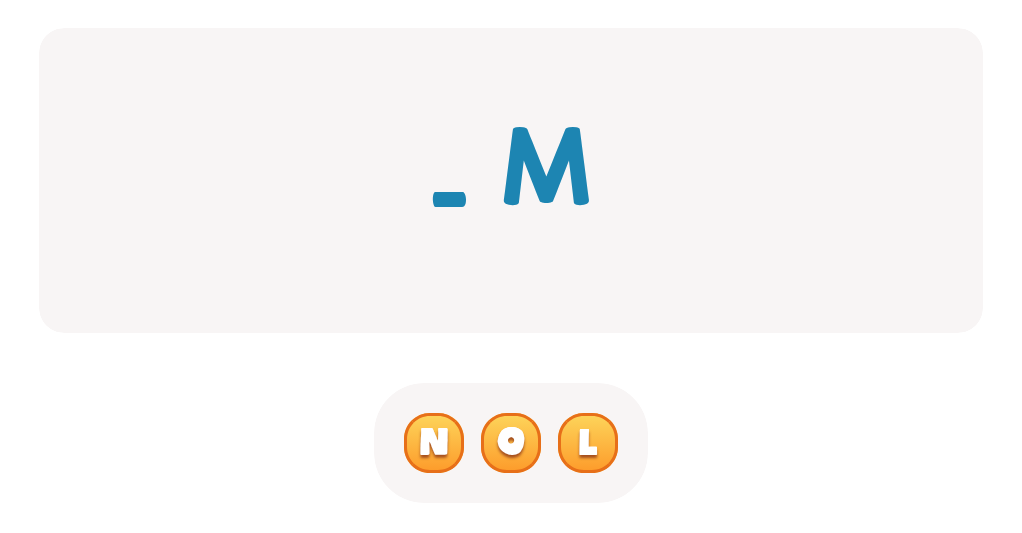
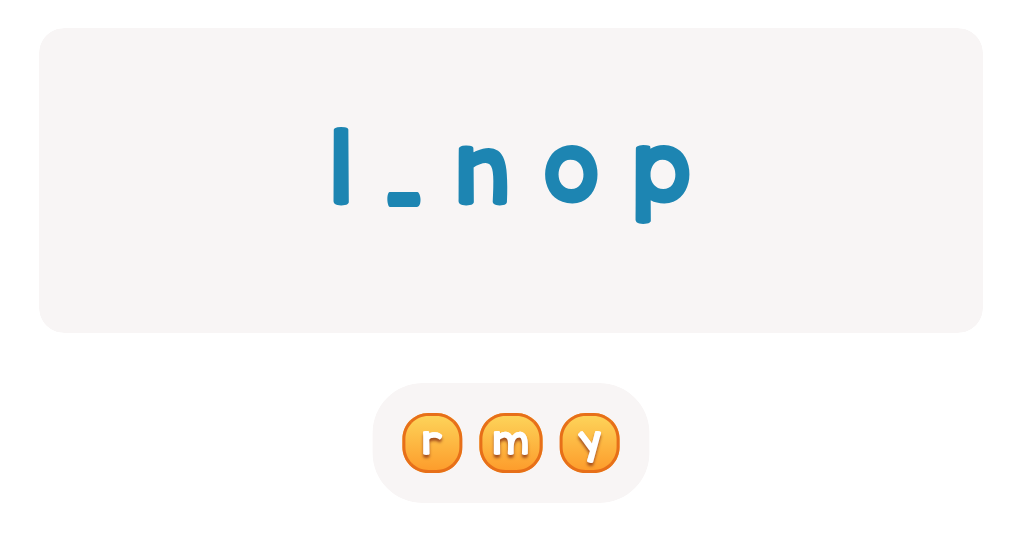
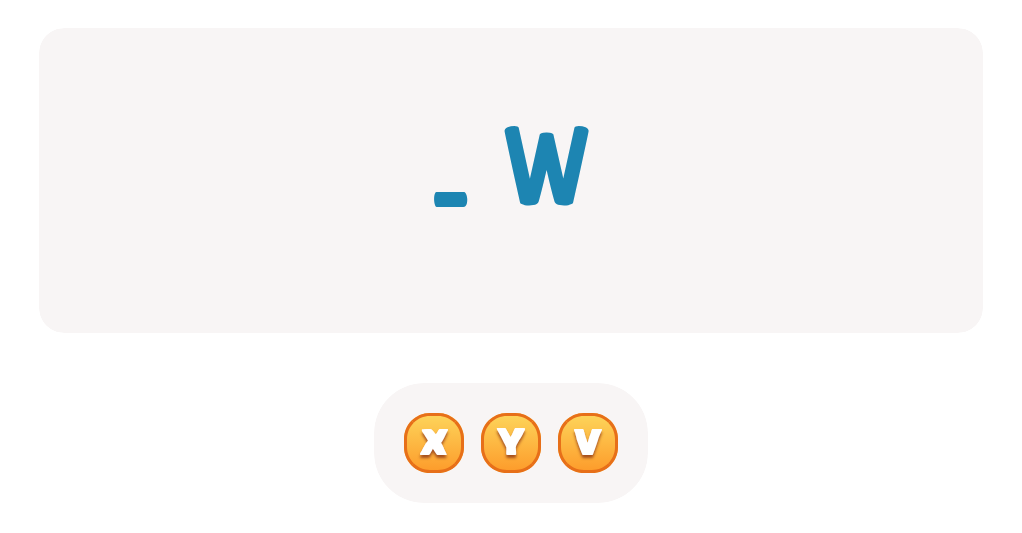
Handwriting practice ABC Letters Worksheets for Ages 4-6 - Page 2
26 filtered results
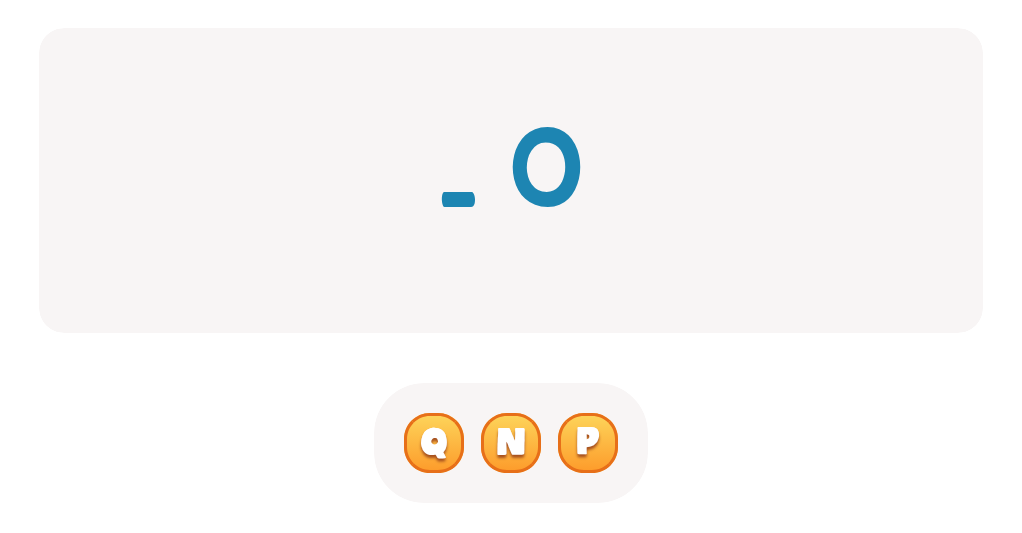
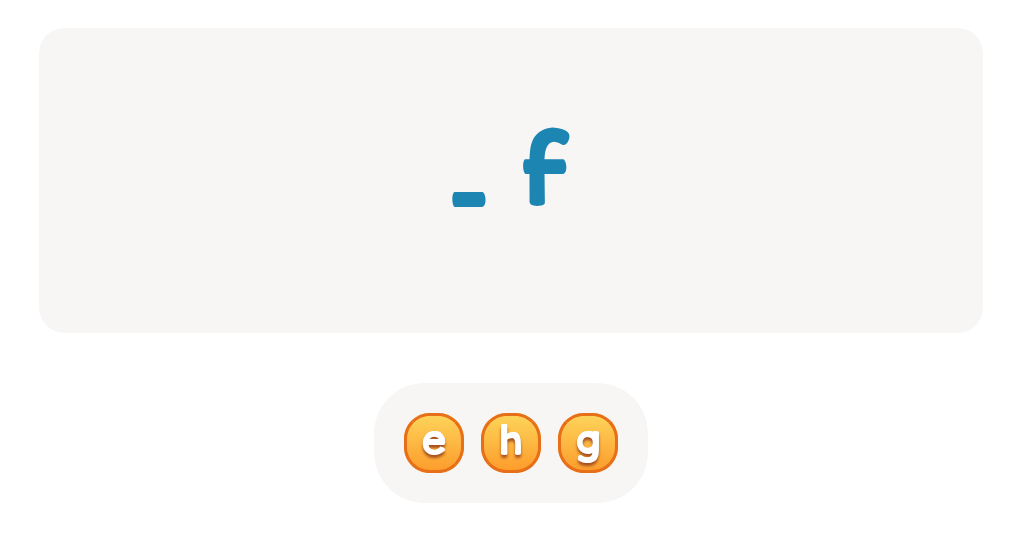
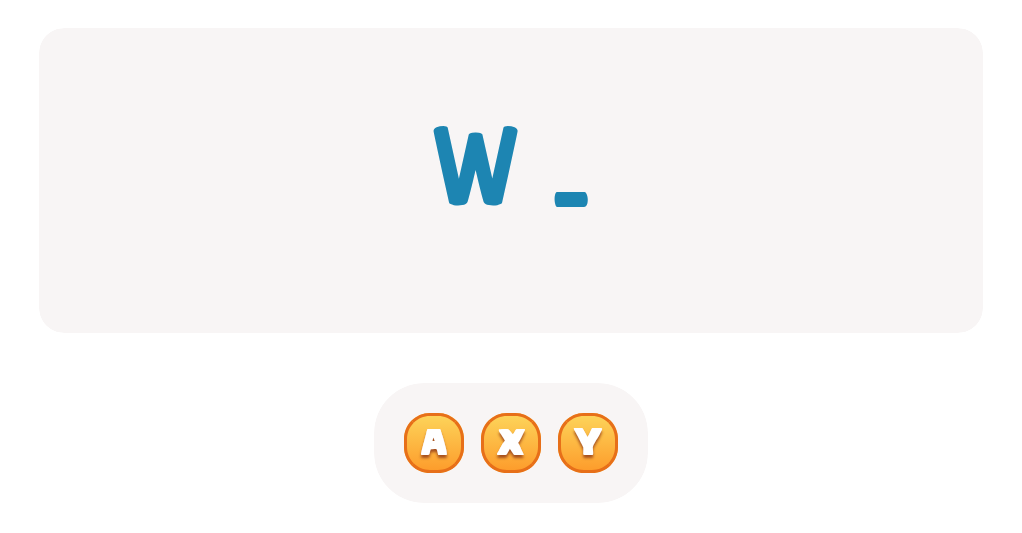
-
From - To


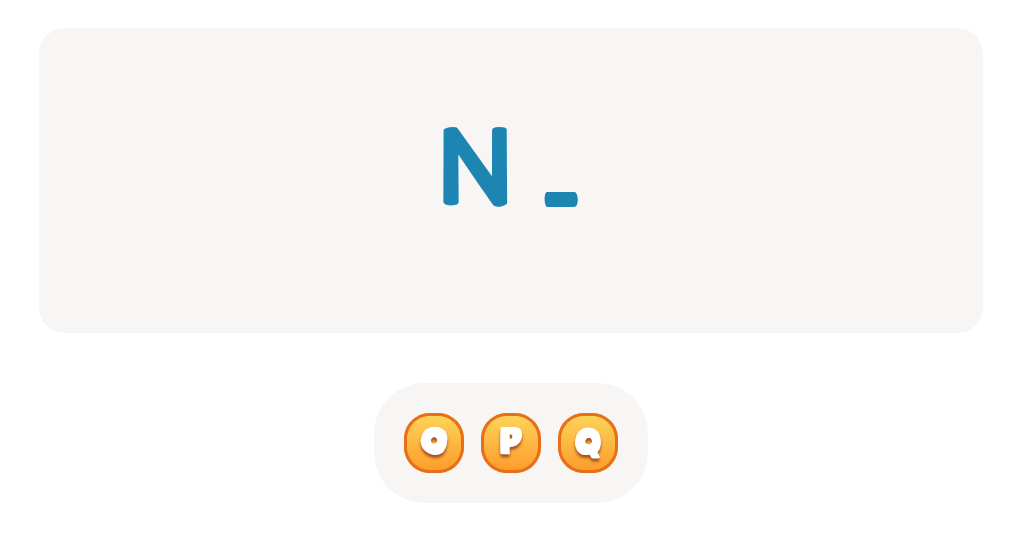
Letter N Coloring Sheet


My Name: Cheerful Balloons Worksheet
Handwriting practice, particularly for preschoolers aged 4-6, plays a crucial role in early childhood development. It is not merely about learning to write letters but is an essential segment of overall motor skill development. Fine motor skills, which are vital for daily tasks, are enhanced when children practice writing—these skills also translate into their abilities to manage scissors, buttons, and other hand-eye coordination activities.
Additionally, handwriting promotes cognitive development. When children engage in the repetitive formation of letters, they begin to recognize letter shapes and sounds, which lays the foundation for reading readiness. This connection between writing and phonics aids in improving literacy skills, essential for academic success as they progress to later grades.
Furthermore, early handwriting practice fosters a sense of achievement and confidence. When children can write their names or simple words, they often feel a greater sense of independence, making learning more engaging and motivating.
Finally, in today’s digital age, instilling the importance of handwriting cultivates a lifelong skill that enhances communication. In sum, investing time in handwriting practice for young children is crucial for their motor skills, cognitive development, emotional well-being, and academic preparedness.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students