Handwriting practice Addition Worksheets for Ages 3-8
5 filtered results
-
From - To
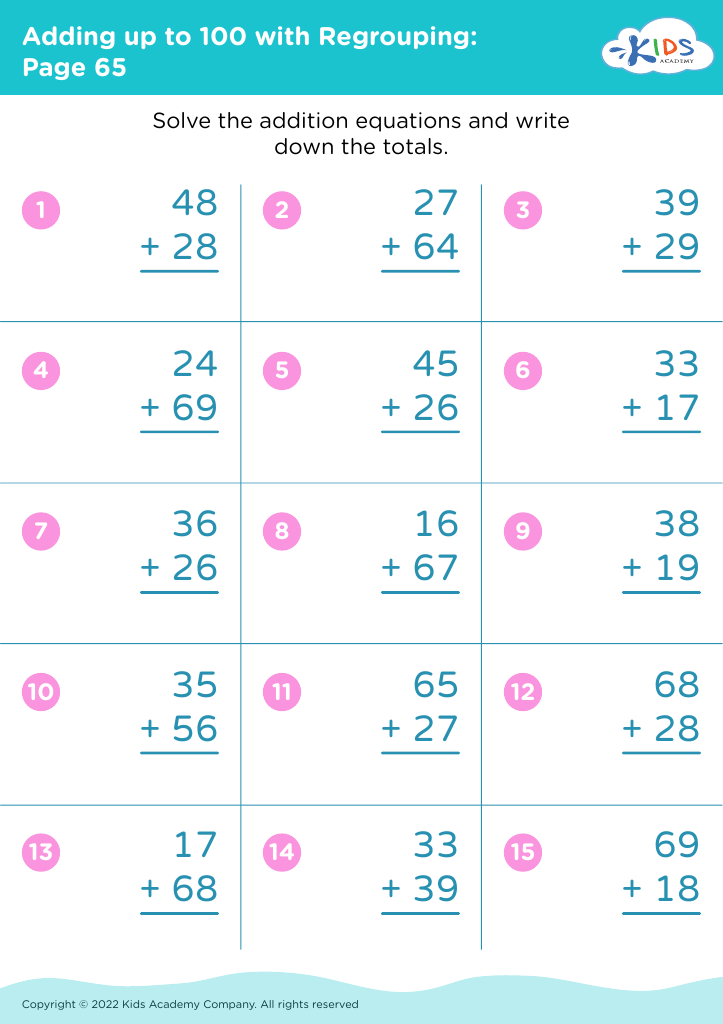
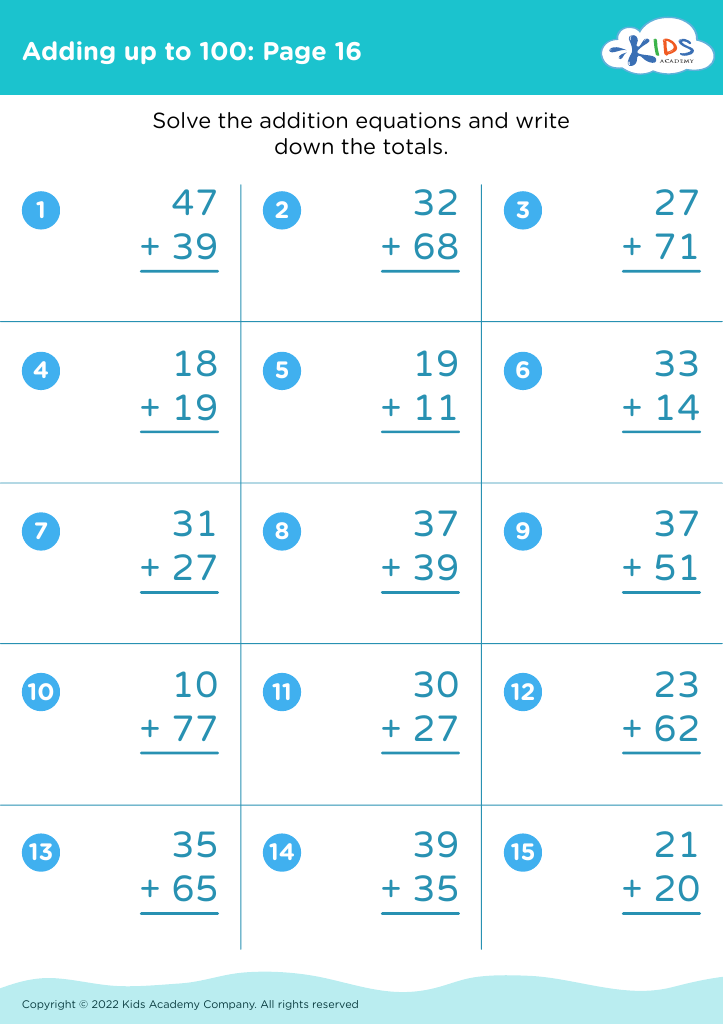
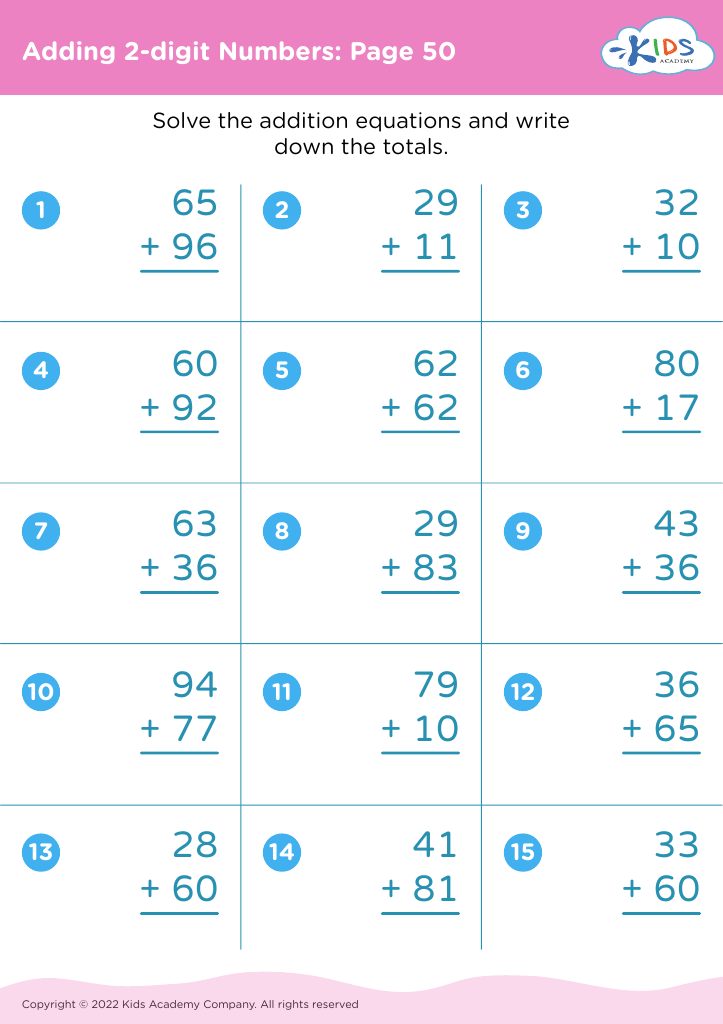
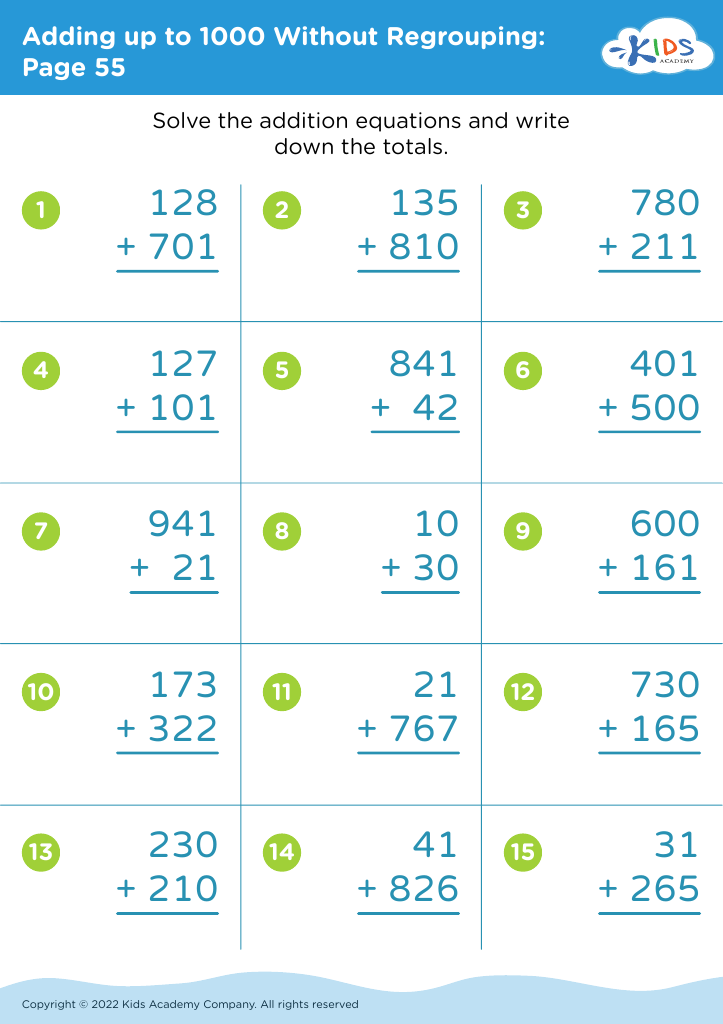
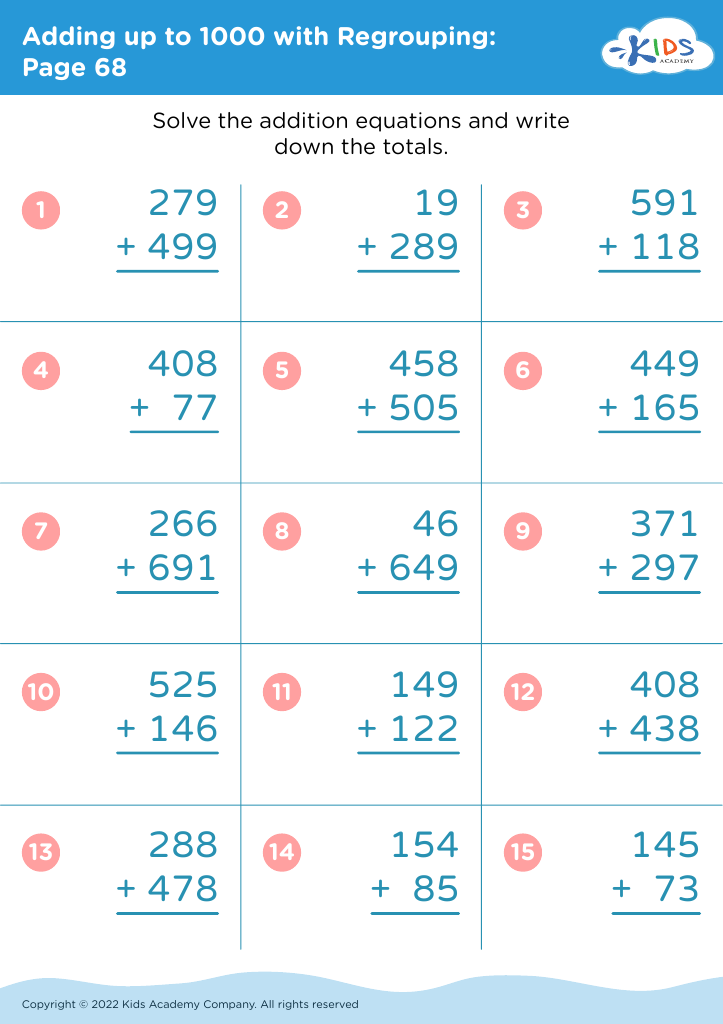
Enhance your child's learning journey with our Handwriting Practice Addition Worksheets designed for children aged 3-8! These engaging worksheets combine fun addition exercises with handwriting skills, helping young learners improve both their math and writing abilities. Each worksheet features colorful illustrations and simple, age-appropriate equations, making practice enjoyable. As your child works through addition problems, they also develop fine motor skills and proper letter formation. Perfect for homeschooling, classroom activities, or extra practice at home, our worksheets foster a love for learning while building confidence in math and writing. Start your child's path to mastery today!
Handwriting practice, particularly for children ages 3-8, is crucial for several reasons. First, it lays the foundation for fine motor skills, essential for various tasks beyond writing, such as using tools and drawing. Developing these skills early helps children enhance their hand-eye coordination and dexterity, benefiting overall development.
Moreover, handwriting is closely linked to literacy. When children learn to form letters and words, they simultaneously develop literacy skills such as spelling and reading. Engaging them in handwriting practice at a young age fosters their ability to express thoughts and ideas, which is vital for their academic growth.
Additionally, handwriting promotes cognitive development. The process of writing by hand requires thought organization and critical thinking, vital in building academic foundations. Children learn to connect sounds to letters and gain a tactile understanding of letter recognition.
Lastly, handwriting practice encourages a sense of accomplishment. As children complete their work, they gain confidence in their abilities, fostering a positive attitude toward learning. In summary, investing time in handwriting practice for young children benefits motor skills, literacy, cognitive development, and emotional well-being, making it a vital component of early education.