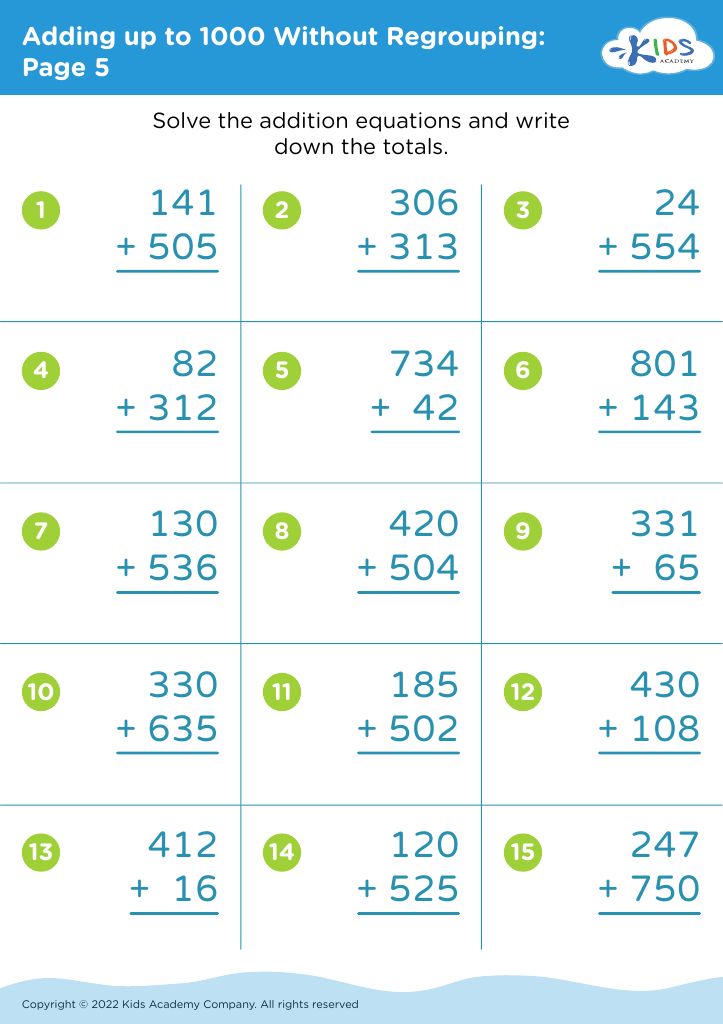
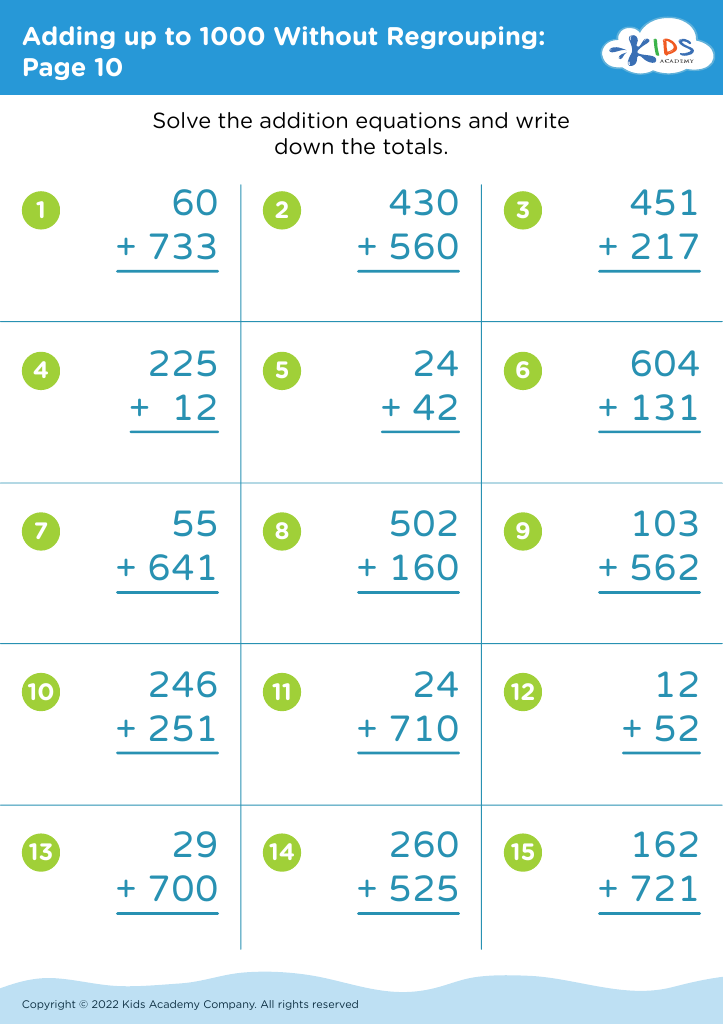
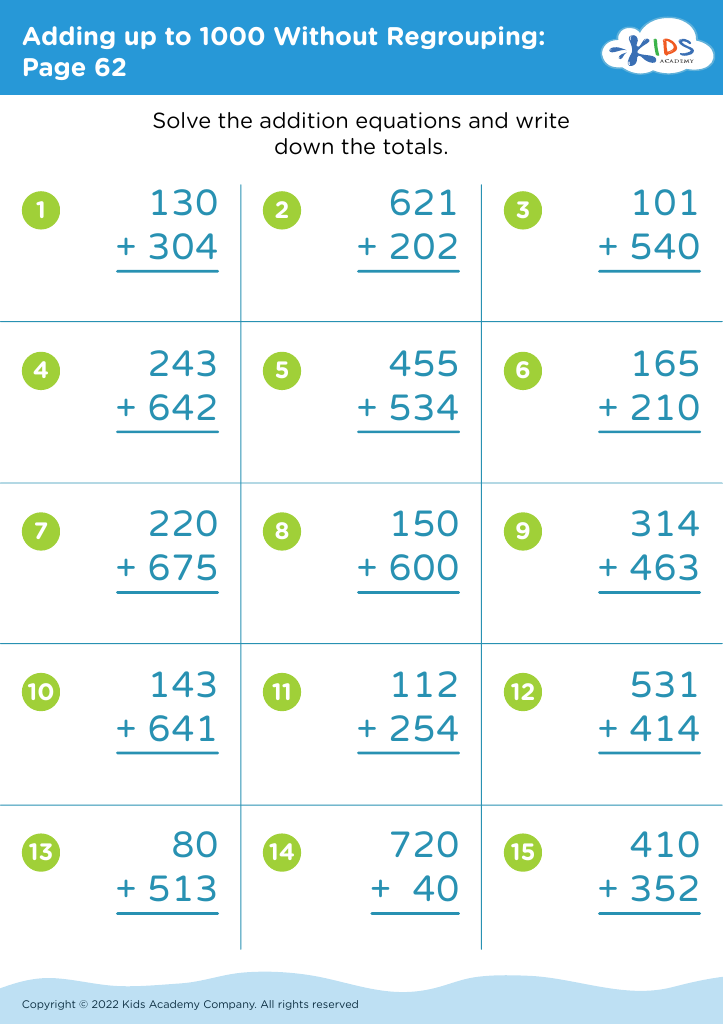
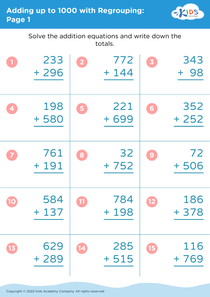
Basic Math Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 4-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Unlock your child’s potential with our expertly designed worksheets focused on "Basic Math Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping". Tailored for ages 4-7, these engaging exercises help young learners master addition without the complexity of regrouping. Each worksheet is crafted to build confidence and reinforce math fundamentals, paving the way for future success. Ideal for both classroom and home learning, our printable resources provide an excellent foundation in arithmetic. Delight your little mathematicians as they discover the joy of learning through these fun, educational activities. Visit our website today to empower your youngster’s mathematical journey!
Basic math skills, particularly the ability to add numbers up to 1000 without regrouping, form an essential foundation for young children's future learning and daily life. For parents and teachers, focusing on this skill with children aged 4-7 is crucial for several reasons:
-
Foundational Skills: Mastering basic addition helps children develop a solid understanding of mathematical principles. It's like building a strong foundation for a house; without it, the structure cannot stand firm over time.
-
Confidence Building: When children consistently experience success in basic math tasks, they gain confidence. This positive reinforcement encourages them to tackle more complex problems as they progress in their education.
-
Cognitive Development: Early skills in addition stimulate cognitive processes such as problem-solving, critical thinking, and logical reasoning, all of which are important in many aspects of life beyond mathematics.
-
Real-World Application: Basic math is used daily, whether in counting money, measuring ingredients for a recipe, or time management. Preparing children with these basic skills equips them for practical situations.
-
School Readiness: Children proficient in basic math are better prepared for more advanced topics in school. This early success can set a positive trajectory for their entire academic journey.
By investing time in teaching and reinforcing the ability to add up to 1000 without regrouping, parents and teachers lay the groundwork for children's academic and personal growth.