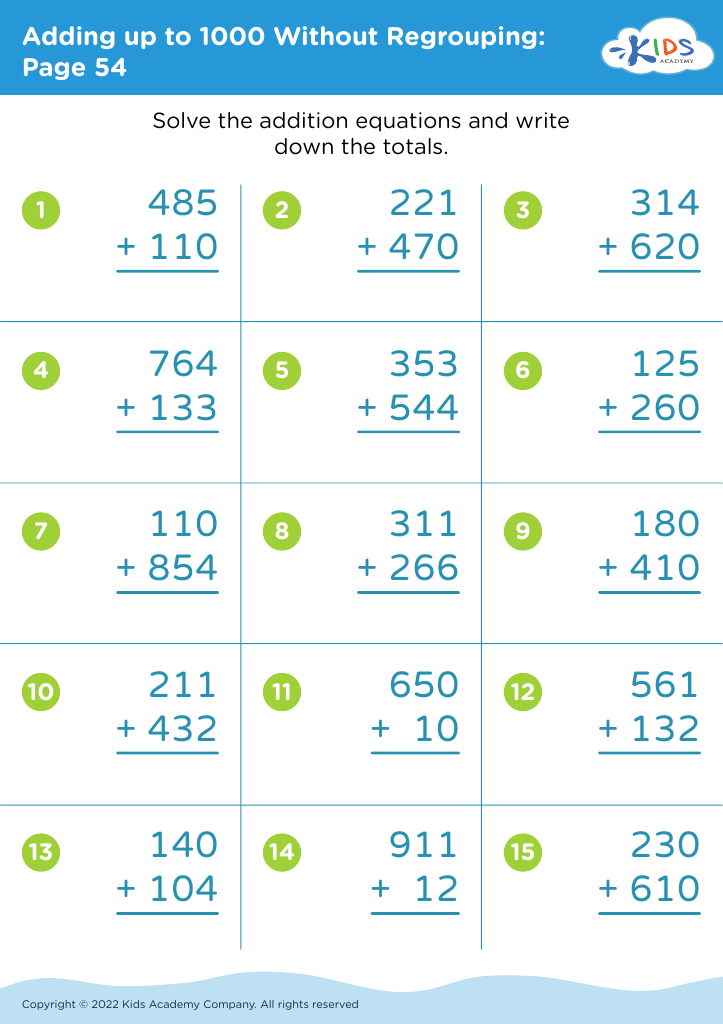
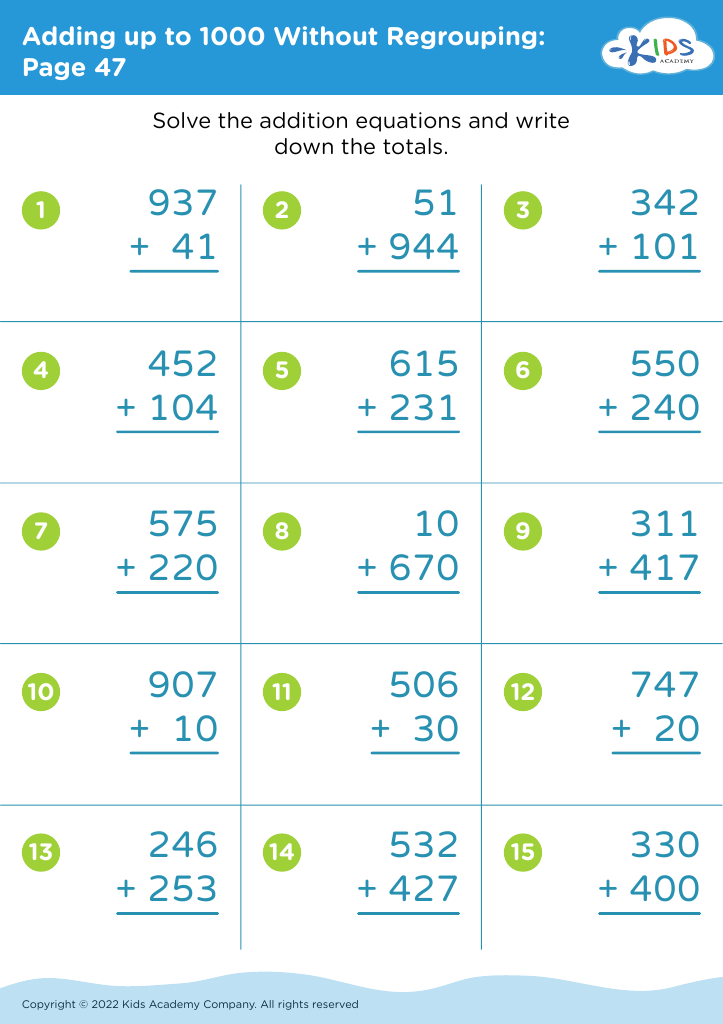
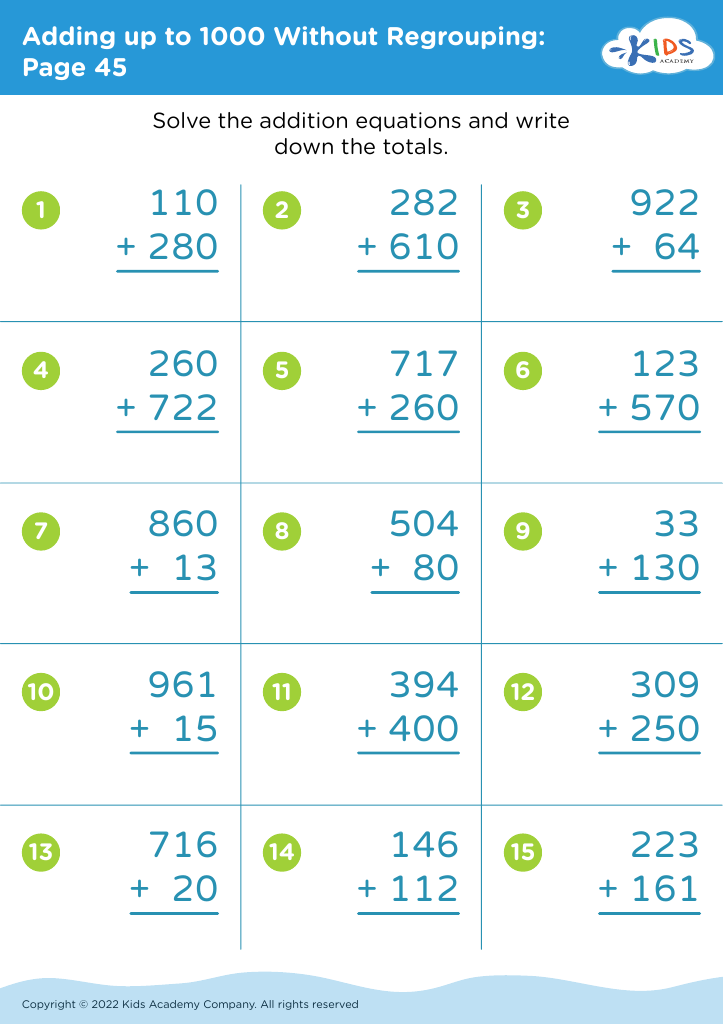
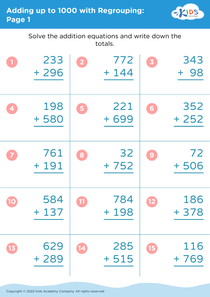
Understanding division Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 7-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Unlock the world of math with our "Understanding Division: Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 7-8". These engaging worksheets are designed to help young learners grasp the basics of division and addition in large numbers, without the complexity of regrouping. Featuring clear instructions and fun exercises, they cater to the unique learning needs of children aged 7-8. Our worksheets boost confidence and enhance essential math skills, paving the way for academic success. Perfect for classroom use or at-home practice, they make challenging concepts accessible and enjoyable for every child. Start your child's math journey today!
Understanding division and addition up to 1000 without regrouping is crucial for children aged 7-8 as it lays a strong foundation for advanced mathematical concepts. At this age, children's cognitive abilities rapidly develop, making it an ideal time to grasp the logic and principles underpinning these operations.
Firstly, mastering addition without regrouping builds familiarity with number relationships and arithmetic processes, fostering accuracy and confidence before introducing more complex methods like regrouping. It helps children understand place value, as they see how digits change in value based on their position.
Secondly, early comprehension of division promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By understanding that division is essentially distributing a total into equal parts, children grasp the concept of fairness and balance. Division also fosters a comprehension of multiplication's inverse relationship, integral for future math learning.
Moreover, foundational skills in basic arithmetic prepare children for real-life applications, such as sharing items equally. These competencies support learning in other academic areas, encourage logical reasoning, and contribute significantly to a child's overall cognitive development.
Ensuring that children are proficient with these fundamental concepts builds their mathematical confidence and paves the way for higher-level math proficiency. Thus, parents and teachers must value and reinforce these skills during their educational journey.