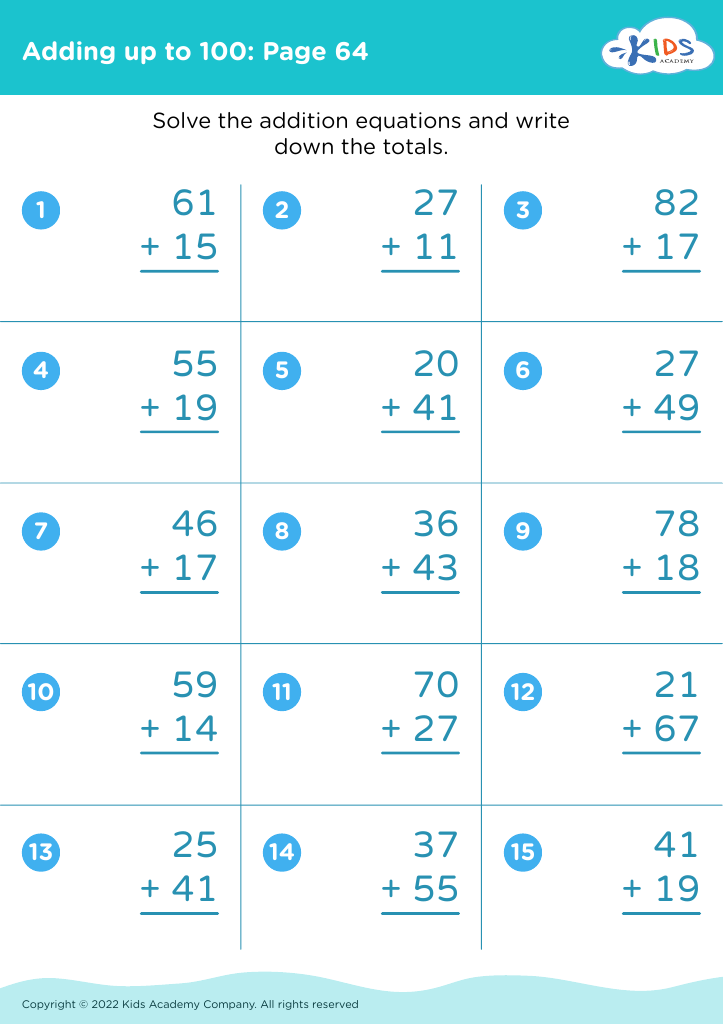
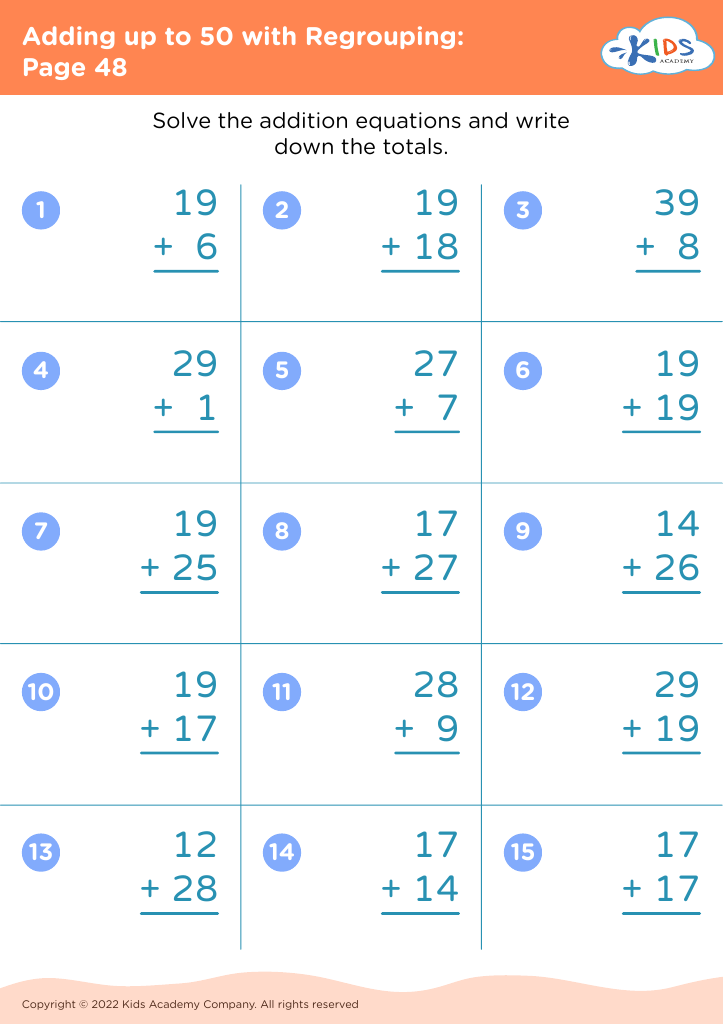
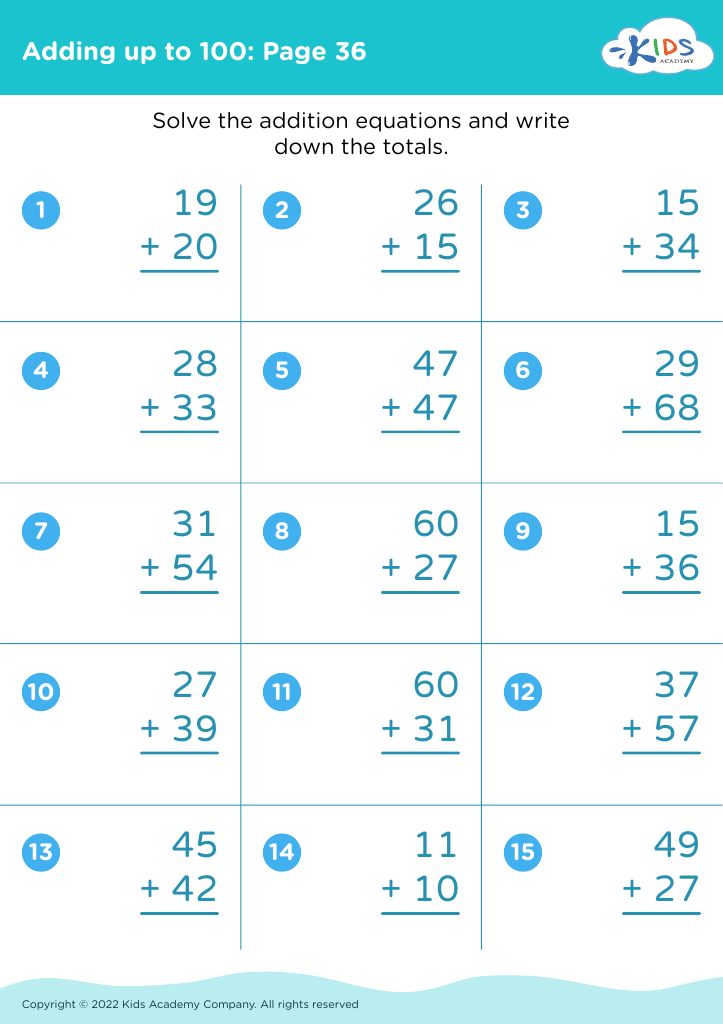
Numerical problem solving Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Welcome to our engaging "Numerical Problem Solving Addition & Subtraction Worksheets" designed for children aged 3-8! These worksheets provide a fun and interactive way for young learners to develop essential math skills. Tailored for various learning levels, our activities focus on mastering addition and subtraction through relatable scenarios that inspire critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Each worksheet is filled with colorful illustrations and hands-on exercises, making math enjoyable and accessible. Perfect for classrooms or at-home learning, these resources foster confidence and competence in early math skills. Equip your child’s journey to numerical fluency with our delightful worksheets today!
Numerical problem solving, particularly addition and subtraction, is a foundational skill for children ages 3-8, and parents and teachers should prioritize it for several reasons. First, these skills form the basis for all future mathematics learning. Early mastery of addition and subtraction helps children understand more complex concepts such as multiplication, division, and basic algebra later on.
Moreover, problem-solving enhances critical thinking and reasoning abilities. When children engage in mathematical questions, they learn to analyze situations, identify solutions, and think logically—skills that extend beyond math into everyday life challenges.
Additionally, early numeracy builds confidence. Children who grasp addition and subtraction feel more empowered to tackle mathematical problems as they progress through their education. This confidence can mitigate math anxiety, leading to a more positive attitude toward learning in general.
Furthermore, engaging in fun, practical problem-solving activities fosters a strong parent-child or teacher-student relationship. By participating together, caregivers can support their child’s development and reinforce learning in a nurturing environment. Ultimately, fostering a solid foundation in addition and subtraction is essential for a child's cognitive development, academic success, and overall lifelong learning.