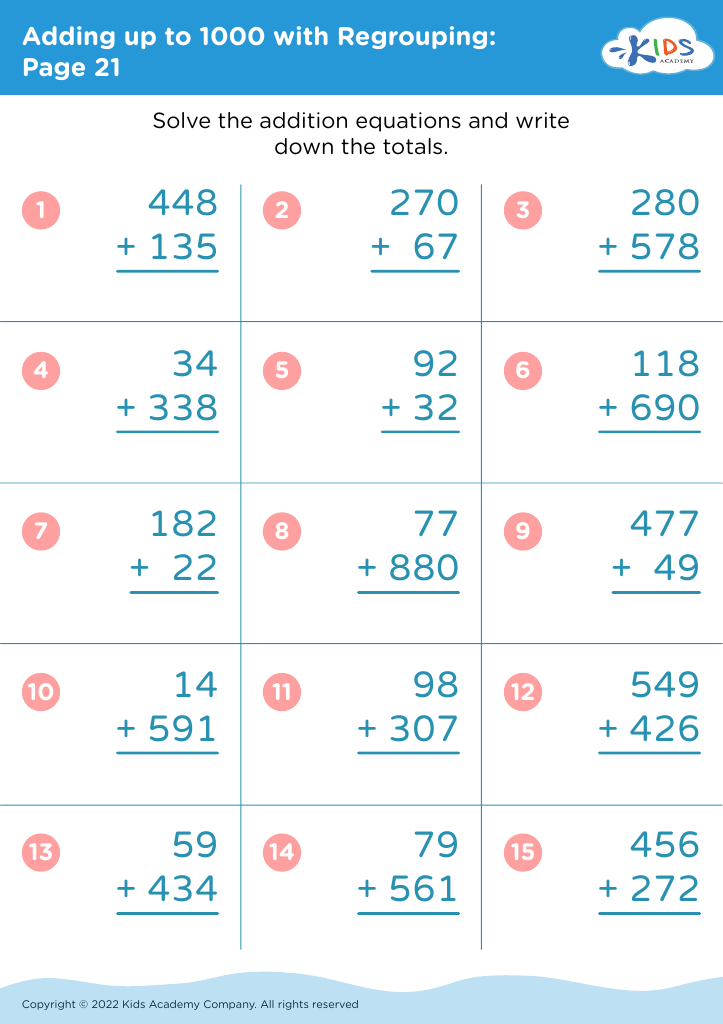
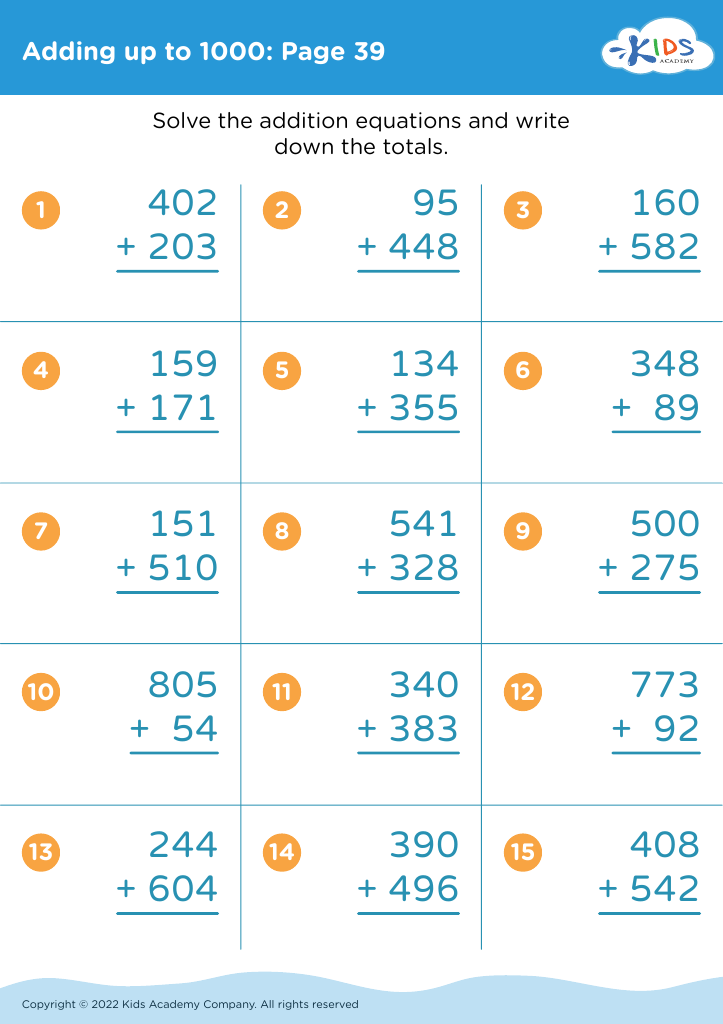
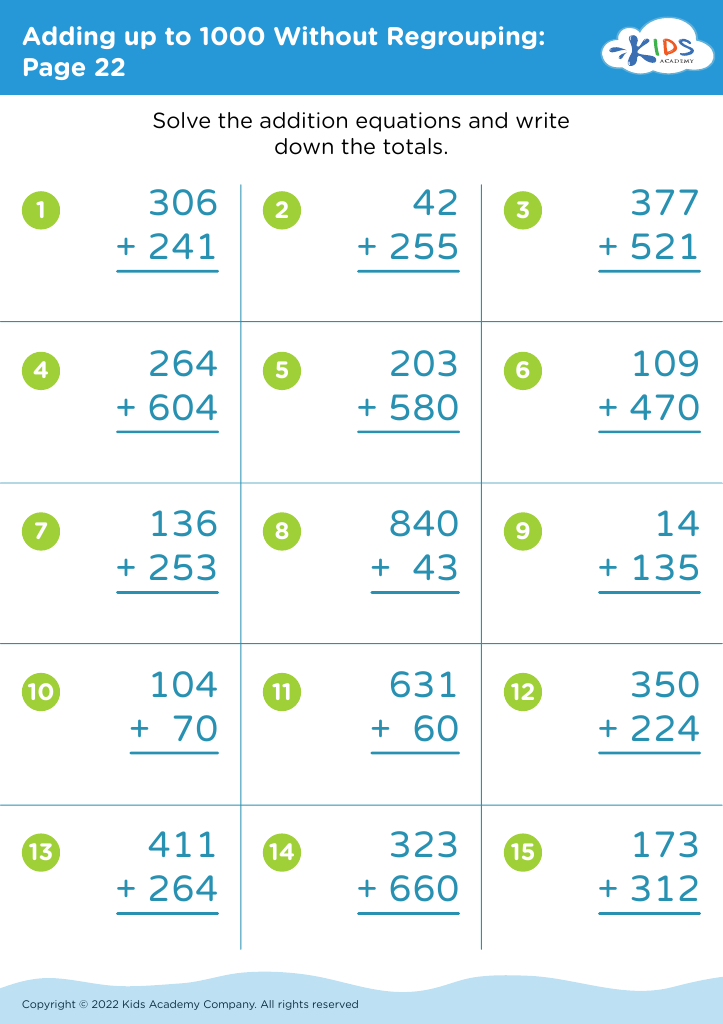
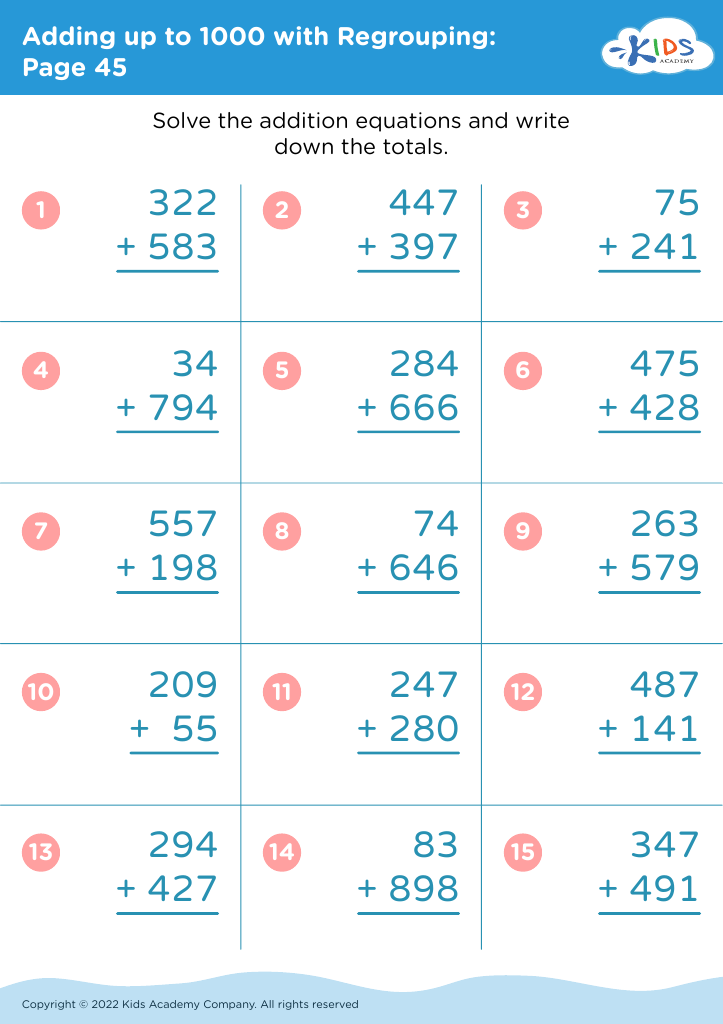
Fine motor skills (writing) Adding up to 1000 Worksheets for Ages 6-9
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's fine motor skills and writing abilities with our "Adding up to 1000 Worksheets" designed specifically for ages 6-9. These engaging worksheets combine fun math exercises with valuable writing practice, helping young learners develop essential skills as they improve their hand-eye coordination and pencil grasp. Each activity encourages children to trace numbers, write solutions, and practice proper letter formation. By integrating fine motor skills with math concepts, these worksheets provide a comprehensive approach to learning that keeps kids motivated and excited about writing and math. Perfect for home use or classroom settings, they are an excellent resource for every young learner!
Fine motor skills are essential for children aged 6-9 as they influence various aspects of development. At this age, children not only improve their writing abilities but also enhance tasks like drawing, cutting, and manipulating objects, which are critical for their academic success. Strong fine motor skills lead to improved handwriting, allowing students to express their ideas clearly and confidently on paper. This, in turn, positively impacts their overall educational engagement and self-esteem.
Additionally, fine motor development plays a vital role in children’s daily lives. Activities that require dexterity and precision—such as buttoning clothes, tying shoelaces, or using utensils—enhance their independence and self-sufficiency. Teachers and parents should prioritize activities that foster these skills, such as arts and crafts, puzzles, or building with blocks.
Moreover, fine motor skills are closely linked to cognitive development, as they often encourage problem-solving and critical thinking. By providing opportunities for children to practice and refine these skills, adults can empower them to navigate both academic challenges and daily life with greater ease. Thus, understanding and supporting fine motor skill development in children ensures they are equipped with the tools necessary for lifelong learning and personal growth.