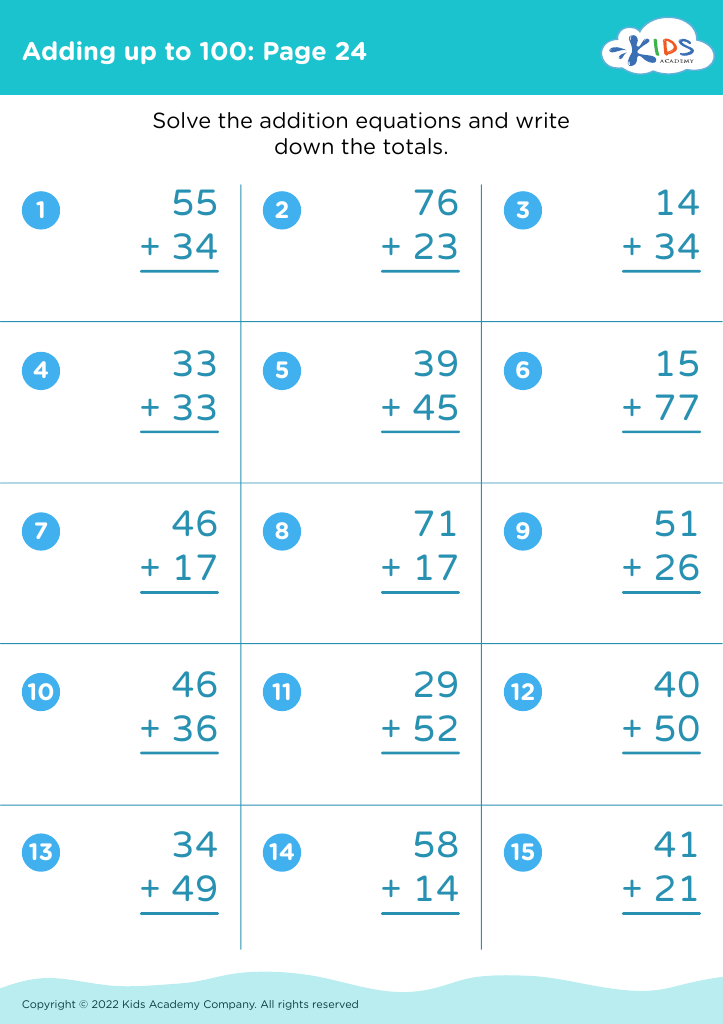
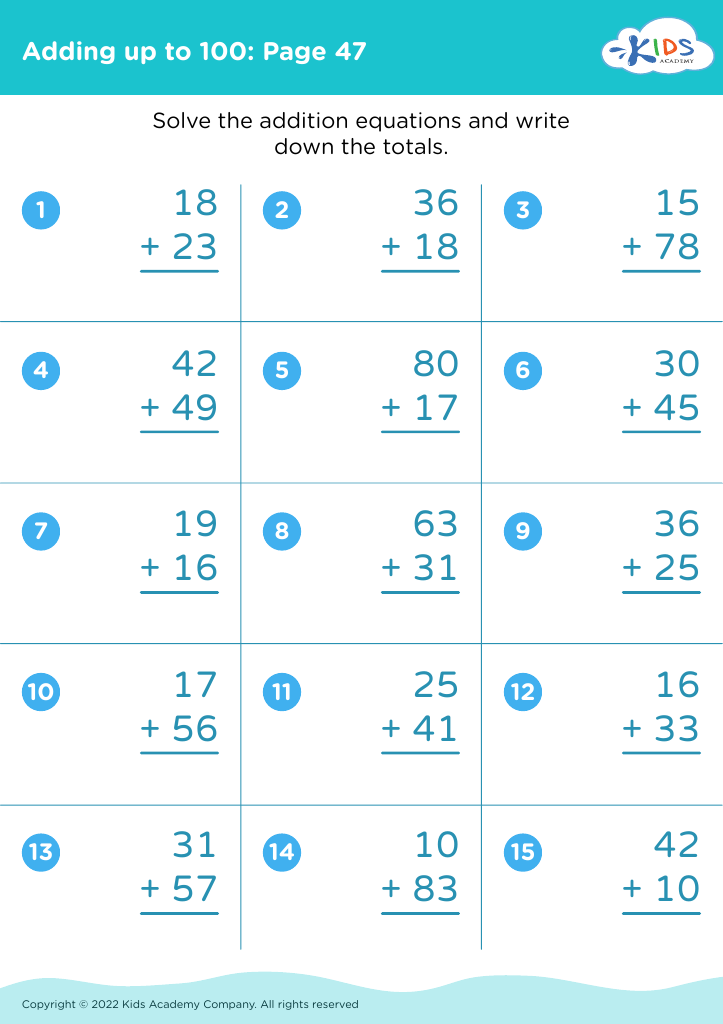
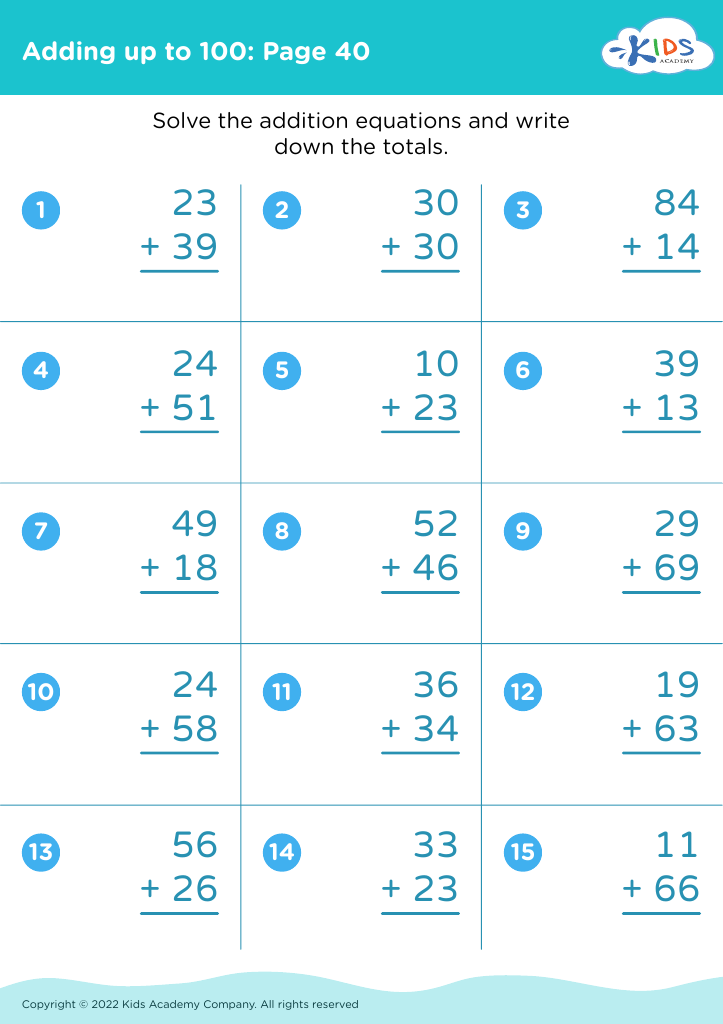
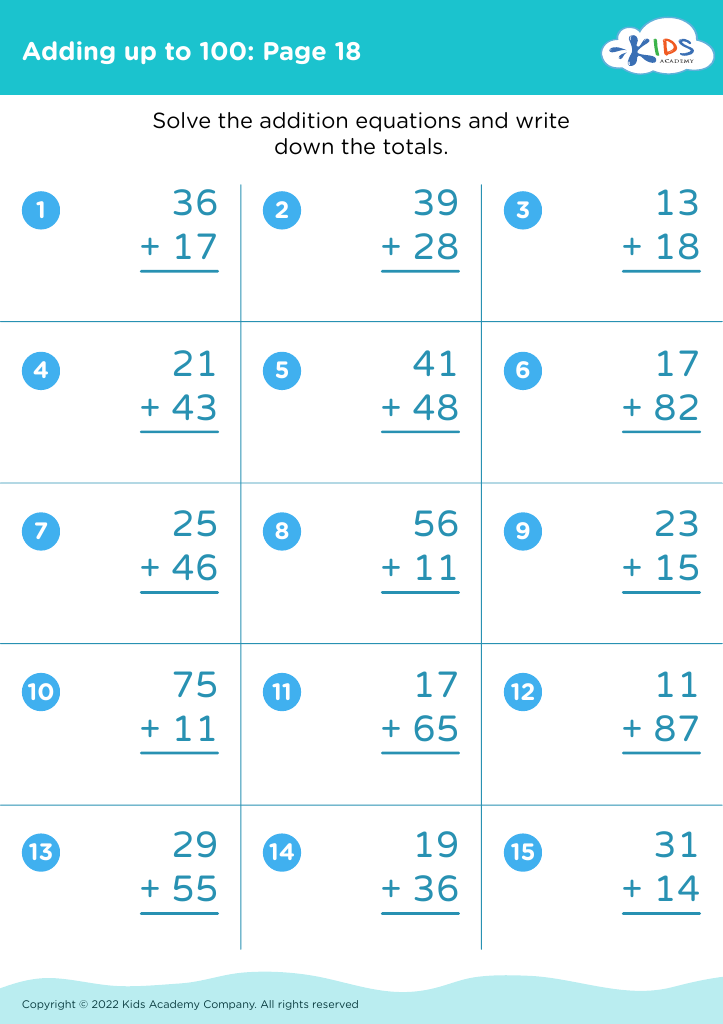
Develop fine motor skills Adding up to 100 Misc Worksheets for Ages 3-8
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Explore our engaging collection of worksheets designed to help children aged 3-8 develop fine motor skills while mastering math concepts like addition up to 100. These meticulously crafted resources offer a variety of interactive activities that encourage children to practice essential hand-eye coordination, letter and number formation, and pencil control. By combining learning with creativity, our worksheets include coloring, tracing, and cutting tasks that keep young learners excited and engaged. Perfect for homeschooling or classroom use, these tools make it easy for educators and parents to foster critical fine motor development while instilling a love for math in early learners.
Developing fine motor skills is crucial for children aged 3-8 as it lays the foundation for their overall development and future learning. Fine motor skills involve the coordinated movement of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are essential for everyday tasks and academic success. As children engage in activities such as cutting, drawing, and manipulating small objects, they enhance their hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and concentration.
Parents and teachers should care about nurturing these skills because they directly influence a child's ability to write, draw, and perform tasks independently, which are fundamental for school readiness. Furthermore, fine motor skills are linked to cognitive development; as children master these abilities, they often demonstrate improved problem-solving and critical-thinking skills.
Involving children in fine motor activities, like crafting, puzzles, or even simple games, not only makes learning enjoyable but also helps bridge the gap between playful learning and essential skill development. Engaging in these activities promotes confidence and a sense of accomplishment, which are vital for a child’s self-esteem and motivation. Therefore, prioritizing fine motor skill development will equip children with the tools they need for success both academically and in everyday life.