Improve fine motor skills Worksheets for Ages 3-9
4 filtered results
-
From - To
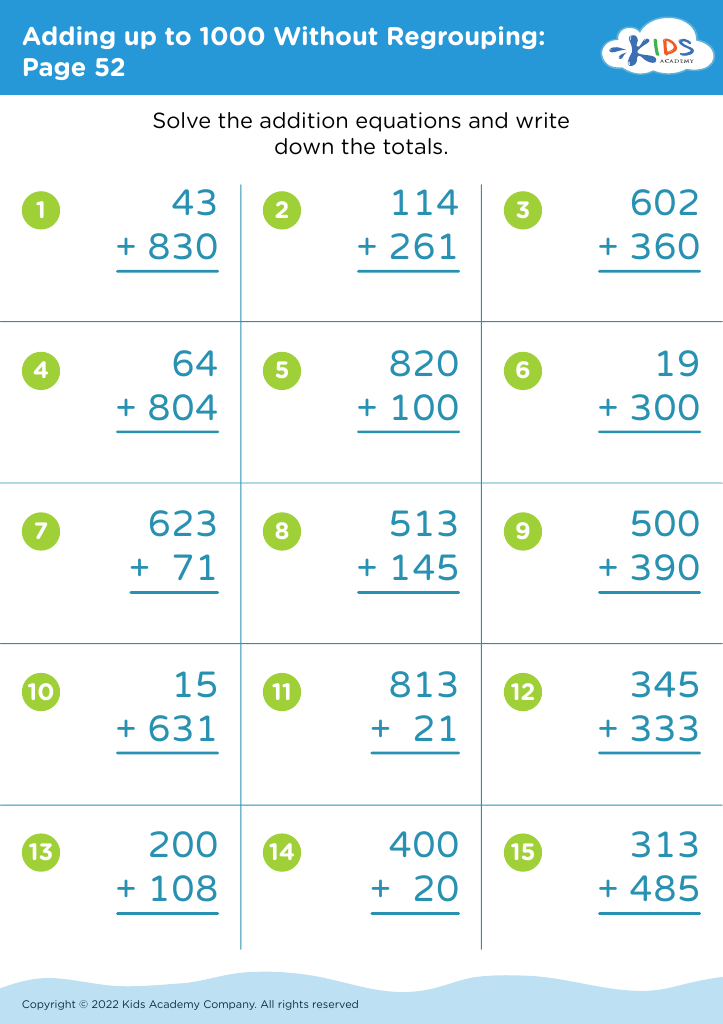
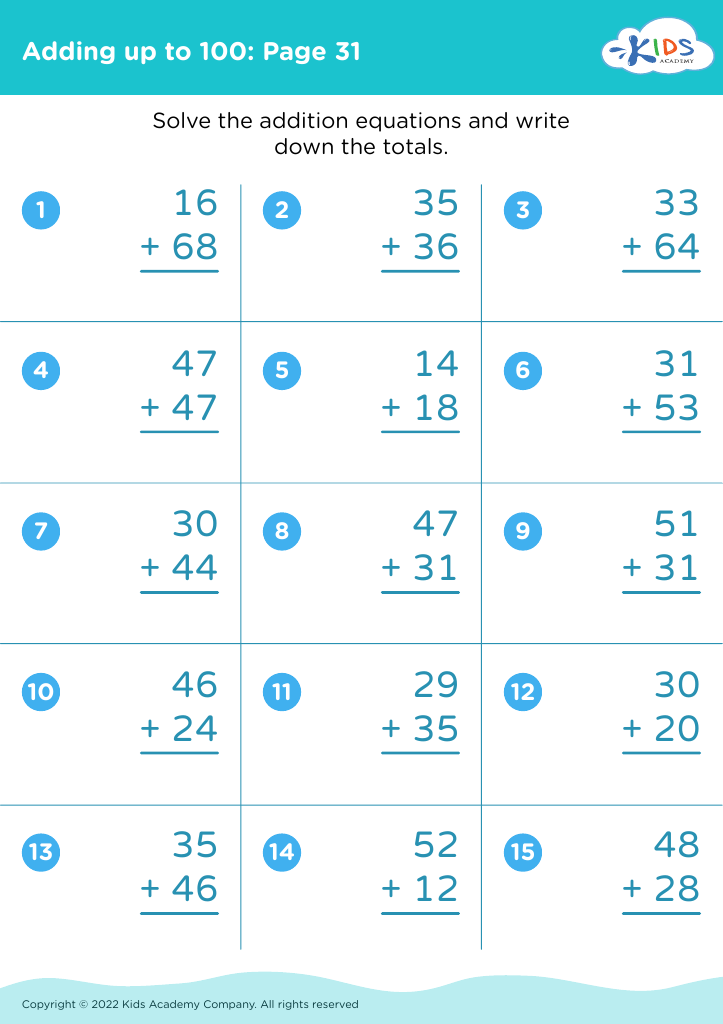
Discover our "Improve Fine Motor Skills Worksheets" designed for children aged 3-9! These engaging, printable activities are perfect for enhancing coordination and dexterity. Through fun tasks like coloring, cutting, and tracing, kids can strengthen the muscles in their hands and fingers, essential for writing and other everyday tasks. Each worksheet supports developmental milestones while keeping learning enjoyable. Tailored for diverse skill levels, our resources cater to all learners. Embrace creativity and growth with our fine motor skill worksheets, making skill-building enjoyable for both parents and kids. Start your child's journey to improved motor skills today!
Improving fine motor skills in children ages 3-9 is crucial for their overall development and learning success. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers, and are essential for everyday tasks such as writing, using scissors, and tying shoelaces.
For parents and teachers, nurturing these skills can enhance a child's independence and self-confidence. Children with strong fine motor skills are better equipped to engage in age-appropriate activities, leading to a greater sense of achievement and a more positive attitude toward learning. Additionally, fine motor proficiency is closely linked with cognitive development—children who practice these skills often experience improved hand-eye coordination, problem-solving abilities, and focus.
Moreover, fostering fine motor skills can help prevent future educational challenges. Children who struggle with these skills may become frustrated with academic tasks, especially those involving writing or crafting, which can hinder their overall performance in school. By incorporating play-based activities, such as puzzles, arts and crafts, and hands-on problem-solving tasks, teachers and parents can create a conducive environment for skill development. Thus, prioritizing fine motor skills is essential not just for immediate success, but for laying the groundwork for lifelong learning and independence.