Critical Thinking Normal Reading Worksheets for Ages 5-6 - Page 2
27 filtered results
-
From - To


The Boy Who Cried Wolf Worksheet


Look at the Pictures: The Princess and the Pea Worksheet


Princess and the Pea Questions Worksheet
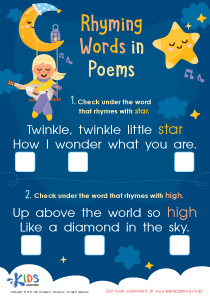
Critical thinking skills are essential for young learners, particularly in the formative years of ages 5-6. At this stage, children are developing foundational cognitive abilities that shape their future learning and problem-solving skills. Normal reading activities tailored for this age group provide an excellent platform for enhancing critical thinking.
When parents and teachers engage children in discussions about stories, characters, and plot developments, they help encourage inquiry and reasoning. For example, asking questions like "What do you think will happen next?" or "Why did the character make that choice?" sparks curiosity and promotes analytical thinking. Additionally, critical thinking encourages children to make connections between their own experiences and the material they read, fostering empathy and creativity.
Investing time in normal reading that emphasizes critical thinking not only enhances literacy skills but also prepares children for future academic challenges. These skills support them in understanding complex texts and reasoning through problems in various subjects. As skilled critical thinkers, children develop confidence in their ability to analyze information, remain open-minded, and articulate their thoughts, laying a strong foundation for lifelong learning. Ultimately, nurturing critical thinking through normal reading enables children to thrive both academically and personally.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students