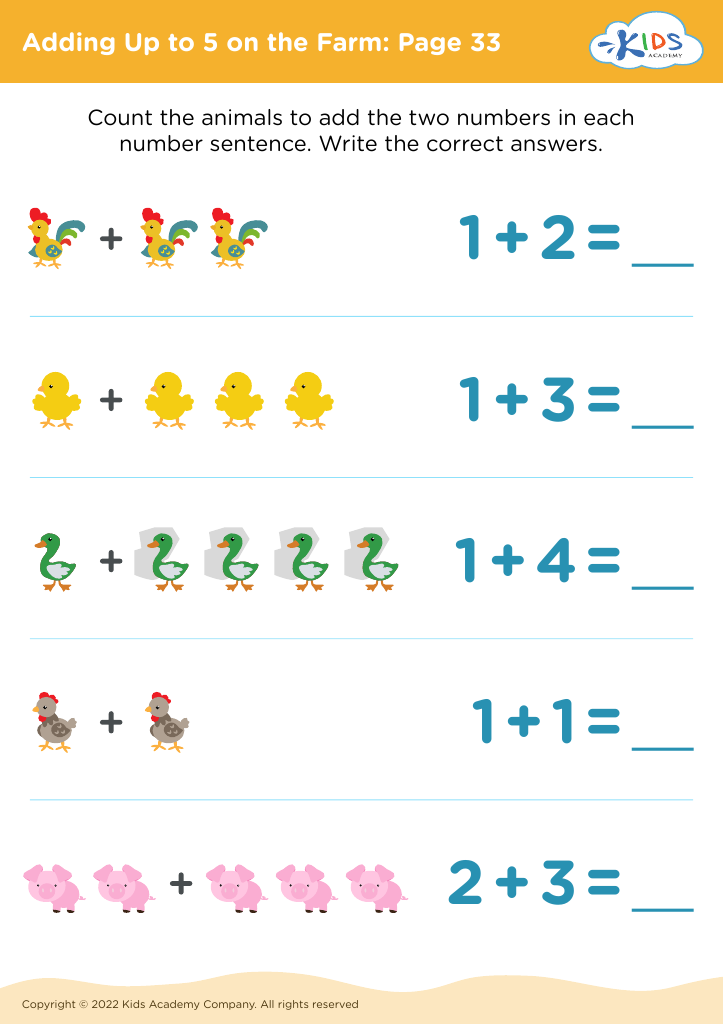Developing fine motor skills Worksheets for Ages 3-4
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging "Developing Fine Motor Skills Worksheets for Ages 3-4," designed to support your child's growth in vital motor skills through fun and interactive activities. These printable worksheets encourage young learners to practice skillful hand movements while cutting, tracing, and coloring. As children explore these creative tasks, they improve dexterity, hand-eye coordination, and pencil grip. Ideal for parents and educators, our resources aim to foster independence and confidence in early learners. Make learning a joyful experience that lays the foundation for academic success! Visit our website to explore a variety of worksheets that cater to your child's developmental needs.
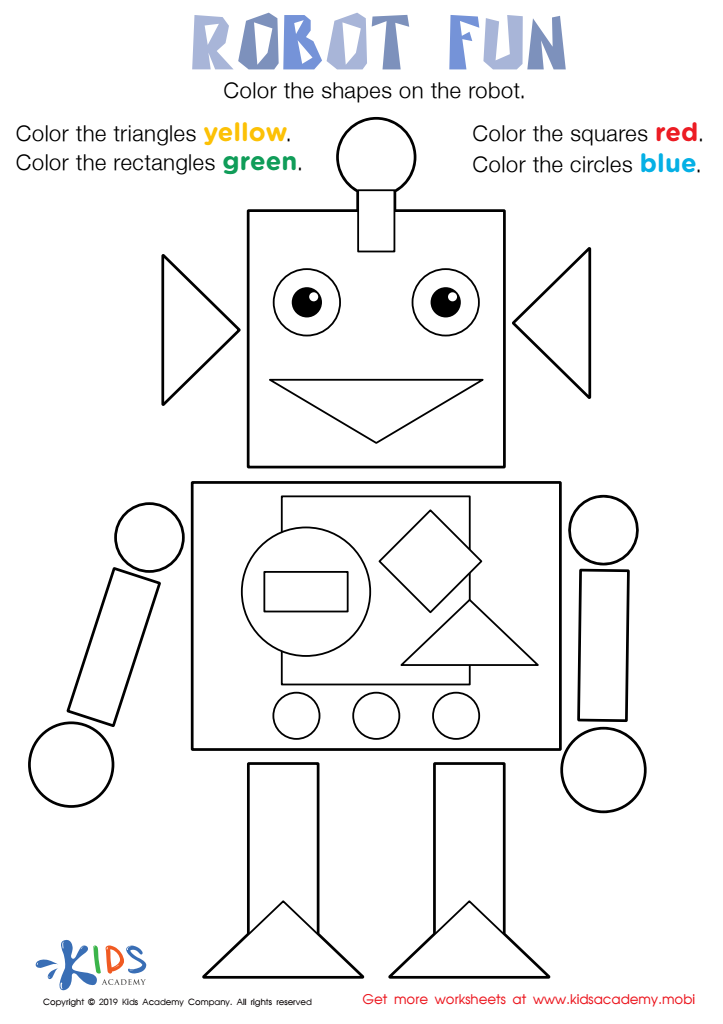

Robot Fun Worksheet
Developing fine motor skills in children aged 3-4 is crucial for their overall growth and learning. These skills refer to the ability to use small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are essential for everyday activities such as grasping objects, writing, and self-feeding. During this formative stage, children are naturally curious and eager to explore their environment, making it an ideal time for fine motor development.
Strong fine motor skills contribute to better hand-eye coordination and dexterity, which are foundational for academic success. For example, children who can grip a pencil properly are more likely to express themselves effectively in writing. Moreover, fine motor activities such as cutting with scissors, threading beads, or building with blocks can enhance concentration and problem-solving abilities, fostering cognitive development.
Parents and teachers play a vital role in this process by providing activities that promote fine motor practice, such as arts and crafts, puzzles, and sensory play. Engaging in these activities not only helps children build skill and confidence but also offers opportunities for bonding and collaboration. Supporting fine motor development prepares children for future school tasks and lays the groundwork for a lifelong love of learning and exploration.


 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students