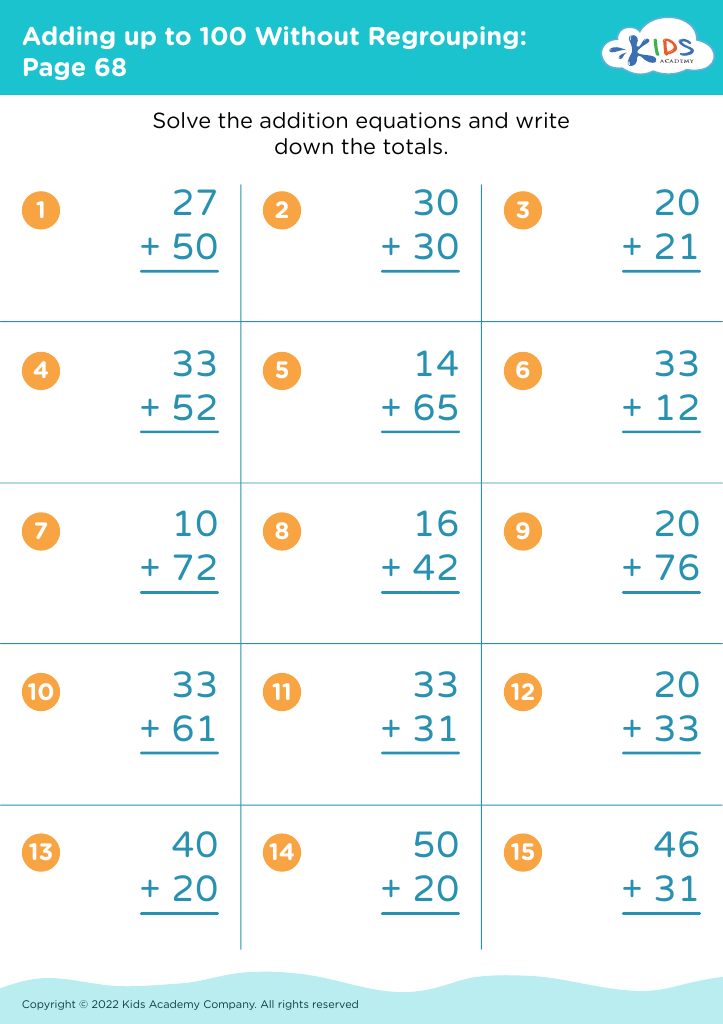
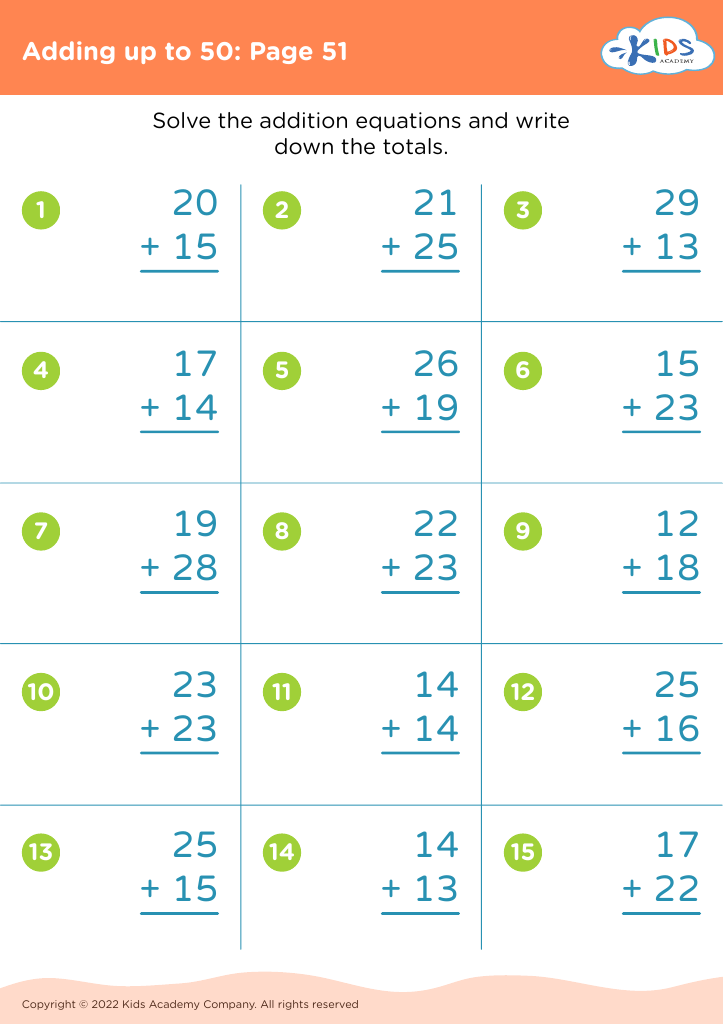
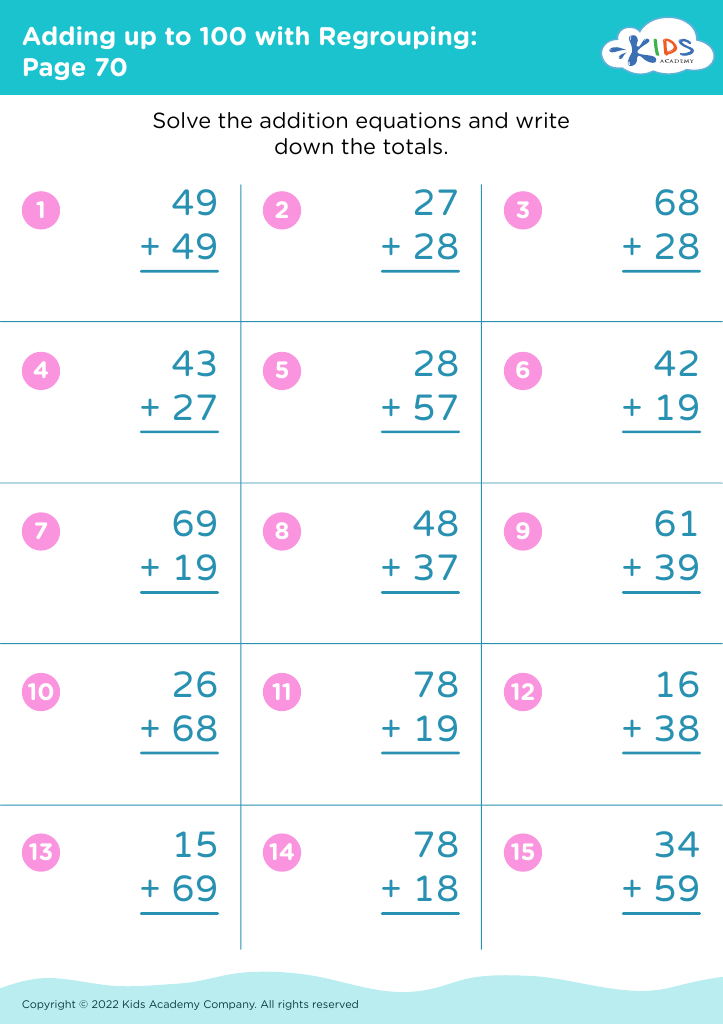
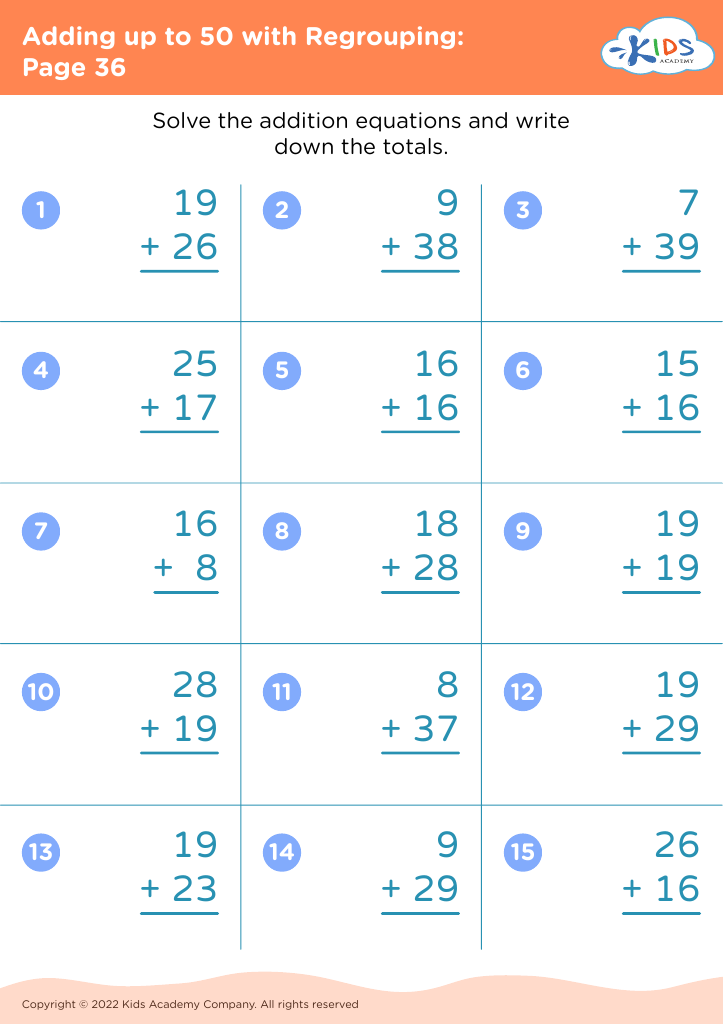
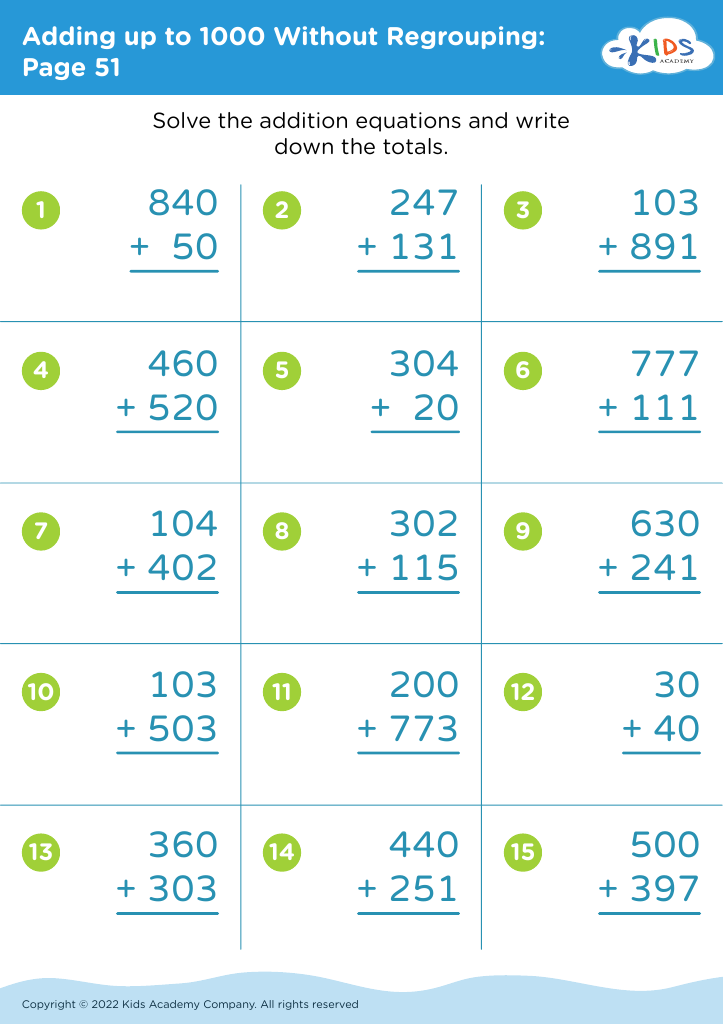
Developing problem-solving skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 3-8
6 filtered results
-
From - To
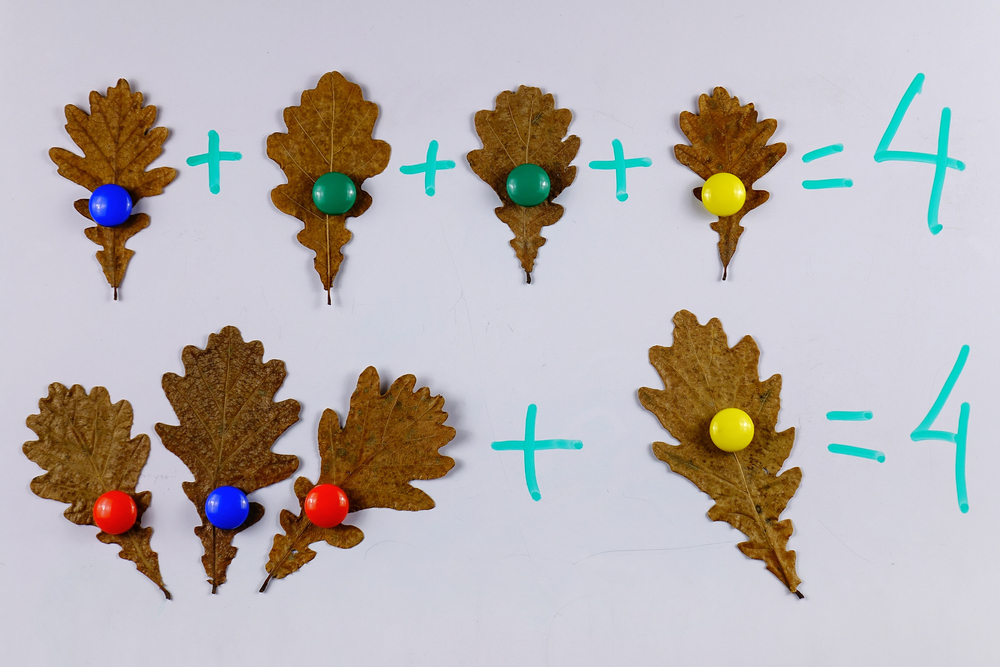
Explore our engaging "Developing Problem-Solving Skills Addition Worksheets" designed for children ages 3-8. These interactive worksheets help young learners master basic addition while enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Our resources feature colorful illustrations and age-appropriate problems, making math fun and appealing. As children tackle various addition scenarios, they cultivate resilience and creativity, key components of effective problem-solving. Ideal for homeschool parents and teachers, these worksheets support skill development in an entertaining way. Encourage your child's mathematical journey and empower them to approach challenges with confidence! Start enhancing their problem-solving skills today with our thoughtfully crafted addition worksheets.
Developing problem-solving skills, particularly in addition, is crucial for children aged 3-8 because it lays the foundation for future mathematical understanding and logical reasoning. At this young age, children's brains are particularly receptive to new concepts, and engaging them in addition-related problem-solving enhances their cognitive abilities. These skills not only boost mathematical fluency but also encourage critical thinking, allowing children to approach challenges with confidence and creativity.
Moreover, learning through problem-solving encourages perseverance. Children learn that making mistakes is a part of the learning process, fostering resilience and a growth mindset. As they navigate through addition problems, they develop strategies that can be applied in various contexts beyond math, such as reading comprehension, social interactions, and everyday decision-making.
Parents and teachers have a role in facilitating this learning by providing engaging, hands-on activities that make addition fun, measurable, and relatable to real-life situations. For instance, using toys or food items to solve addition problems can ignite interest and understanding. Therefore, prioritizing problem-solving skills in early education ensures that children not only succeed in math but also become independent thinkers prepared for future challenges.