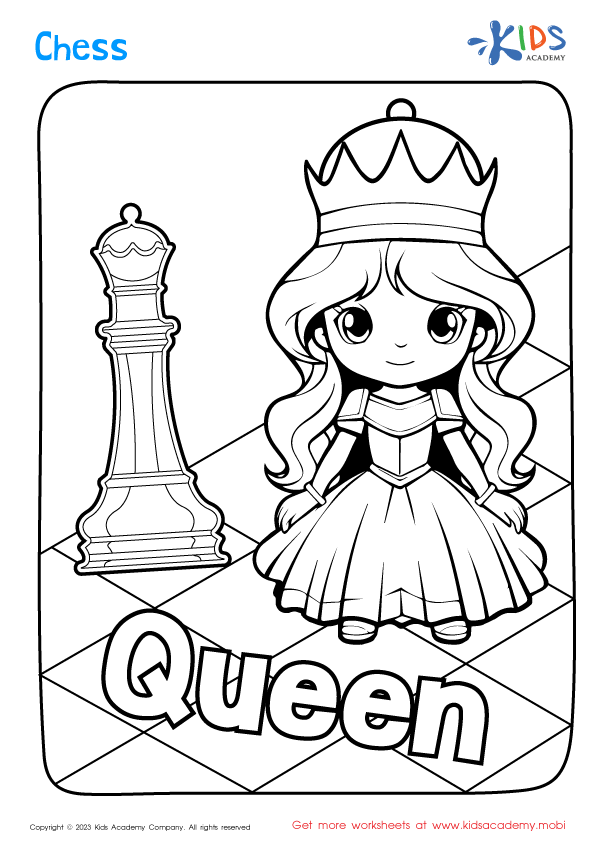
Chess piece identification Worksheets for Ages 3-6
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Introduce your young learners to the exciting world of chess with our engaging Chess Piece Identification Worksheets designed for ages 3-6! These worksheets are an excellent tool for teaching kids the names, shapes, and functions of each chess piece, fostering essential cognitive and motor skills. With colorful illustrations and fun activities, children will easily recognize pawns, knights, bishops, rooks, queens, and kings. Perfect for educators and parents, these resources promote problem-solving, critical thinking, and number recognition in a playful manner. Download our printable worksheets today and watch your little ones develop a love for chess while enhancing their learning experience!


Chess Pieces Quest Worksheet

Rook and Bishop Worksheet
Chess piece identification is an important skill for children aged 3-6, and parents and teachers should prioritize it for several reasons. Firstly, recognizing different chess pieces—such as pawns, knights, and bishops—helps develop cognitive skills. Identifying and naming these pieces requires memory, visual recognition, and language capabilities, promoting early literacy and critical thinking.
Secondly, learning chess piece identification fosters strategic thinking. As children understand the unique movements and abilities of each piece, they begin to grasp the fundamentals of strategy and planning. These skills are transferable and can enhance problem-solving abilities in various contexts beyond the chessboard.
Moreover, chess promotes social skills. Engaging with peers or family members in playing chess offers opportunities for cooperation and healthy competition. It teaches respect for opponents and patience in learning and executing strategies, which are crucial values for personal development.
Lastly, chess serves as a preventive measure against screen dependency. Introducing the game to young children provides a constructive, engaging alternative that stimulates their minds without the drawbacks associated with excessive screen time. In summary, emphasizing chess piece identification equips young learners with vital cognitive, social, and emotional skills that benefit them in many aspects of life.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students

















