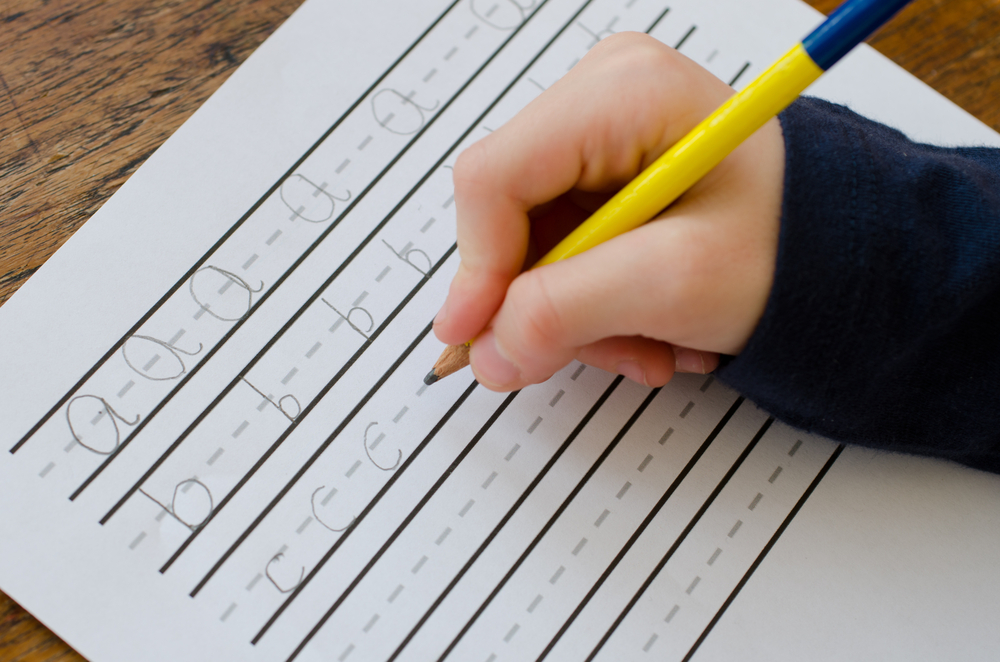
Hand-eye Coordination Cursive Letters Worksheets for Ages 3-8
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's hand-eye coordination with our Cursive Letters Worksheets designed for ages 3-8. Created to boost writing skills, each printable worksheet provides engaging activities that seamlessly blend fun with learning. Young learners improve their motor skills while mastering cursive letter formations. These worksheets offer structured practice aligning with educational standards to cultivate legible and fluent writing. Perfect for parents and teachers, they make learning delightful while promoting developmental milestones. Help your child build a strong foundation with exercises that transform cursive practice into an enjoyable adventure. Ready for print, this resource sparks curiosity and skill in early education.


Cursive ABCs: Uppercase E


Cursive ABCs: Uppercase F

Cursive ABCs: Uppercase C


Cursive ABCs: Lowercase c


Cursive ABCs: Lowercase h


Cursive ABCs: Uppercase H
Hand-eye coordination is crucial for children aged 3-8, as it plays a significant role in their overall development and academic success. During these formative years, one of the most effective ways to enhance this skill is through practicing cursive letters. Handwriting in cursive requires the brain to integrate visual information (seeing the letter), with motor control (writing the letter), thereby boosting coordination between the eyes and hands.
For parents and teachers, focusing on cursive handwriting can offer multiple benefits. Improved hand-eye coordination is directly linked to better fine motor skills, which are essential not just for writing but also for other daily tasks such as dressing, eating, and even playing. Enhanced coordination and fine motor skills lead to greater confidence and independence in children.
Additionally, cursive handwriting helps in cognitive development. The complexity of cursive writing engages various parts of the brain, enhancing synaptic connections and improving memory retention. This cognitive exercise also encourages better alphabet recognition and reading confidence, aiding literacy development.
Investing time and effort into developing these skills early can set a strong foundation for children's educational journeys. It ensures they have the necessary tools to perform a variety of academic and non-academic tasks effectively, thus promoting overall balance and well-being.















