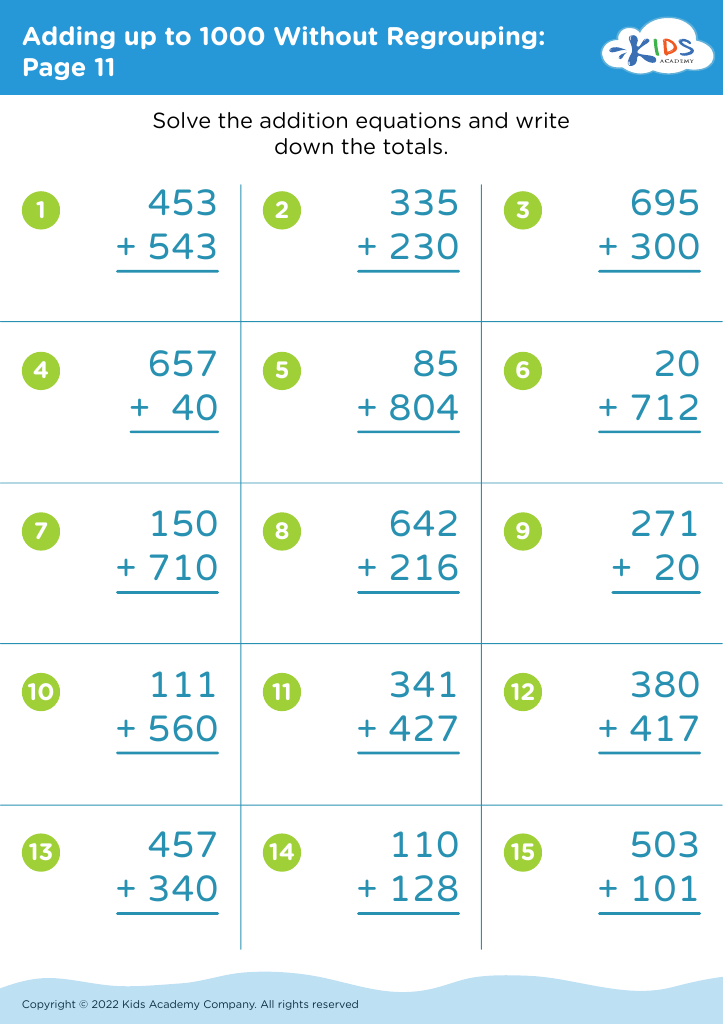
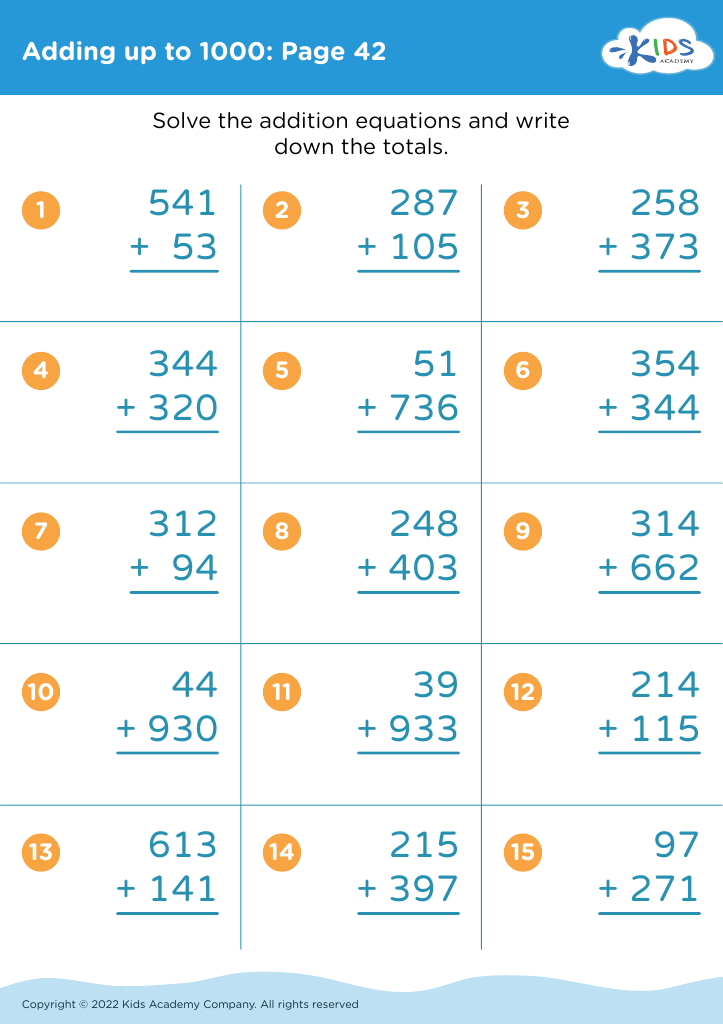
Counting skills form the foundational groundwork for future mathematical learning and problem-solving abilities. For children ages 3-8, developing counting skills, especially up to 1000, serves several critical purposes. Early grasp of numbers fosters numerical literacy, allowing kids to understand quantity, order, and the basics of addition and subtraction.
By mastering counting at an early age, children enhance their ability to process and understand more complex concepts as they grow. For example, the skill of counting by ones, twos, fives, and tens naturally introduces patterns and sequences, important for higher-level math. Further, strong counting skills cultivate children's confidence and enthusiasm toward math, making it a fun rather than intimidating subject. It also aids in everyday tasks like counting money or tracking time, enhancing practical life skills.
For teachers and parents, encouraging counting up to 1000 ensures that children are better prepared for academic success. Early numerical literacy links directly to improved performance in math assessments and a greater ability to grasp advanced math topics in later grades. Therefore, investing time in nurturing competent counting skills at this stage positively impacts both academic achievement and daily functioning, providing children with the tools and confidence needed for continued educational growth.