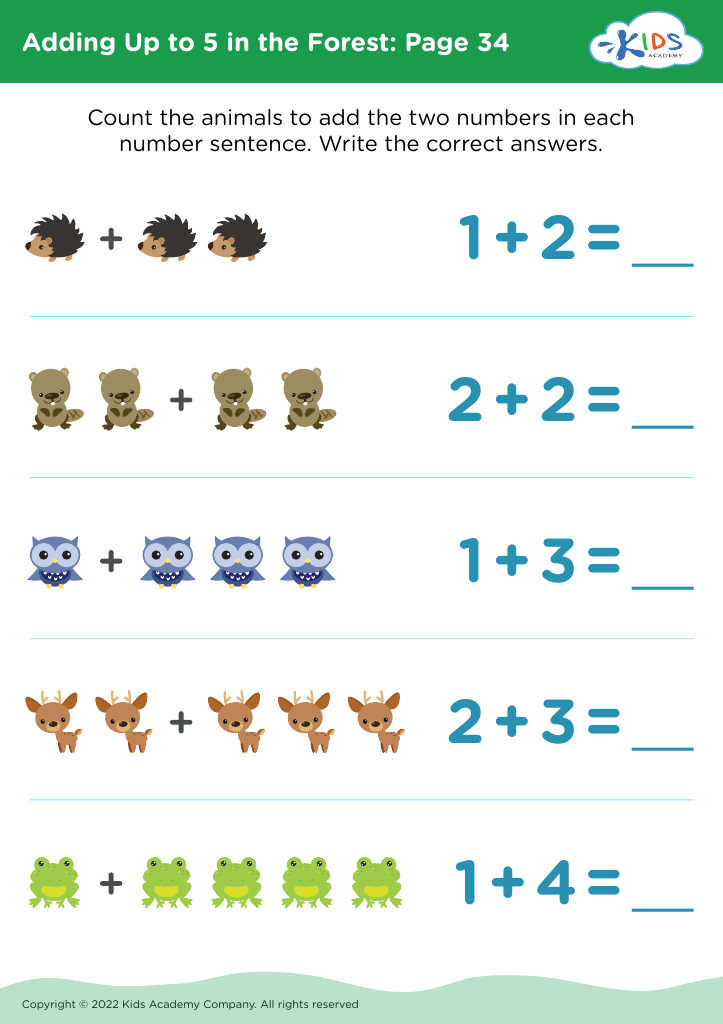Fine motor development Addition Worksheets for Ages 3-9
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Unlock your child's potential with our Fine Motor Development Addition Worksheets for ages 3-9! Designed to enhance essential motor skills while introducing foundational math concepts, these engaging worksheets offer a fun and interactive approach to learning addition. Your child will enjoy colorful, hands-on activities that promote hand-eye coordination and dexterity, seamlessly integrating fine motor skills practice with basic arithmetic. Each worksheet progressively challenges your little learner, making math accessible and enjoyable. Perfect for home or classroom use, our resources help foster confidence and proficiency in early math, laying a solid foundation for future learning. Start your child's educational journey today!
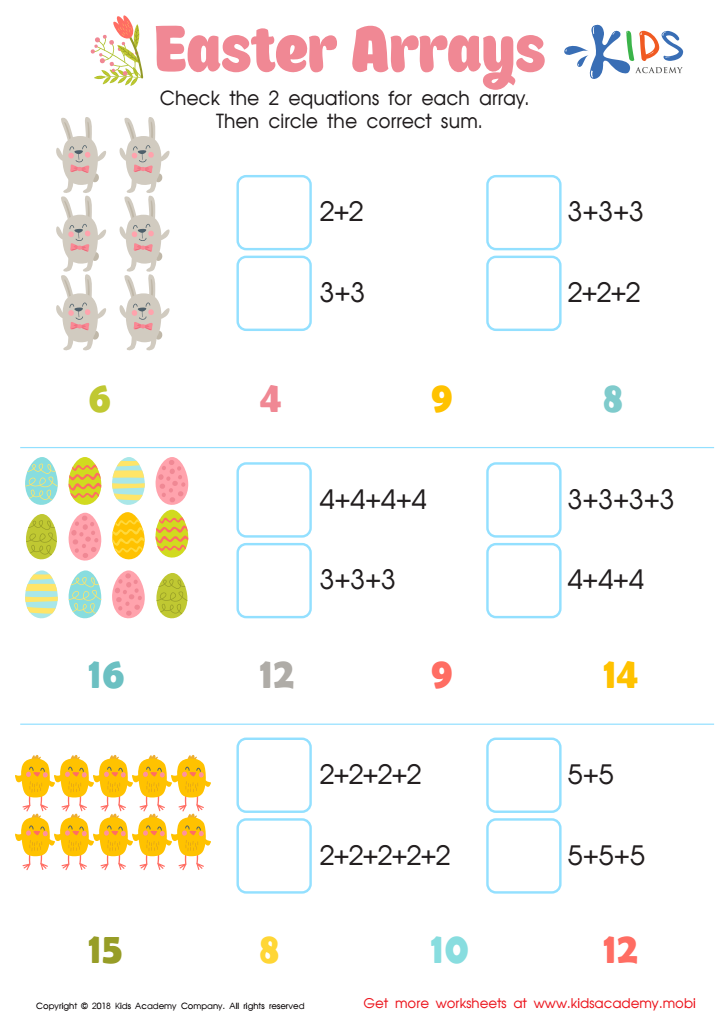

Easter Arrays Worksheet
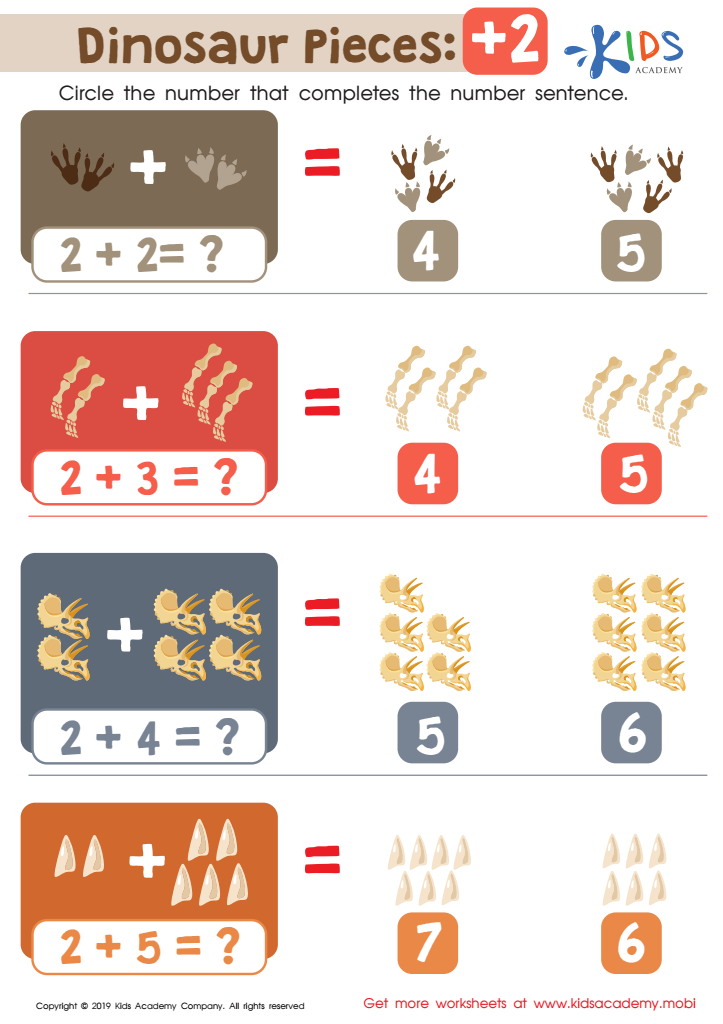


Dinosaur Pieces: +2 Worksheet
Fine motor development is a crucial aspect of early childhood growth, particularly for children aged 3-9. This stage of development involves the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, enabling children to perform tasks such as writing, cutting, and manipulating small objects. Parents and teachers should care about fine motor skills because they underpin a child’s ability to perform essential daily activities and academic tasks.
Firstly, strong fine motor skills enhance independence in children. As they learn to dress themselves, eat, and engage in play, they gain confidence and self-esteem. Additionally, fine motor development is linked directly to academic success, particularly in literacy and math. Precise grip and control are essential for writing letters and numbers, as well as for completing tasks that involve counting and measuring.
Moreover, engaging activities that promote fine motor skills foster creativity and enjoyment. By participating in arts and crafts, building with blocks, or engaging in sensory play, children practice and enhance these skills while having fun. Encouraging fine motor development provides a foundation for lifelong learning, helping children navigate both their educational journeys and daily lives with greater ease and confidence. Hence, parents and teachers should prioritize these skills in early education settings.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students