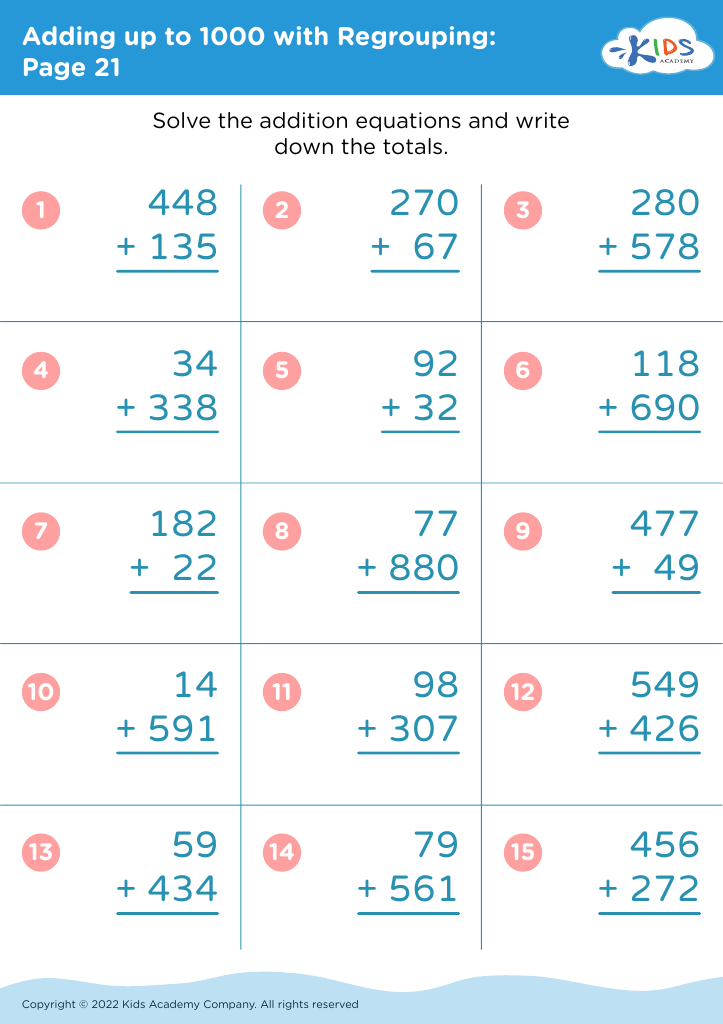
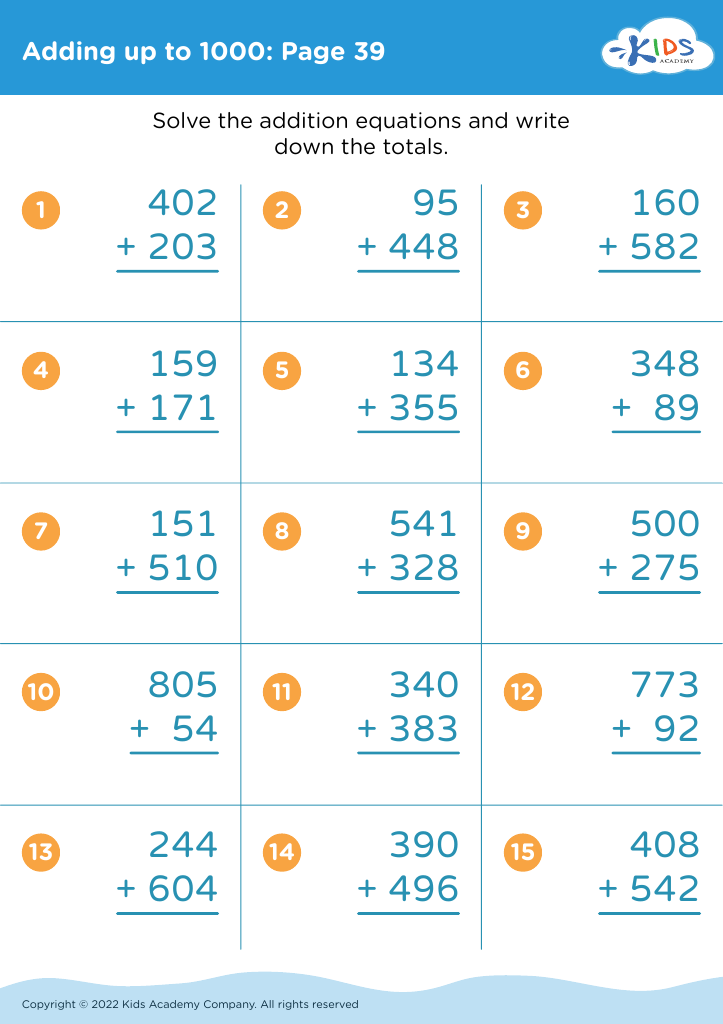
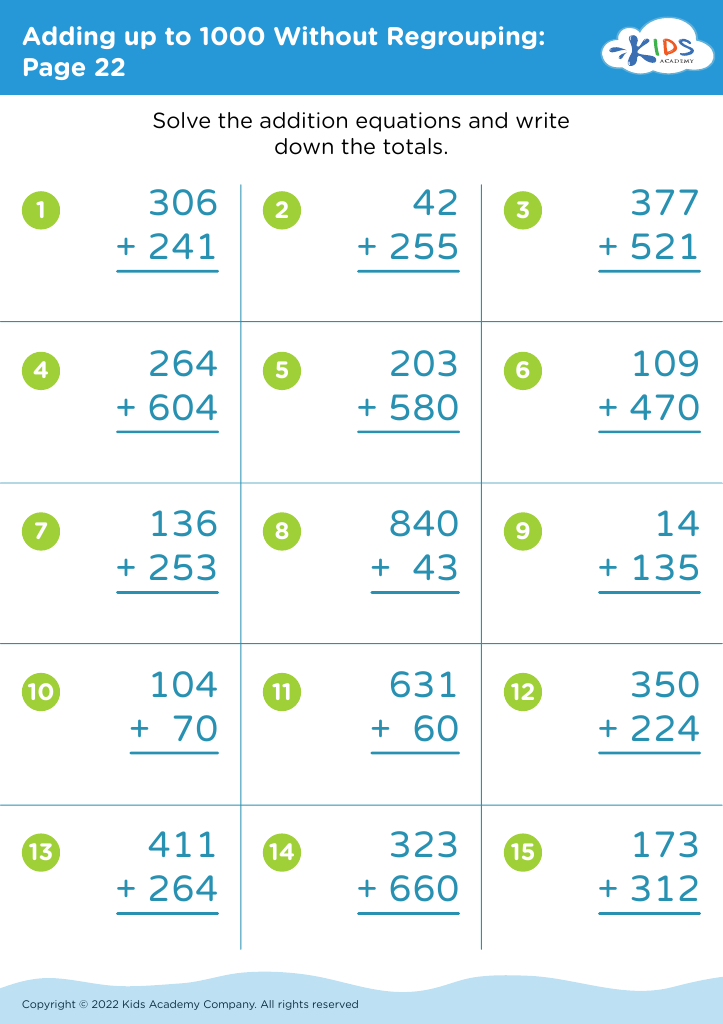
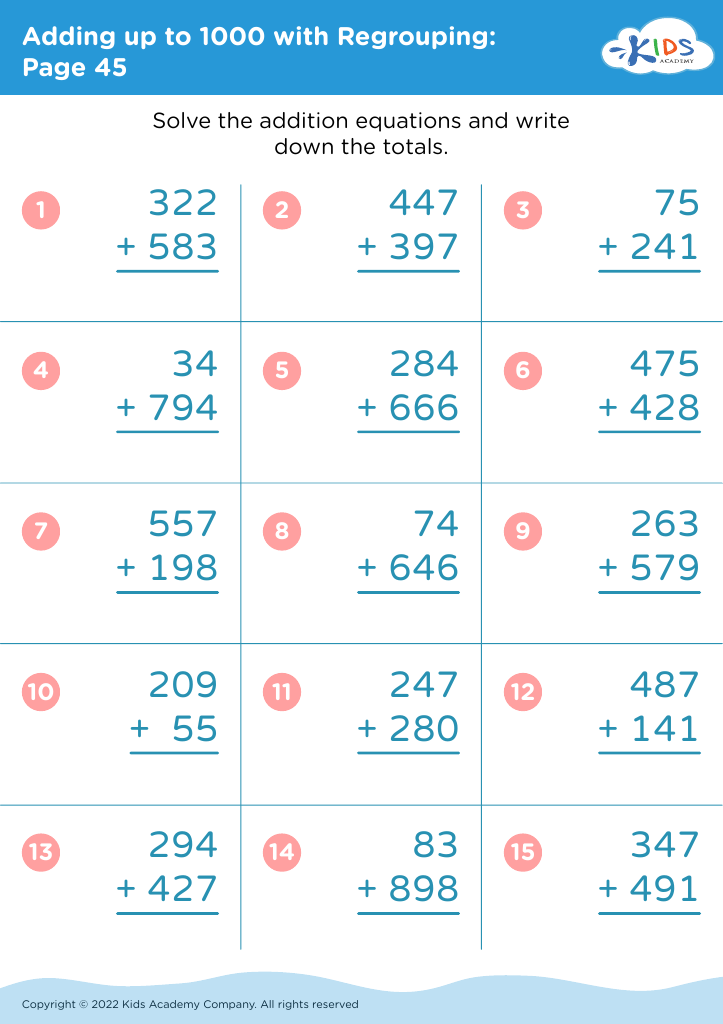
Fine motor skills (writing) Adding up to 1000 Worksheets for 7-Year-Olds
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your 7-year-old's fine motor skills with our engaging "Adding Up to 1000" worksheets! Designed specifically for young learners, these worksheets combine math and writing practice to improve hand coordination and control. Your child will enjoy completing fun activities that require them to practice writing numbers, tracing, and problem-solving, all while effectively increasing their confidence in mathematical concepts. Each worksheet is thoughtfully crafted to support development and keep kids motivated, making learning enjoyable. Perfect for home or school, these resources help sharpen fine motor skills essential for their academic journey. Start your child's engaging learning experience today!
Fine motor skills are essential for a child's development, particularly in writing, which is a fundamental skill for academic success. For 7-year-olds, these skills play a vital role not just in their ability to write but also in their overall confidence and self-esteem. When children can grip a pencil properly and form letters accurately, they are better equipped to express their thoughts and ideas on paper.
Teachers and parents should care about developing fine motor skills because they directly influence a child's learning capacity. Children with stronger fine motor abilities can complete written assignments more efficiently and focus on the content rather than the mechanics of writing. This can lead to improved performance across subjects, as writing is vital for communicating knowledge.
Moreover, fine motor skills contribute to everyday tasks beyond academics, such as tying shoelaces, buttoning shirts, and using utensils. By nurturing these skills, parents and teachers help children gain independence and confidence in their abilities. Early intervention and practice can make a significant difference, paving the way for a smoother transition into more complex writing tasks in later grades.
In summary, fostering fine motor skills at this age supports both academic achievement and daily life skills, benefiting children in numerous ways.