Motor skills development Normal Alphabet Worksheets for Ages 3-5
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's fine motor skills and alphabet recognition with our Motor Skills Development Normal Alphabet Worksheets for Ages 3-5. Designed thoughtfully for early learners, these engaging worksheets help young minds practice tracing letters, enhancing pencil control and hand-eye coordination. As children navigate through playful exercises, they develop essential pre-writing skills and muscle strength. Our worksheets combine fun illustrations with structured activities, fostering both creativity and learning in a joyful setting. Perfect for parents and educators, these downloadable resources support your child's foundational development and set the stage for future academic success. Nurture your child's learning journey today!
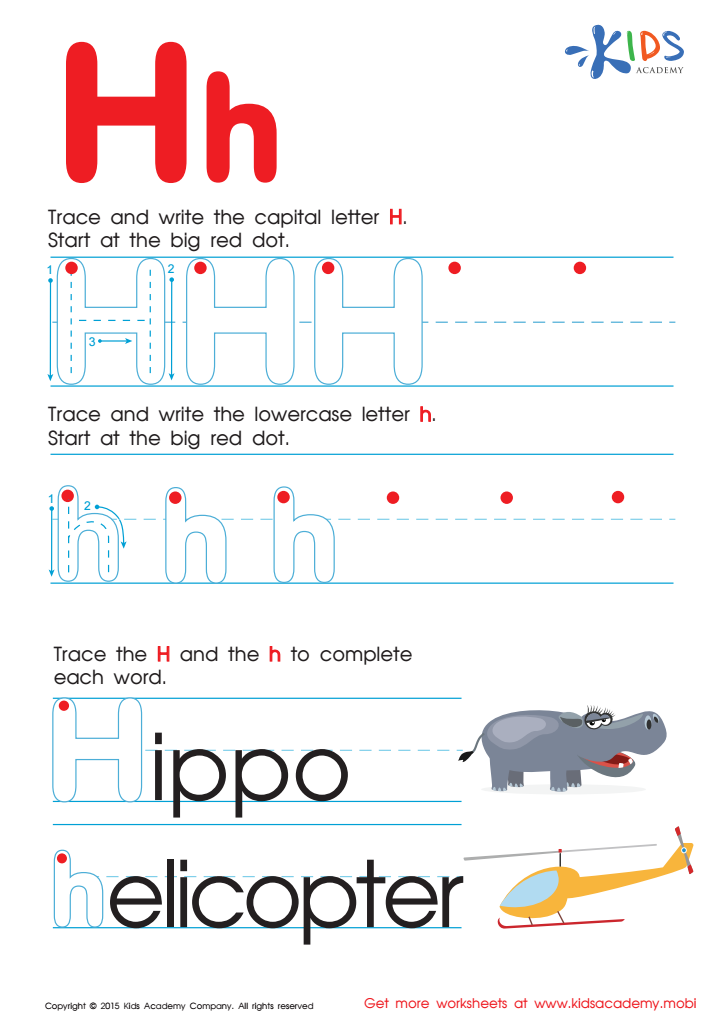

Letter H Tracing Page


Letter O Coloring Sheet
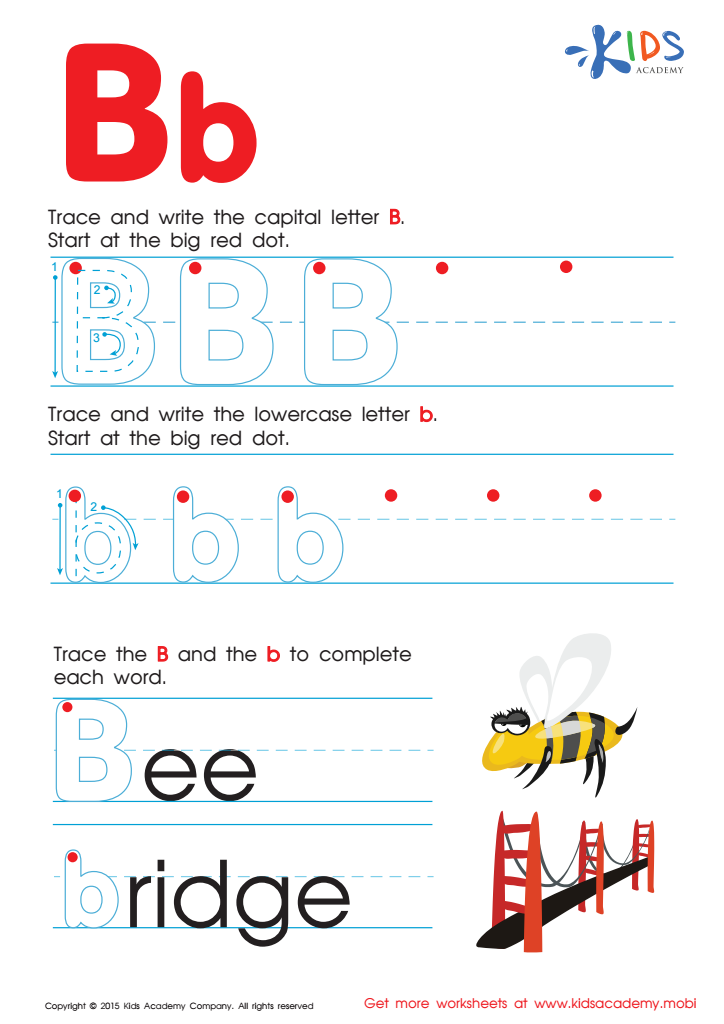

Letter B Tracing Page
Motor skills development is crucial for children between the ages of 3-5 because it lays the foundation for their overall physical, cognitive, and social-emotional growth. Parents and teachers play a vital role in supporting this aspect of a child's development.
Firstly, fine motor skills, such as holding a pencil, using scissors, or buttoning a shirt, are essential for daily self-care and academic tasks. Developing these skills helps children gain independence and confidence, enabling them to perform a variety of tasks without constant adult assistance.
Secondly, gross motor skills—such as running, jumping, and climbing—are equally important as they contribute to a child's physical fitness and coordination. Enhanced motor skills also improve hand-eye coordination, which is critical for activities like writing, catching a ball, and playing musical instruments.
Moreover, motor skills development is linked to cognitive skills. Activities that improve motor skills, such as puzzles and building blocks, promote problem-solving, spatial awareness, and concentration.
Finally, social-emotional growth is fostered through motor skills development as children participate in group activities like games and sports. These activities teach teamwork, cooperation, and communication skills, promoting healthy relationships with peers.
In essence, monitoring and encouraging motor skills development in early childhood sets the groundwork for more complex learning and skills in later years, making it a critical focus for parents and teachers.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students














