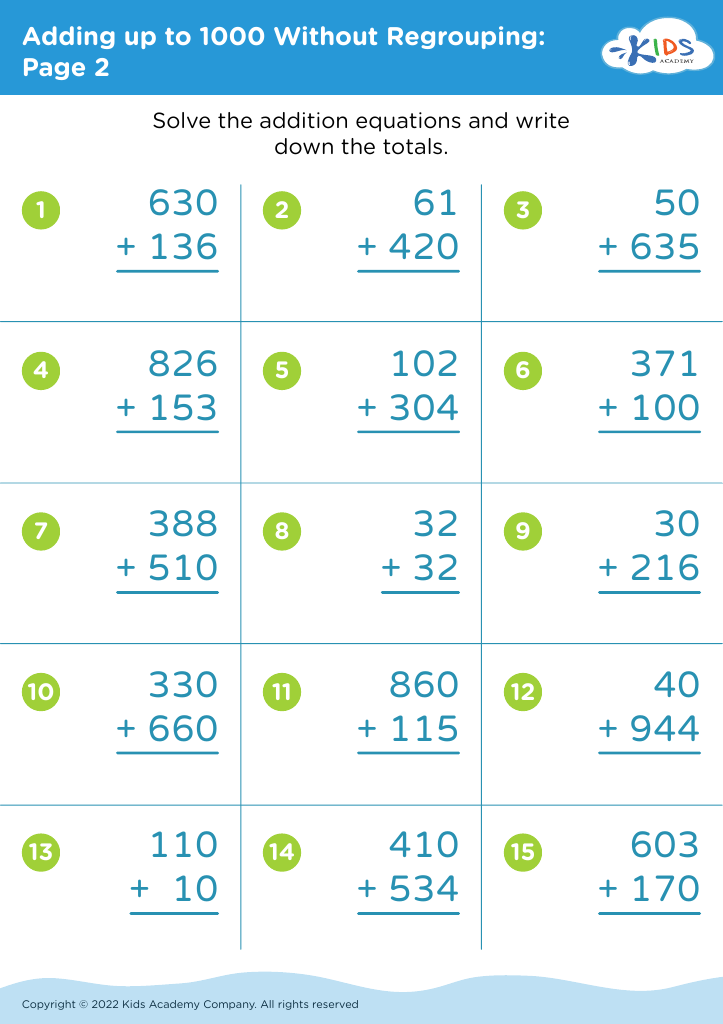
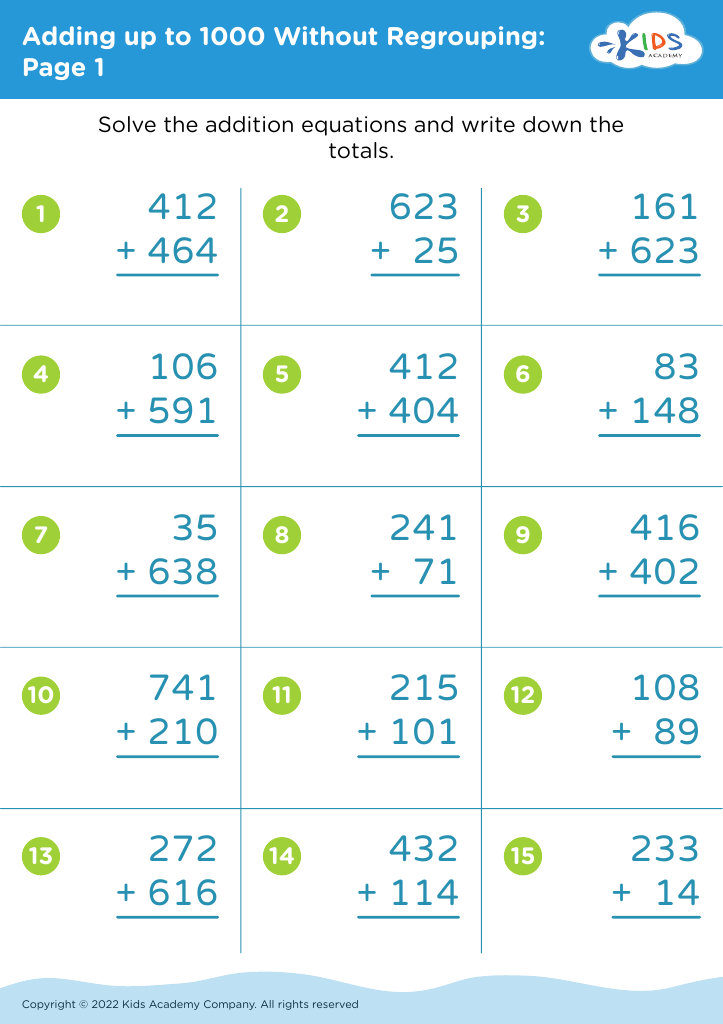
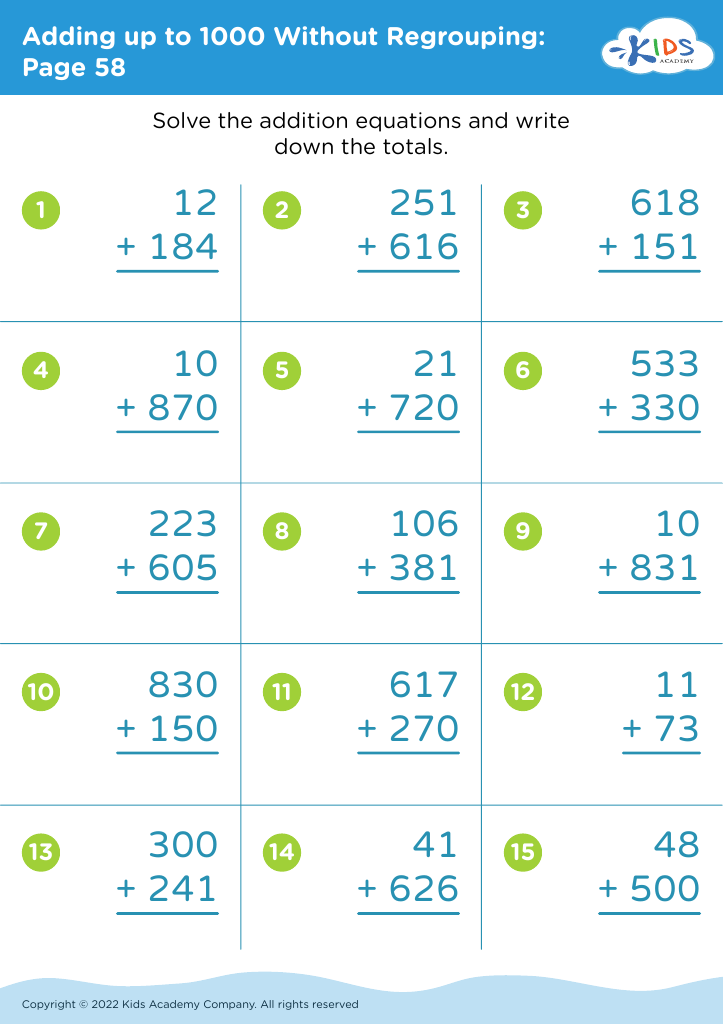
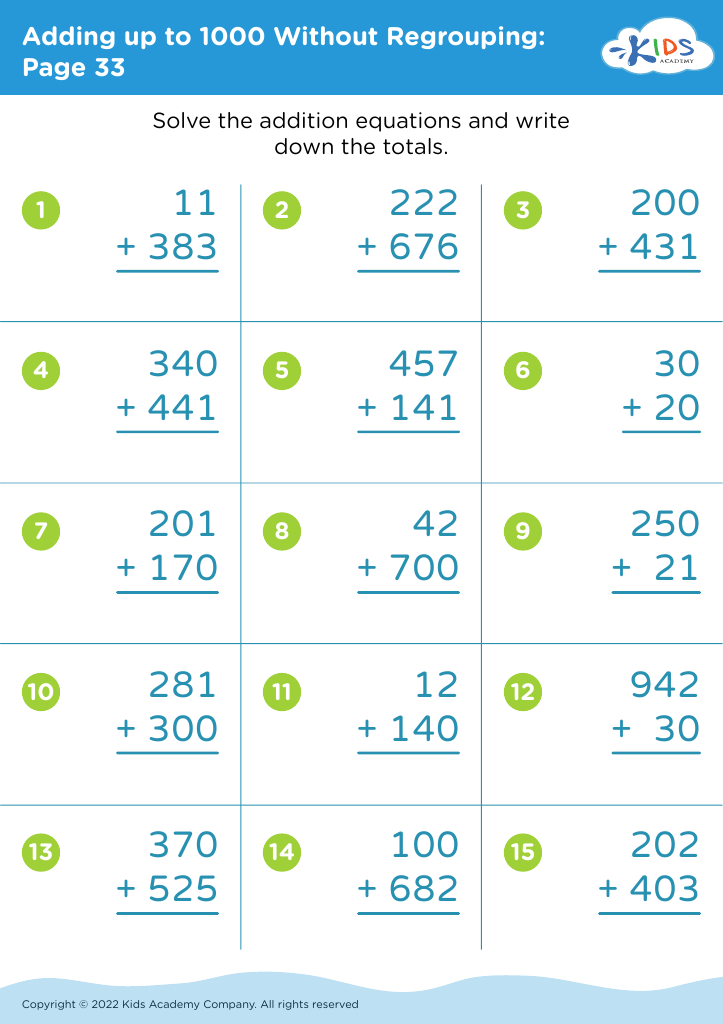
Counting practice Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 3-9
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's math skills with our "Counting Practice: Adding Up to 1000 Without Regrouping" worksheets, designed specifically for ages 3-9! These engaging worksheets provide a perfect platform for young learners to practice addition and boost their confidence in basic math. Children will explore addition techniques without regrouping, helping them understand concepts in a fun and approachable manner. With colorful designs and varying difficulty levels, students will enjoy hours of educational entertainment that supports their cognitive development. Perfect for classrooms or home learning, these worksheets make mastery of numbers enjoyable and effective. Start your child’s math journey today!
Counting practice, particularly adding up to 1000 without regrouping, is vital for young learners aged 3 to 9. This foundational skill fosters a strong number sense, aiding in the development of mathematical concepts they will encounter in higher grades. Engaging children in counting activities interacts with critical cognitive skills, enhancing their problem-solving abilities and logical reasoning.
For parents and teachers, encouraging such practice helps to instill confidence in children as they learn to interact with numbers. Making math fun and approachable helps eradicate math anxiety, often seen in older students. Early counting skills lead to greater proficiency in later arithmetic operations and can also strengthen language skills as children learn to verbalize quantities.
Moreover, developing intuition for numbers at a young age cultivates a lifelong appreciation for math and its applications in everyday life, from budgeting to cooking. Encouraging counting up to 1000 without regrouping advances their grasp of grouping and makes larger numbers more tangible and salient.
Involving strategies like games, manipulatives, and visual aids, parents and teachers can make this learning experience enjoyable, ensuring that children see mathematics as an engaging and relevant part of their world. This foundational approach fosters strong learners prepared for academic challenges ahead.