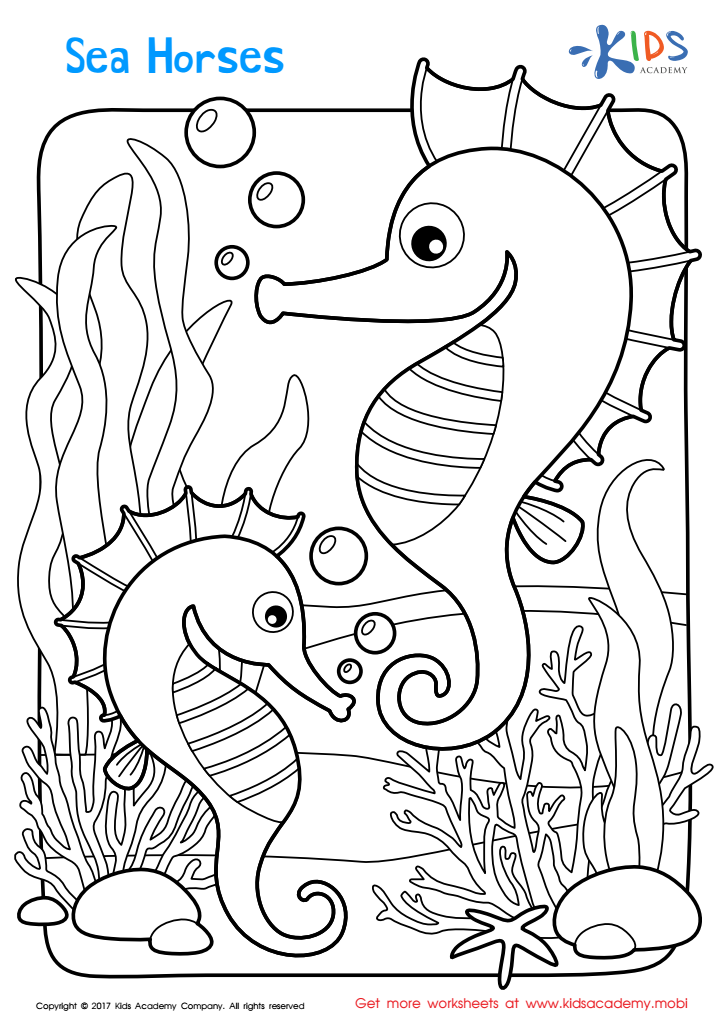


Sea Horses Printable


Learning to Draw Crescents And Triangles Worksheet


Find Lowercase Letters y z Worksheet


Letter E Tracing Worksheet


Prickly Nature Worksheet


Letter I Coloring Sheet


Let's Review! Big Letters Worksheet

Long and Short U Worksheet


Hungry Caterpillar Maze Worksheet

Recognizing Shape Sides Worksheet

The Wheels on the Bus Coloring Page

Sweet Counting - Part 2 Worksheet


Letter W Coloring Sheet


Feed the Whale Worksheet


Tracing Fun Worksheet
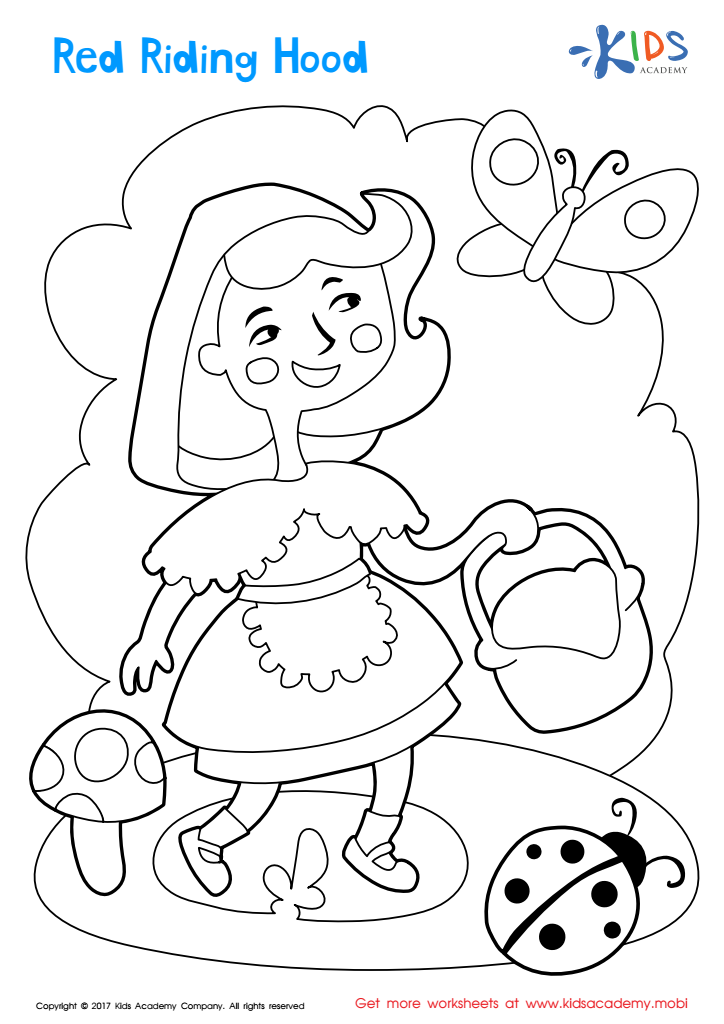


Red Riding Hood Coloring Page
Fine motor skills, which involve the coordination of small muscles in actions like writing, buttoning, and cutting, play a crucial role in childhood development for ages 3-6. During these formative years, children undergo substantial brain development, and fine motor skills are integral to many self-care tasks and learning activities. Mastery of these skills fosters independence and confidence, as children can dress themselves, feed themselves, and take on other personal responsibilities. Moreover, fine motor proficiency is foundational for academic success. Tasks such as holding a pencil, controlling scissors, and manipulating small objects are all essential for school readiness, impacting a child's ability to write, draw, and perform basic math operations.
Parents and teachers should be particularly vigilant about developing these skills because delays or difficulties can signal broader developmental issues that might need special attention. Integrating fine motor skill activities into early education settings doesn’t just ensure children achieve important milestones; it also identifies those who may require additional support. Engaging, playful activities that promote fine motor development, such as puzzles, bead threading, or simple crafts, provide a stimulating environment conducive to growth. By prioritizing and nurturing fine motor skills, parents and educators set children on a path for academic and personal success, turning everyday tasks into opportunities for growth and development.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















