Fine motor skills (writing) Math Worksheets for Ages 4-6 - Page 2
36 filtered results
-
From - To


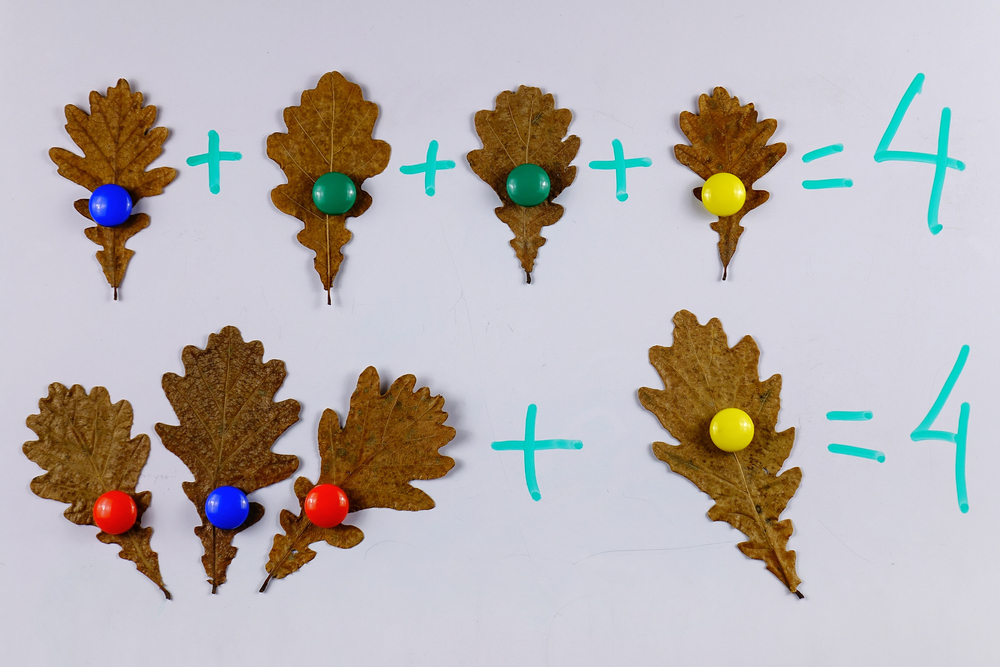
Counting Flowers Worksheet
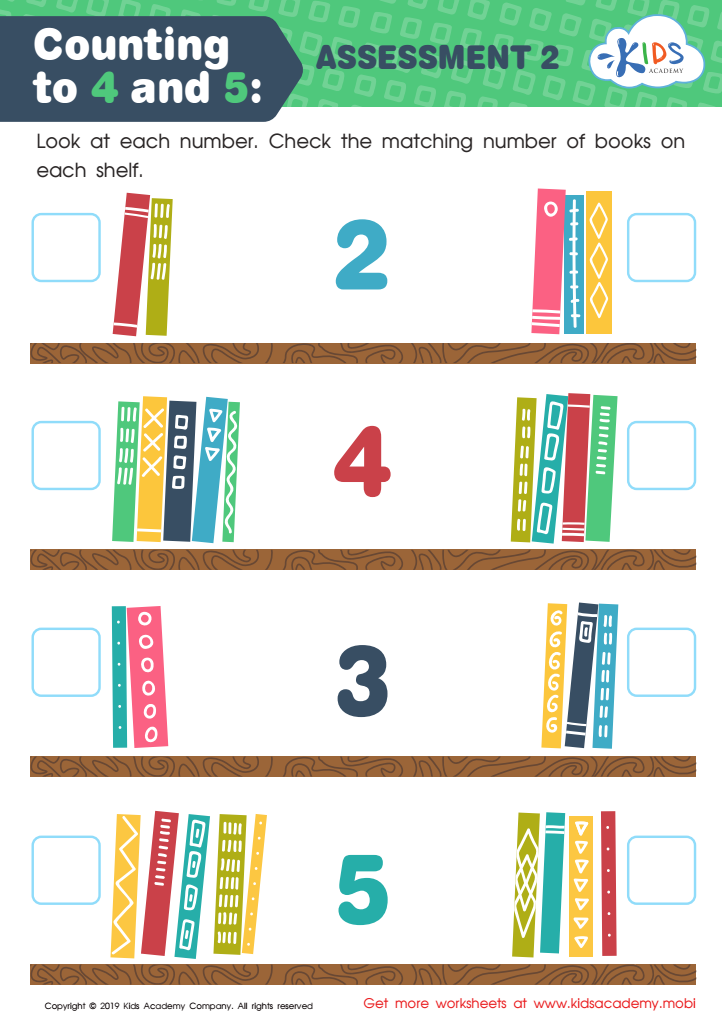

Counting to 4 and 5: Assessment 2 Worksheet
Parents and teachers should prioritize fine motor skills and math development in children aged 4-6 because these abilities form foundational building blocks for future academic success and daily life functioning. Fine motor skills, such as writing, involve the precise use of small muscles in the fingers and hands, which are crucial for various tasks including drawing, buttoning clothes, and eventually, handwriting. Strengthening these skills enhances hand-eye coordination and dexterity, laying the groundwork for more complex activities as children grow older.
Math skills introduced at this age, like recognizing numbers, basic counting, and understanding shapes, ignite cognitive processes essential for logical thinking, problem-solving, and reasoning. Early math experiences help children grasp concepts essential for higher-order math that they will encounter as they advance in school.
Integrating fine motor skills and math development in early childhood fosters a well-rounded educational foundation. Activities that blend these skills, such as counting beads on a string or drawing shapes, effectively combine cognitive and physical learning. By focusing on these areas, parents and teachers assist children in gaining confidence and competence, promoting a positive attitude toward learning that will benefit them throughout their educational journey and beyond.



 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students








%20(1).jpg)











