Fine Motor Skills Normal Worksheets for Ages 4-6 - Page 3
124 filtered results
-
From - To


Letter G Tracing Page

Easter Holiday Printable


Letter C Coloring Sheet

Counting Eggs Worksheet

First Words: Let's Trace Lines Worksheet


Preschool Geometry Match Up Worksheet


Find Uppercase Letters A, B, and C Worksheet


Sea Horses Printable


Learning to Draw Crescents And Triangles Worksheet


Find Lowercase Letters y z Worksheet


Letter E Tracing Worksheet


Prickly Nature Worksheet


Letter I Coloring Sheet


Let's Review! Big Letters Worksheet

Long and Short U Worksheet


Hungry Caterpillar Maze Worksheet
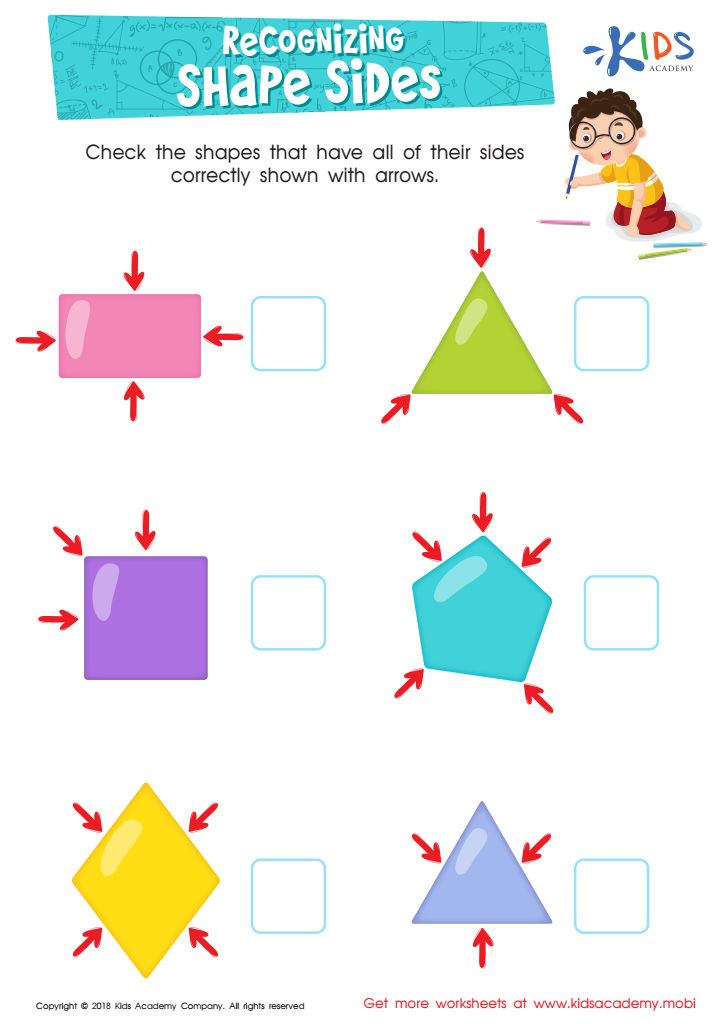

Recognizing Shape Sides Worksheet

The Wheels on the Bus Coloring Page
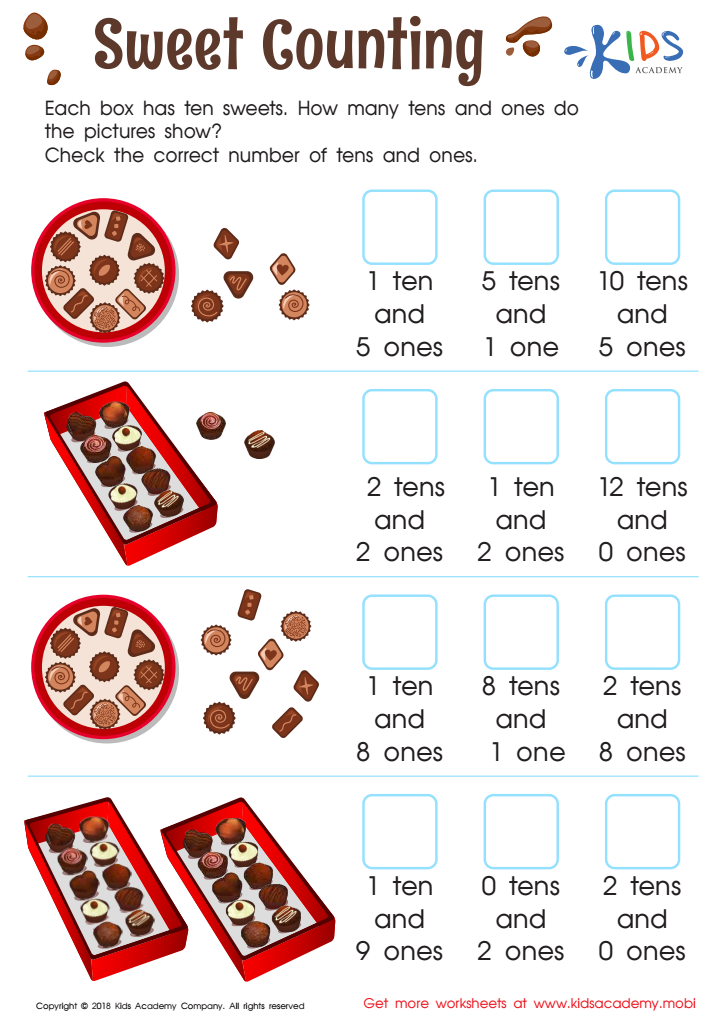

Sweet Counting - Part 2 Worksheet


Letter W Coloring Sheet


Feed the Whale Worksheet


Tracing Fun Worksheet


Red Riding Hood Coloring Page
Fine motor skills are essential for young children ages 4-6 as they involve the use of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are crucial for everyday activities and academic success. Parents and teachers should prioritize the development of fine motor skills during these formative years for several reasons:
-
Academic Readiness: Fine motor skills are foundational for writing, drawing, and using scissors—key activities in early education. Children who struggle with these skills might face difficulties in performing classroom tasks, potentially affecting their overall academic performance and self-confidence.
-
Self-Care Independence: Mastering fine motor skills enables children to perform essential self-care tasks such as buttoning clothes, tying shoelaces, and using utensils. This independence bolsters their confidence and plays a crucial part in their daily routines.
-
Cognitive Development: Engaging in activities that develop fine motor skills also supports cognitive development. Tasks such as puzzles and games that require precise finger movements foster problem-solving abilities and hand-eye coordination.
-
Social Interaction: Children who are proficient in fine motor tasks can more easily participate in group activities and play, which fosters social skills and peer relationships.
Ensuring that children develop strong fine motor skills lays the groundwork for ongoing physical, cognitive, and social development, supporting their overall growth and success both in and out of school.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students

















