Comparing quantities Adding up to 50 Worksheets for Ages 3-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging "Comparing Quantities Adding Up to 50 Worksheets" designed for children ages 3-8. These worksheets provide a fun and interactive way for young learners to practice basic math skills by comparing different quantities and understanding numerical relationships. With vibrant visuals and age-appropriate exercises, children will enhance their ability to recognize greater than, less than, and equal to concepts, all while delighting in the learning process. Perfect for home or classroom use, these resources support early math development and build a strong foundation for future mathematical skills. Start building confidence in math today with our exciting worksheets!
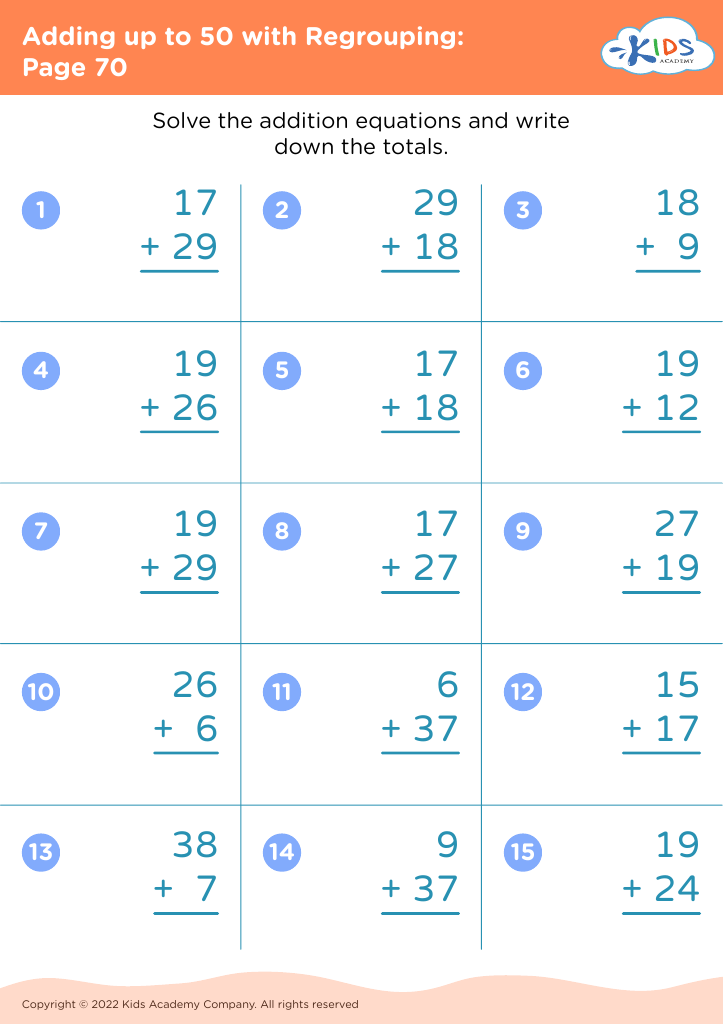
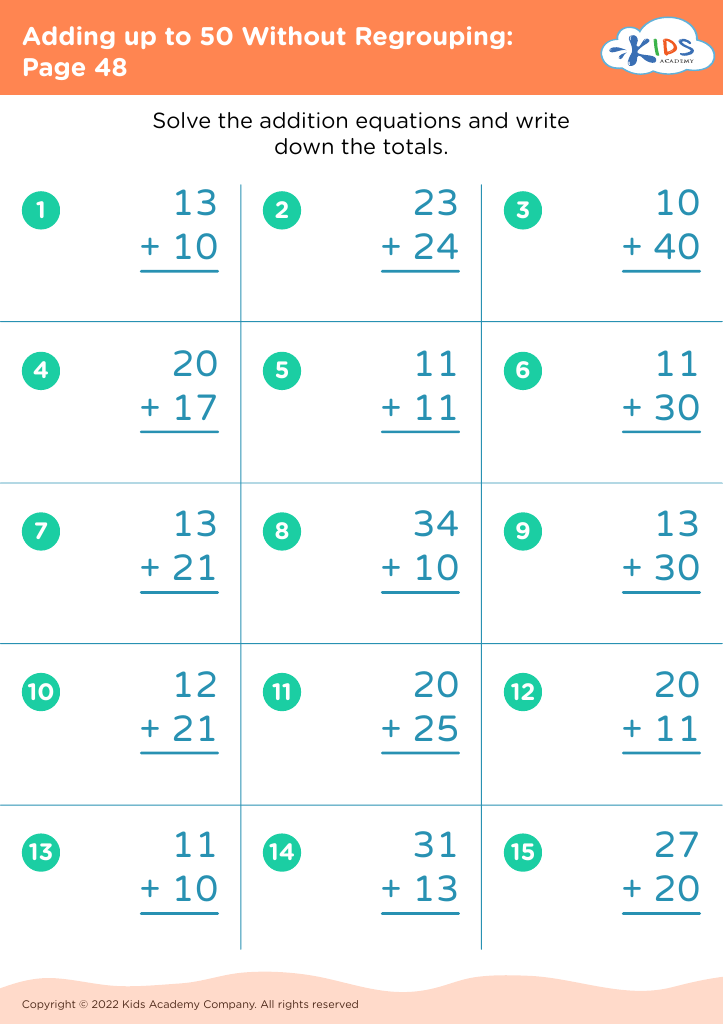
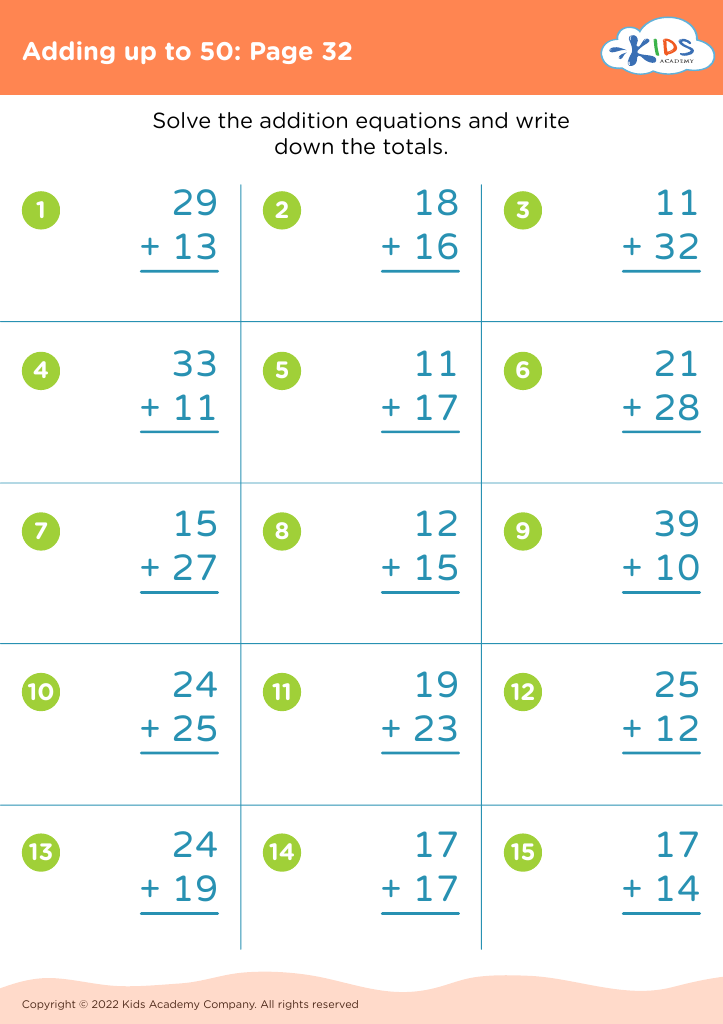
Comparing quantities and understanding addition up to 50 are foundational skills for children aged 3-8 years, laying the groundwork for more complex mathematical concepts later on. For parents and teachers, nurturing these skills is essential for several reasons.
Firstly, these skills enhance critical thinking and cognitive development. By comparing quantities, children learn to analyze and distinguish between greater and lesser amounts, fostering their ability to make judgments based on numerical values. Understanding addition up to 50 helps children grasp the concept of combining numbers, which is a stepping stone to more advanced arithmetic.
Secondly, these skills encourage problem-solving abilities. Engaging in activities that involve counting objects, grouping items, or adding visual cues promotes active participation and hands-on learning. This engagement not only makes learning fun but also reinforces the practical application of mathematics in everyday life.
Lastly, fostering early math skills promotes confidence in children. A solid foundation in basic arithmetic equips them for success in school and in future educational settings. By emphasizing comparing quantities and addition, parents and teachers empower children to embrace math with enthusiasm and curiosity, cultivating a lifelong appreciation for learning. Ultimately, these foundational skills are crucial for preparing young minds for future academic challenges.