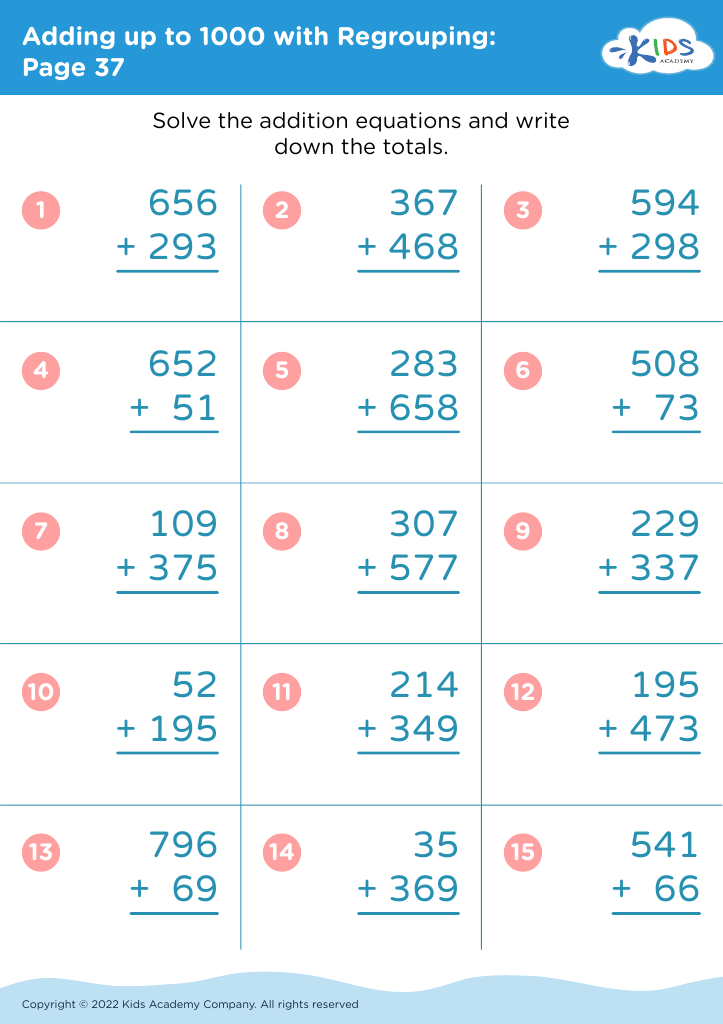
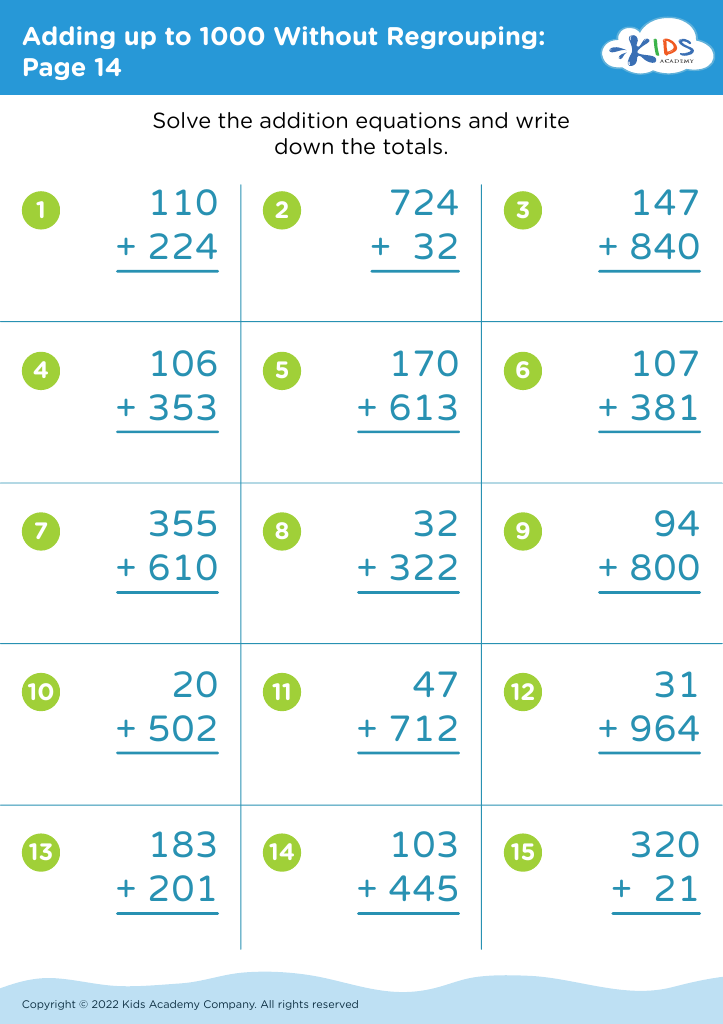
Fine motor skills development Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Explore our engaging collection of fine motor skills development worksheets focused on addition and subtraction for children ages 3-8. Our worksheets are designed to strengthen essential hand-eye coordination and dexterity while making math fun and accessible. Each activity encourages little hands to practice writing numbers, counting objects, and solving simple math problems in a playful manner. These interactive sheets not only enhance early math skills but also build confidence in young learners. Perfect for teachers and parents seeking to support their child's educational journey, our worksheets are easy to print and ready to use. Start the adventure in learning today!
Fine motor skills development is crucial for children aged 3-8 as it significantly impacts their ability to perform everyday tasks and foundational academic skills, including addition and subtraction. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are essential for tasks such as writing, drawing, cutting, and manipulating objects. As children engage in activities that enhance fine motor skills, they are simultaneously building visual-motor integration, hand-eye coordination, and overall physical dexterity.
Moreover, fine motor skills play a vital role in mathematical understanding. For instance, when children use tools such as counters or tools for hands-on activities involving addition and subtraction, their grip and control over these objects enable them to visualize and grasp mathematical concepts effectively. Such sensory experiences help children understand quantity, number relationships, and problem-solving strategies.
Parents and teachers should prioritize fine motor skills development by incorporating play and practical activities into learning experiences. This focus not only supports academic success in mathematics but also fosters independence, confidence, and a love for learning, ensuring that children are well-equipped for future educational challenges and life skills. Investing time and resources in fine motor development ultimately lays a solid foundation for holistic child growth.