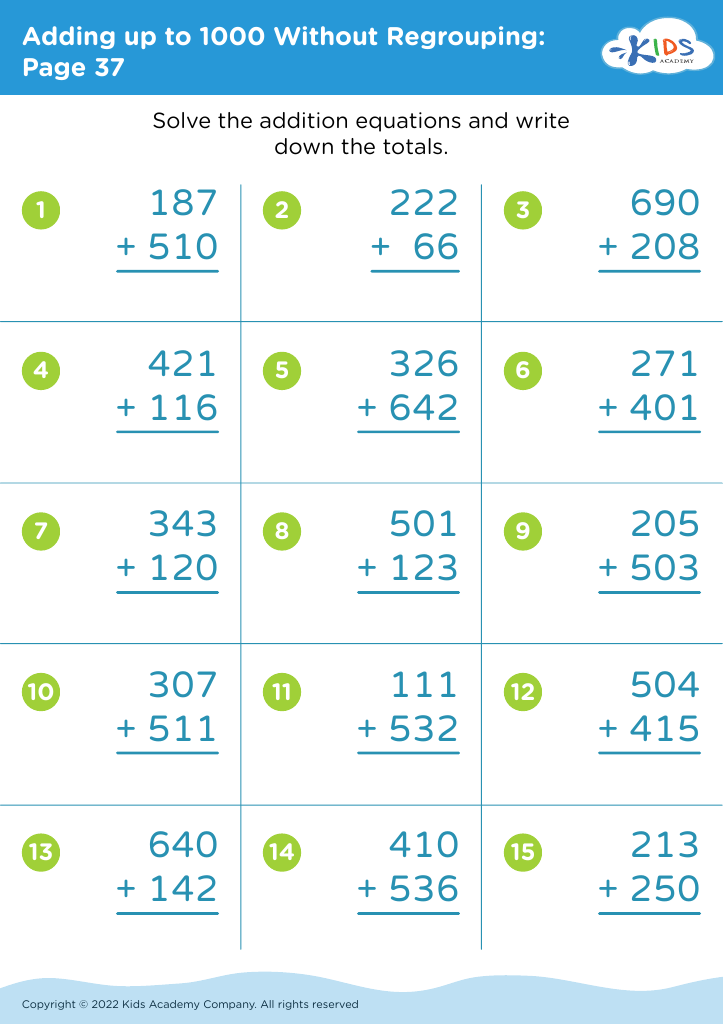
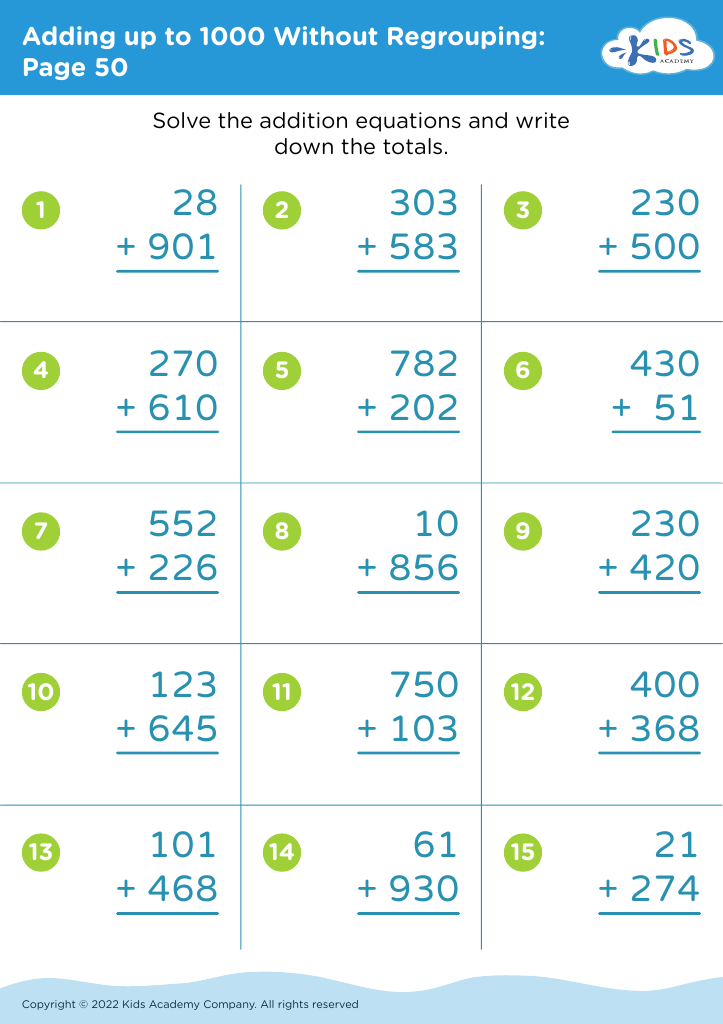
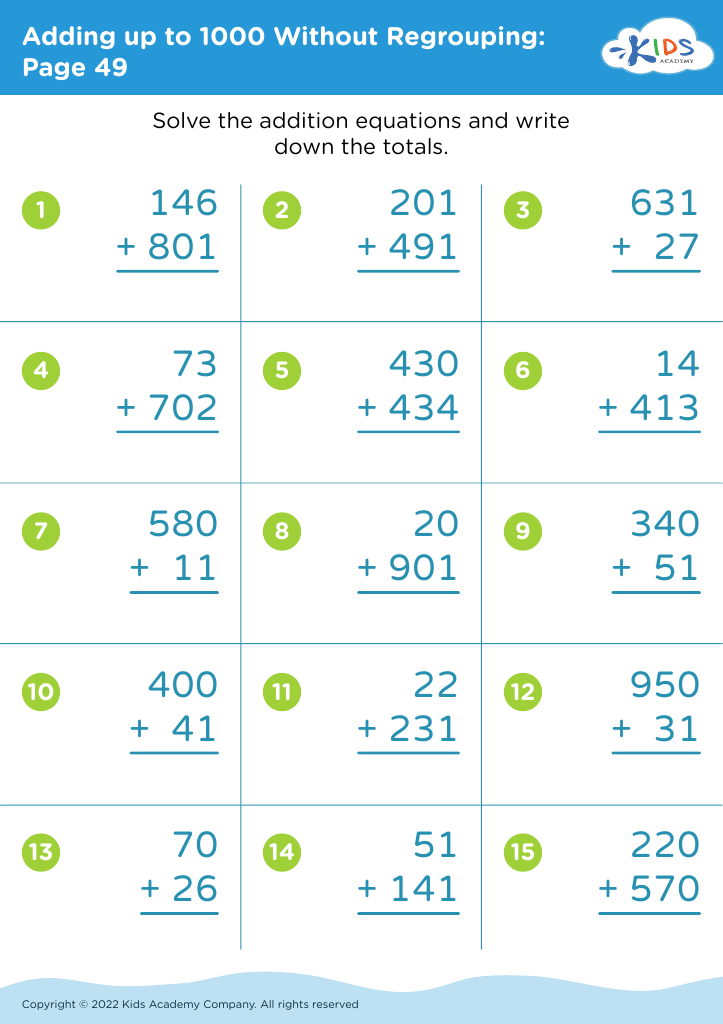
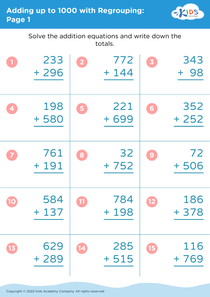
Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 5-9
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Unlock the potential of your child's fine motor skills with our expertly crafted worksheets designed for ages 5-9! Focused on adding up to 1000 without regrouping, these worksheets provide engaging exercises that enhance dexterity, precision, and muscle control essential for writing and daily activities. Each worksheet combines fun math challenges with hands-on practice, guiding young learners through exciting math adventures while fostering strong and steady pencil grips. Perfect for home or classroom use, our fine motor skills worksheets are an enjoyable way to boost your child's math confidence and motor abilities. Access free worksheets now and watch their skills soar!
Fine motor skills are crucial for children ages 5-9, as they impact a variety of essential life and academic tasks, including the ability to add up to 1000 without regrouping. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles in hands and fingers, which are fundamental for writing, manipulating objects, and performing daily activities. When children engage in activities like adding numbers up to 1000, it can significantly enhance their fine motor skills by requiring meticulous pencil control and accurate placement of numerals within columns.
Parents and teachers should care about the development of these skills because they directly influence a child's academic success and self-esteem. Strong fine motor skills allow children to participate effectively in classroom tasks, such as writing, drawing, and using manipulatives for math. This not only maximizes their learning potential but also fosters independence and confidence. Moreover, mathematical activities such as adding without regrouping reinforce cognitive skills like concentration, memory, and problem-solving—a foundation for more complex mathematical concepts.
In essence, promoting fine motor skills through educational activities supports holistic development and prepares children for future academic challenges and everyday tasks. Ensuring that children practice these skills through engaging, hands-on activities can significantly benefit their overall growth and learning journey.