Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets for 7-Year-Olds
3 filtered results
-
From - To
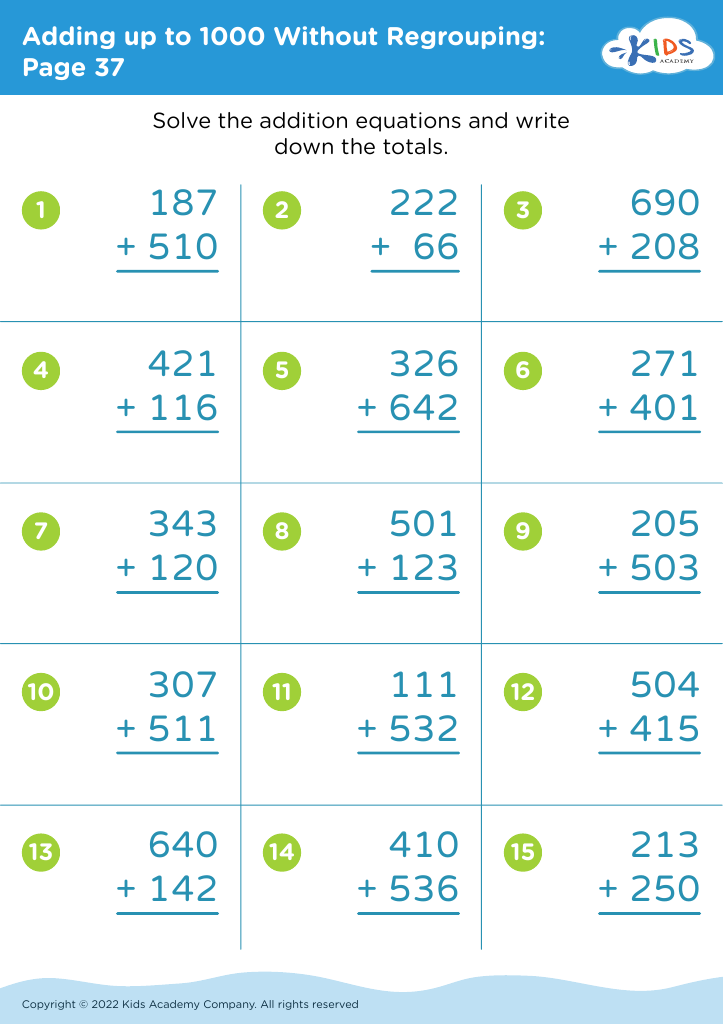
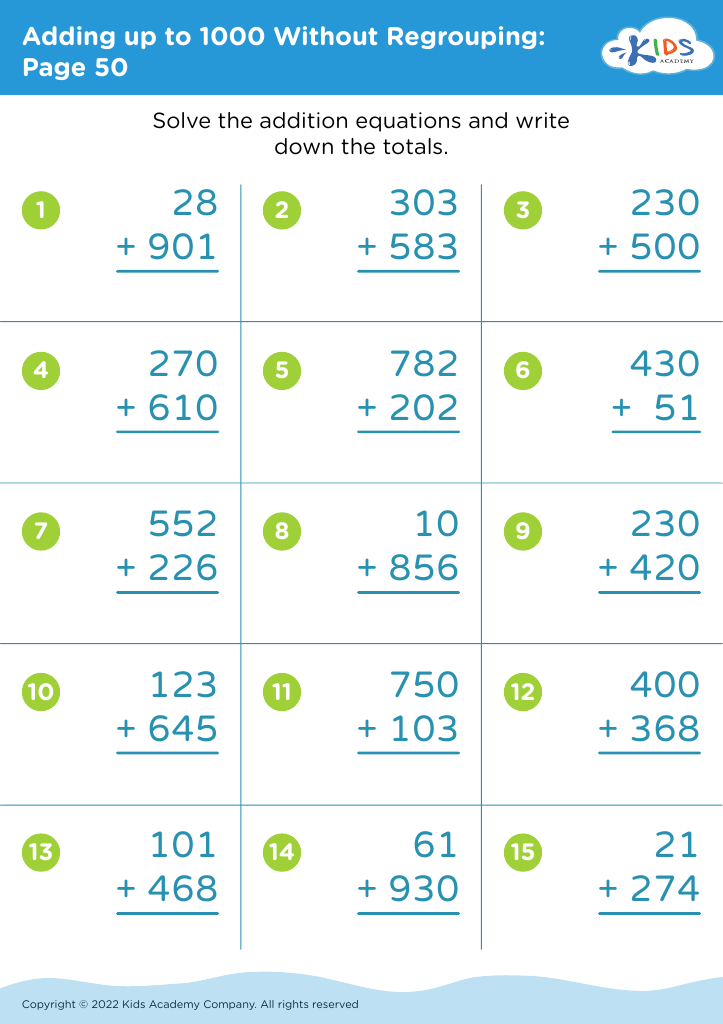
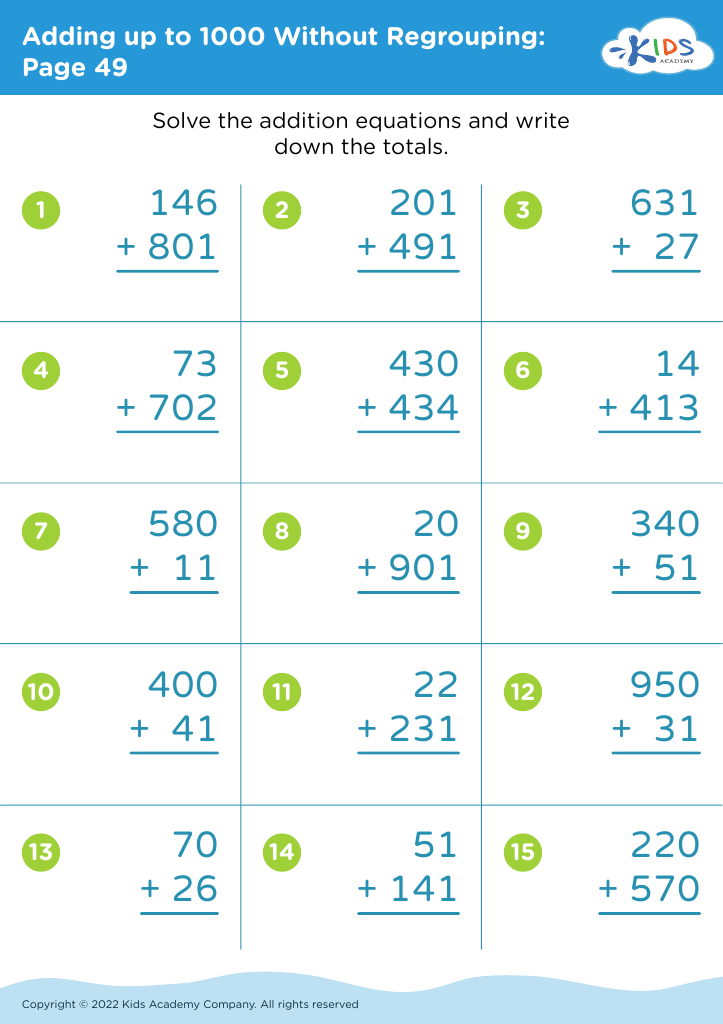
Explore our "Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets" designed specifically for 7-year-olds! These engaging worksheets not only enhance math proficiency by allowing students to practice addition up to 1000 without regrouping, but they also incorporate fine motor skill development crucial for young learners. With colorful designs and interactive exercises, children can improve their hand-eye coordination and handwriting while practicing fundamental math concepts. Perfect for at-home learning or classroom activities, these worksheets promote a fun and effective way to combine math and motor skill mastery. Start your child’s journey to academic success today!
Fine motor skills are crucial for young children, especially at the age of seven, when they are refining their ability to perform tasks that involve hand-eye coordination and precise movements. Teaching fine motor skills alongside mathematical concepts, such as adding numbers up to 1000 without regrouping, is beneficial for several reasons.
Firstly, fine motor skills are essential for everyday activities like writing, using scissors, and buttoning clothes. These skills lay the groundwork for academic success, promoting increased confidence and independence as children master tasks. By engaging in activities like writing numerals or drawing tally marks during math lessons, children enhance their dexterity while learning.
Secondly, mastering addition up to 1000 without regrouping directly fosters cognitive development. It strengthens a child's numerical understanding and enhances problem-solving abilities. Teachers and parents who incorporate fine motor skill activities into math lessons can make learning more engaging and interactive.
Practicing fine motor tasks, such as counting with manipulatives or organizing numbers with colored markers, not only builds arithmetic skills but also develops hand-eye coordination and spatial awareness. In summary, integrating fine motor skill development with math learning enriches a child's educational experience, promoting both academic and personal growth.