Fine Motor Skills Normal 2D Shapes Worksheets for Ages 6-9
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child’s fine motor skills with our engaging 2D shapes worksheets designed specifically for ages 6-9. These worksheet activities combine fun and education, helping young learners master essential skills while exploring geometric shapes. Perfect for home or classroom use, each worksheet encourages creativity and coordination through tracing, coloring, and shape recognition exercises. As children interact with vibrant designs and hands-on tasks, they will improve their hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Our carefully crafted activities are aligned with early education standards, ensuring that children grasp foundational math concepts while developing critical fine motor skills. Empower your child’s learning journey today!


Preschool Geometry Match Up Worksheet


Learning to Draw Crescents And Triangles Worksheet
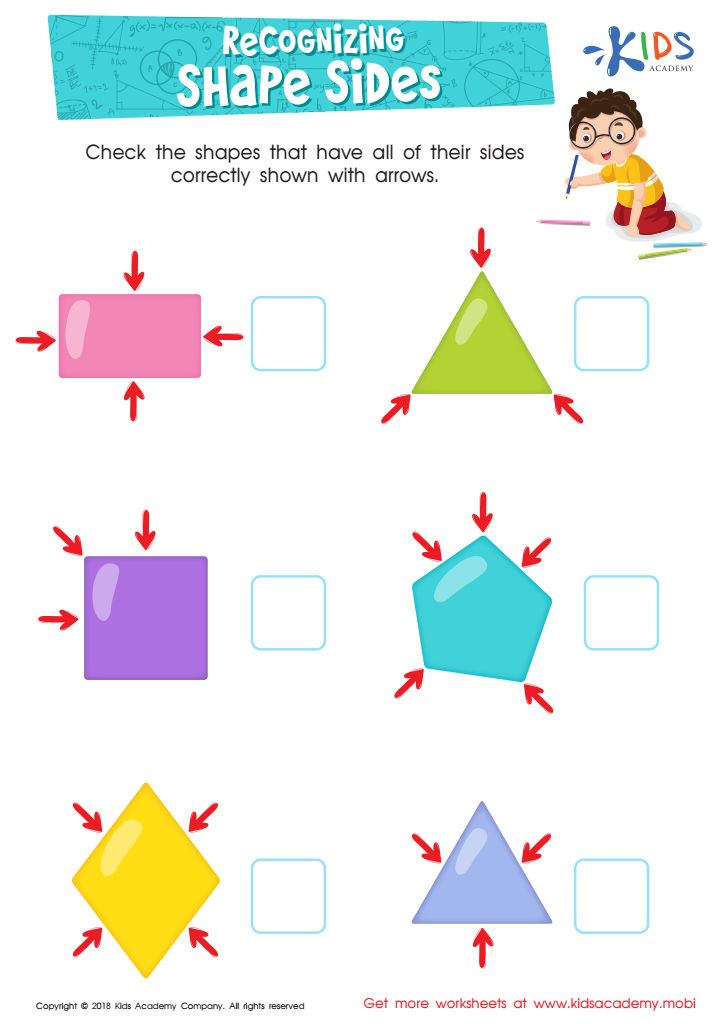

Recognizing Shape Sides Worksheet


Easy Drawing of Ovals And Rectangles Worksheet
Fine motor skills are essential for children's overall development, especially within the 6-9 age range when they are building foundational abilities. Understanding and manipulating normal 2D shapes—such as squares, circles, triangles, and rectangles—enhances these skills in several ways.
Firstly, fine motor skills are crucial for tasks such as writing, cutting, and drawing. Mastery of 2D shapes aids children in forming letters, numbers, and even more complex figures, bolstering their handwriting and artistic skills. Second, recognizing and working with shapes supports cognitive development by enhancing spatial awareness and geometric understanding. These concepts are building blocks for future mathematics learning.
Additionally, engaging in activities focused on shapes—like cutting out, coloring, and arranging—allows children to practice precision and coordination, nurturing their hand-eye coordination essential for everyday tasks. This engagement not only is a source of fun and creativity but can also reduce frustration in academic settings, bolstering confidence.
Finally, when parents or teachers emphasize the importance of fine motor skills and 2D shape recognition, they lay the groundwork for future learning and overall cognitive growth. Given their pivotal role in academic success, caregivers should prioritize these skills in everyday activities and learning experiences.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students