Fine motor skills (writing) Adding Up to 5 Worksheets for Ages 3-6 - Page 2
32 filtered results
-
From - To
Parents and teachers should prioritize the development of fine motor skills, especially skills related to writing and basic arithmetic, in children aged 3-6 due to several critical reasons. At this development stage, fine motor skills — movements involving the small muscles in the hands and fingers — serve as the foundation for more advanced tasks children will encounter in their academic and daily lives.
Firstly, enhancing fine motor skills directly impacts a child’s ability to write. Writing is not just about putting letters on paper; it encompasses coordination, control, and precision, all of which are developed through fine motor activities. Mastering these skills improves legibility and ease of writing, fostering better communication and boosting confidence in academic settings.
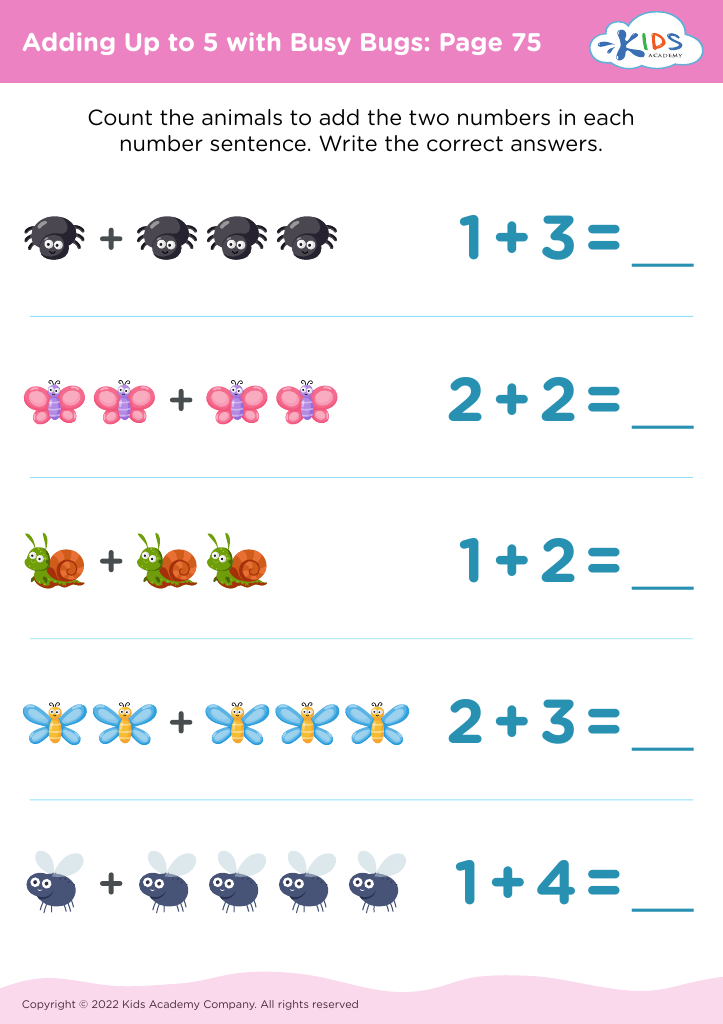
Furthermore, introducing basic arithmetic, such as adding up to 5, at this age lays the groundwork for future mathematical understanding. Engaging children in counting and simple problem-solving promotes cognitive development and critical thinking. Manipulating objects to learn these skills simultaneously refines fine motor capabilities and reinforces number concepts.
In essence, focusing on fine motor skills and elementary mathematics prepares young children more comprehensively for scholastic success. These foundational skills are essential stepping stones, making day-to-day activities easier and engendering a love for learning that can last a lifetime.





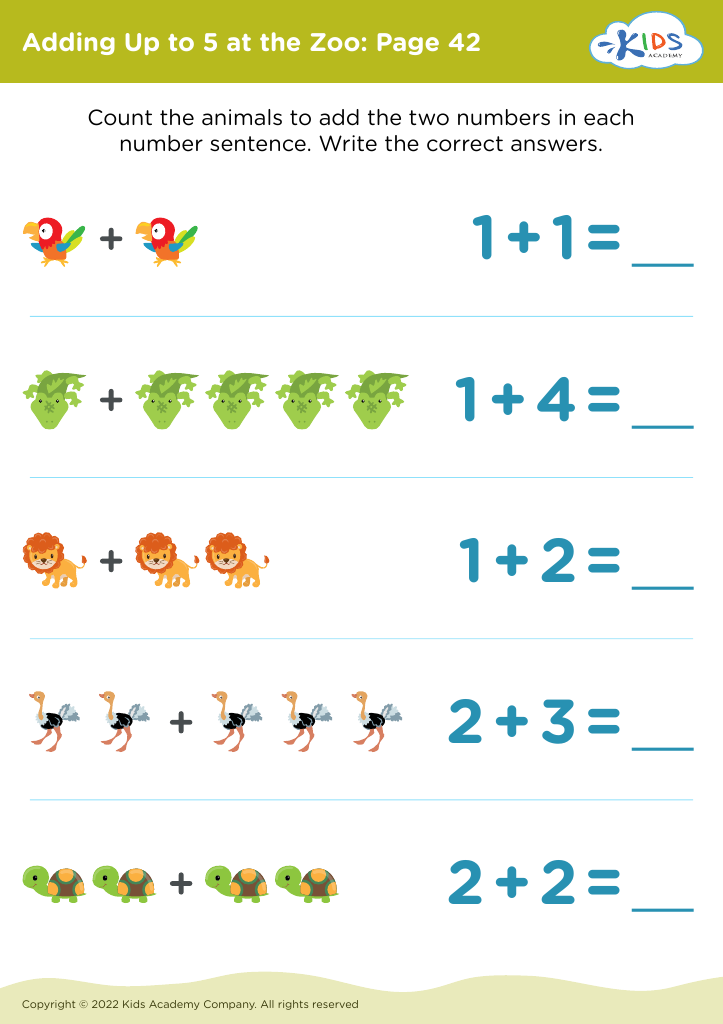









.jpg)








