Logical thinking Grammar Worksheets for Ages 3-6
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging Logical Thinking Grammar Worksheets designed specifically for children ages 3-6! These worksheets provide a fun, interactive way for young learners to enhance their grammar skills while developing critical logical thinking abilities. Each activity encourages kids to think sequentially and solve problems, laying a strong foundation for future learning. With colorful illustrations and age-appropriate exercises, children will enjoy exploring concepts such as sentence structure, word usage, and basic punctuation. Perfect for at-home practice or classroom use, our worksheets empower young minds to think logically and express themselves clearly. Promote creativity and cognitive skills today with our delightful grammar resources!


Find Words Mouse Maze Worksheet

Spider Verbs Worksheet
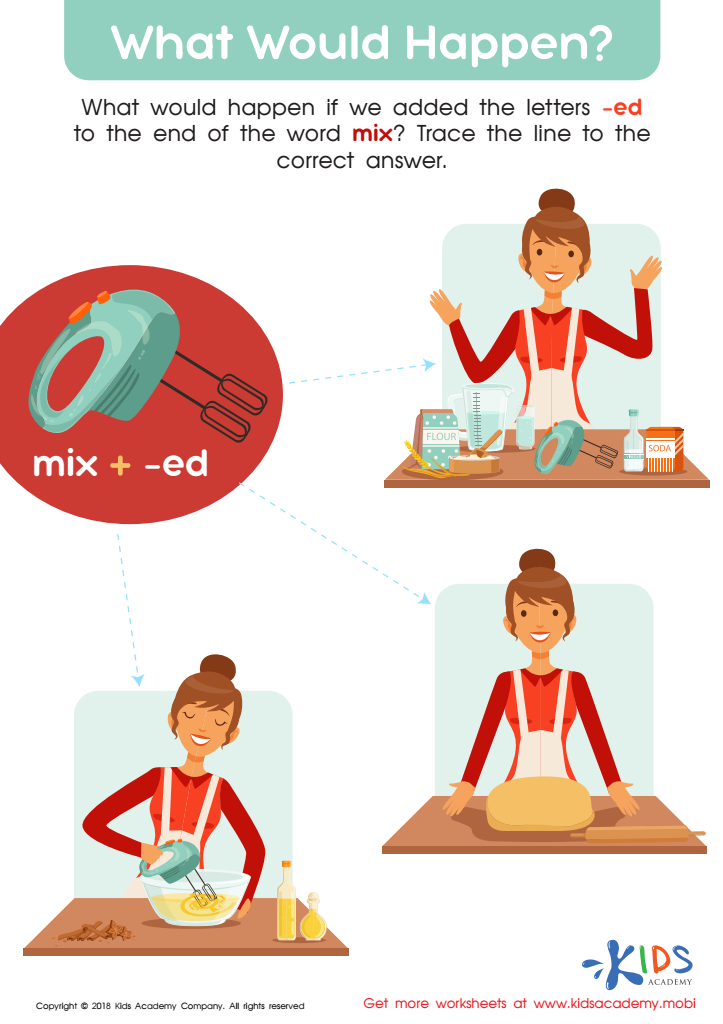


What Would Happen? Worksheet
Logical thinking grammar for children ages 3-6 is essential for their cognitive and linguistic development. At this stage, children are beginning to make sense of the world around them, and fostering logical thinking helps them organize their thoughts and ideas effectively. This foundational reasoning skill enables them to make connections between concepts, leading to improved problem-solving abilities.
Parents and teachers should care about this aspect of grammar because it lays the groundwork for effective communication. When young learners grasp the basics of logical thinking grammar—such as sequencing events, understanding cause-and-effect relationships, and using appropriate language structures—they can express themselves more clearly and confidently. This enhances their interactive skills in social settings, assists with literacy development, and promotes comprehension when engaging with stories and instructions.
Furthermore, logical thinking engages children's curiosity, encouraging them to ask questions and explore concepts more critically, which can positively impact their overall academic readiness. By incorporating playful activities that emphasize logical thinking grammar, caregivers can create enriching learning experiences that prepare children for future educational challenges. Ultimately, nurturing these skills from an early age fosters independent thinkers who can navigate complex information throughout their lives.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















