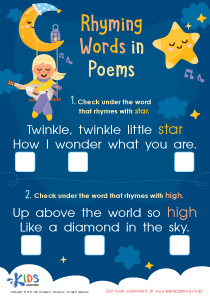
Fine Motor Skills Building Vocabulary Worksheets for Ages 3-9 - Page 2
25 filtered results
-
From - To
Fine motor skills are crucial for children's overall development, particularly between the ages of 3 to 9. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, enabling children to perform tasks such as writing, cutting, and tying shoelaces. Parents and teachers should prioritize building fine motor skills for several reasons.
Firstly, fine motor skills are foundational for academic success. As children enter school, the ability to manipulate small objects and tools becomes essential for writing and engaging in art projects. Improved fine motor skills contribute to a child's confidence in academic settings.
Secondly, these skills support everyday tasks, fostering independence. When children learn to zip their jackets, button shirts, or use utensils effectively, they gain self-reliance and develop a positive self-image.
Moreover, fine motor activities encourage cognitive development. Engaging in tasks that require precision and control can enhance problem-solving skills and concentration.
Finally, fostering a rich vocabulary during fine motor activities, such as talking about the shapes of objects or the actions being performed, integrates language development as children learn to describe their actions and thoughts.
In conclusion, investing time in fine motor skill development not only equips children for school but also enriches their daily lives and promotes holistic growth.










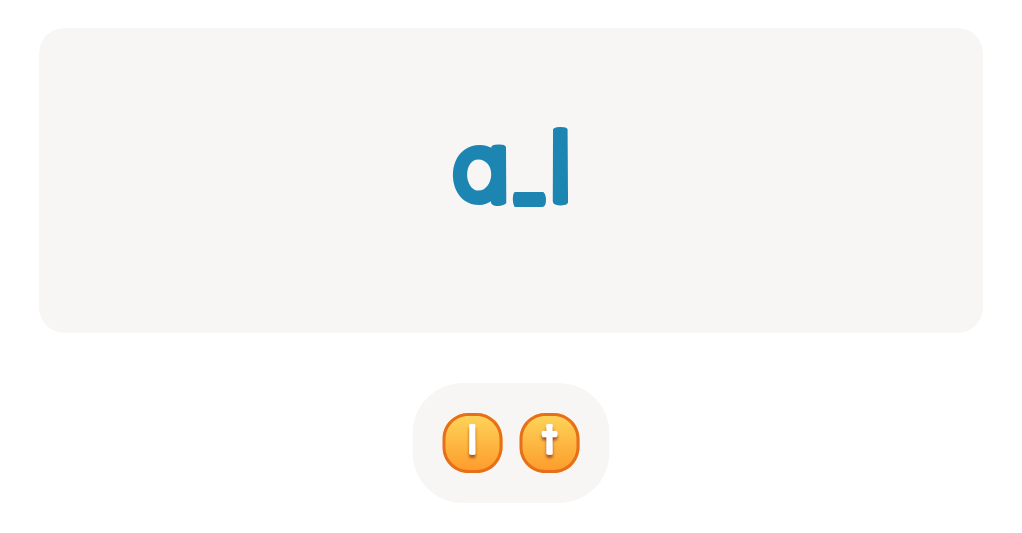





.jpg)