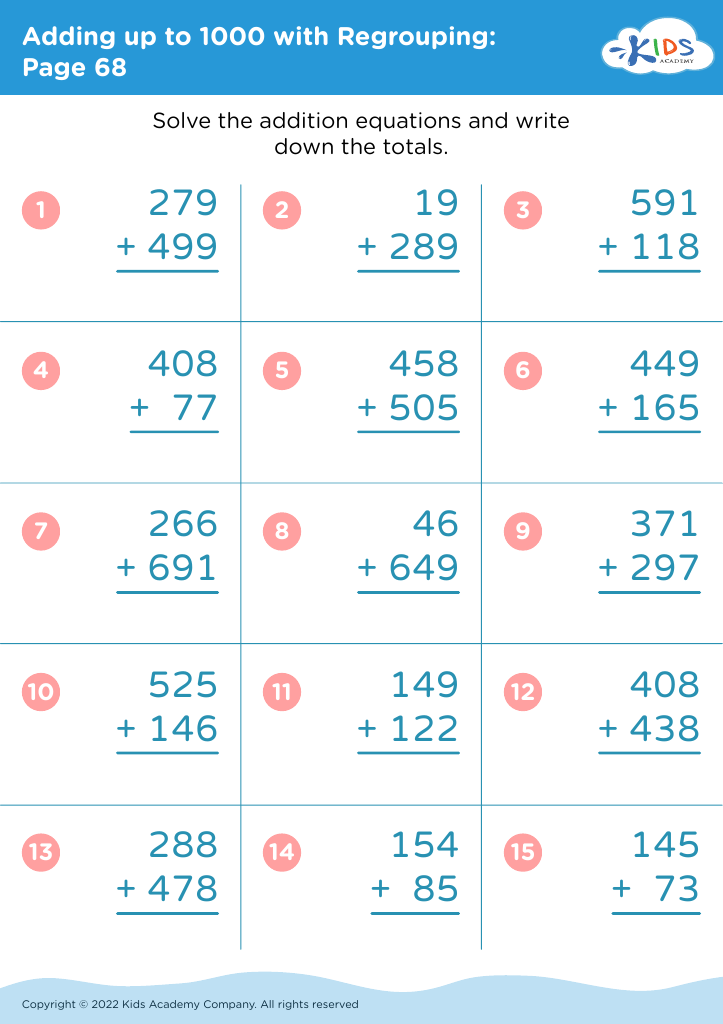
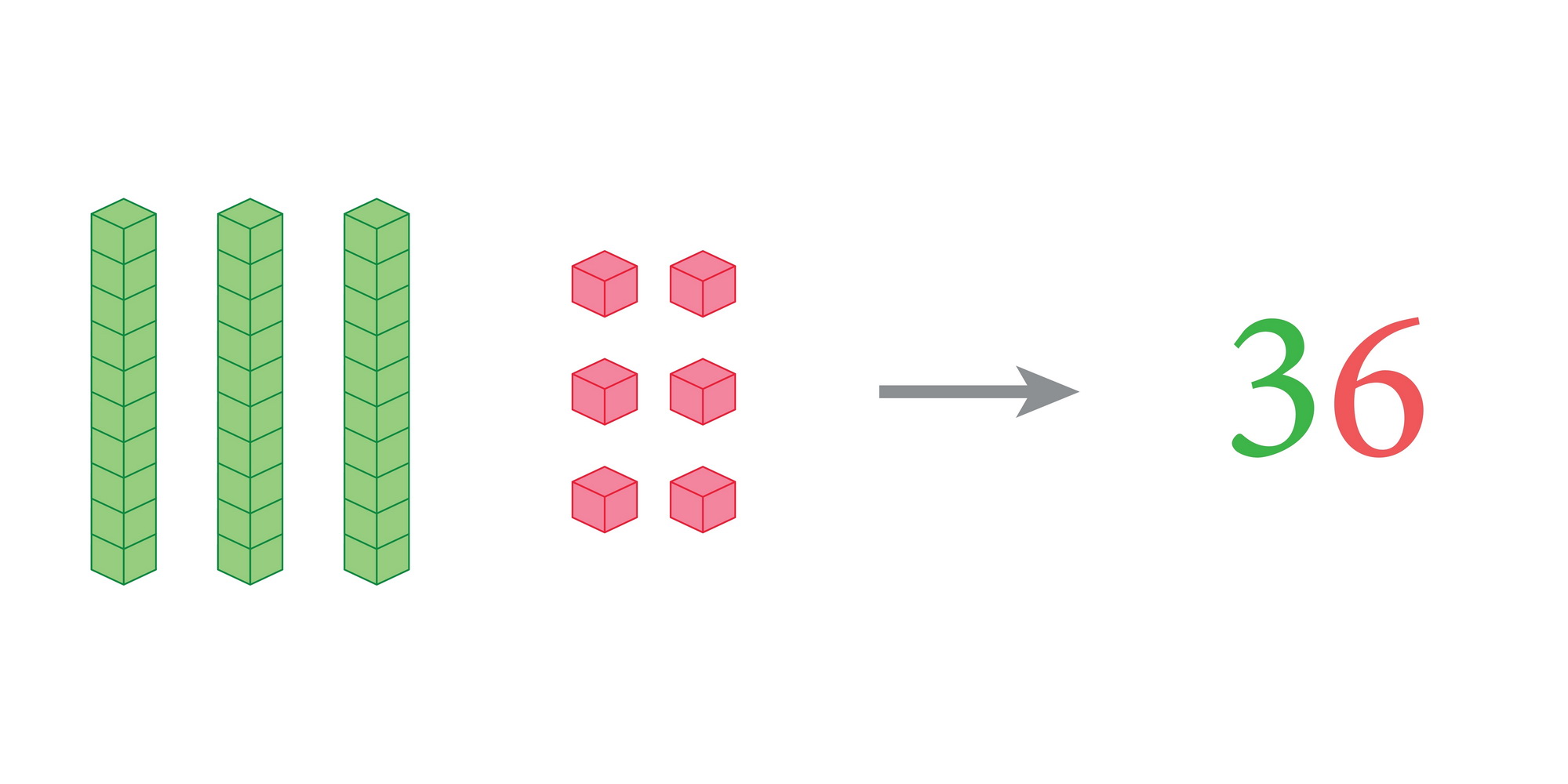
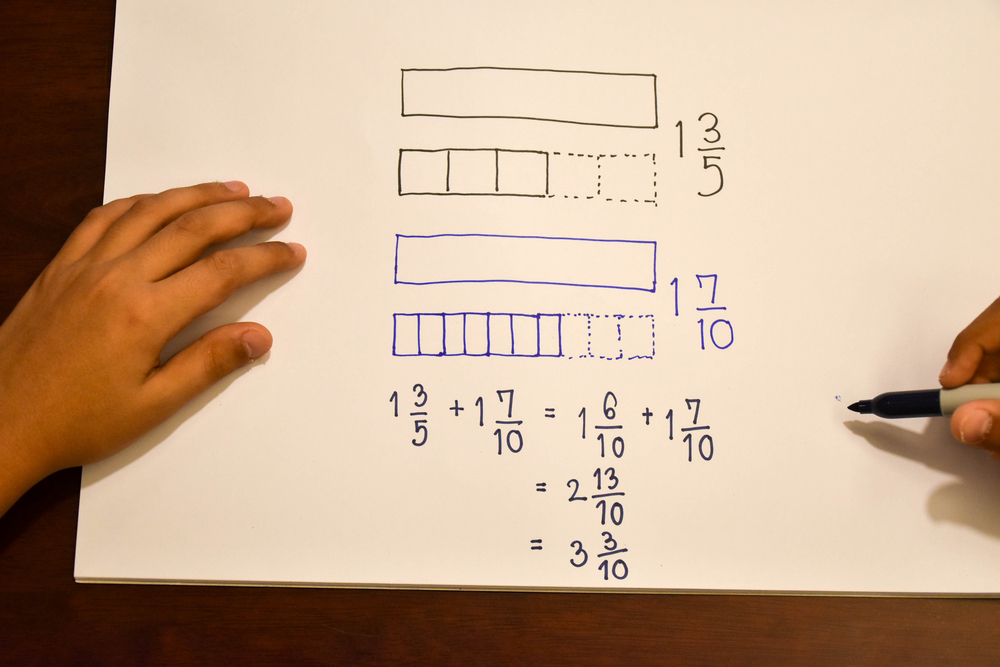
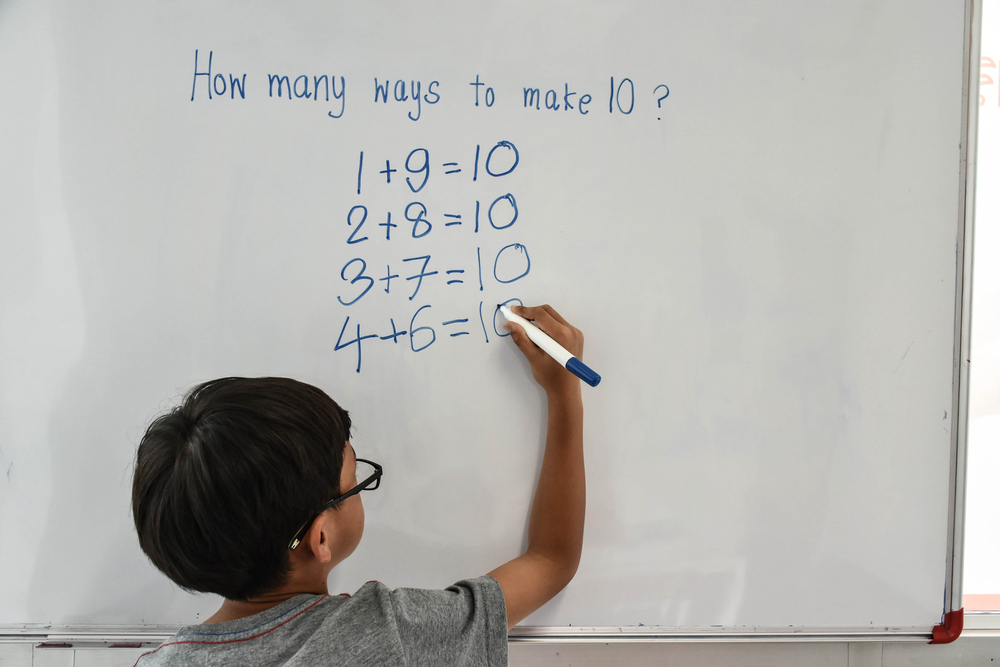Handwriting practice Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-8
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our Handwriting Practice Addition & Subtraction Worksheets designed specifically for children ages 3-8! These engaging worksheets help young learners develop their handwriting skills while mastering basic math concepts. With a mix of colorful illustrations and fun exercises, your child will enjoy practicing their letters and numbers alongside simple addition and subtraction problems. Perfect for at-home or classroom learning, our resources encourage fine motor skills development and build a strong foundation in math. Whether your child is just starting out or needs a little extra practice, these worksheets make learning fun and effective. Start their educational journey today!
Handwriting practice, along with foundational math skills like addition and subtraction, is crucial for children aged 3-8 for several reasons. First, handwriting develops fine motor skills, essential for tasks requiring manual dexterity. Engaging in consistent practice helps strengthen the muscles in the hands and fingers, enhancing control and coordination, which are vital for overall writing fluency.
Moreover, handwriting is linked to cognitive development. Writing numbers and letters encourages children to process information actively, positively impacting their ability to understand mathematical concepts. When children write out math problems, they engage multiple brain regions, reinforcing memory retention and comprehension.
Additionally, integrating handwriting practice with addition and subtraction promotes a multisensory learning experience. By involving visual (seeing the numbers), tactile (writing them out), and auditory (saying the numbers) elements, children are better equipped to grasp fundamental math concepts.
Fostering early experiences with handwriting and basic math helps build confidence and a solid foundation for future academic success. Teachers and parents should prioritize these activities, ensuring that children develop essential skills that will serve them well throughout their education. By focusing on these areas, they pave the way for improved writing and mathematical abilities that extend well beyond the early years.