Writing practice Easy Numbers Worksheets for Ages 3-6
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover a fun and engaging way for children aged 3-6 to develop their writing skills with our Easy Numbers Worksheets! Designed to spark creativity and enhance learning, these worksheets guide young learners in writing numbers while reinforcing their understanding through vibrant illustrations and interactive exercises. Ideal for both classroom and home environments, the worksheets promote fine motor skills and number recognition. Whether your child is just starting their writing journey or looking to practice, our curated collection offers a variety of activities tailored to early learners' needs. Start nurturing your child’s writing abilities today with our captivating number worksheets!


Number 4 Printable
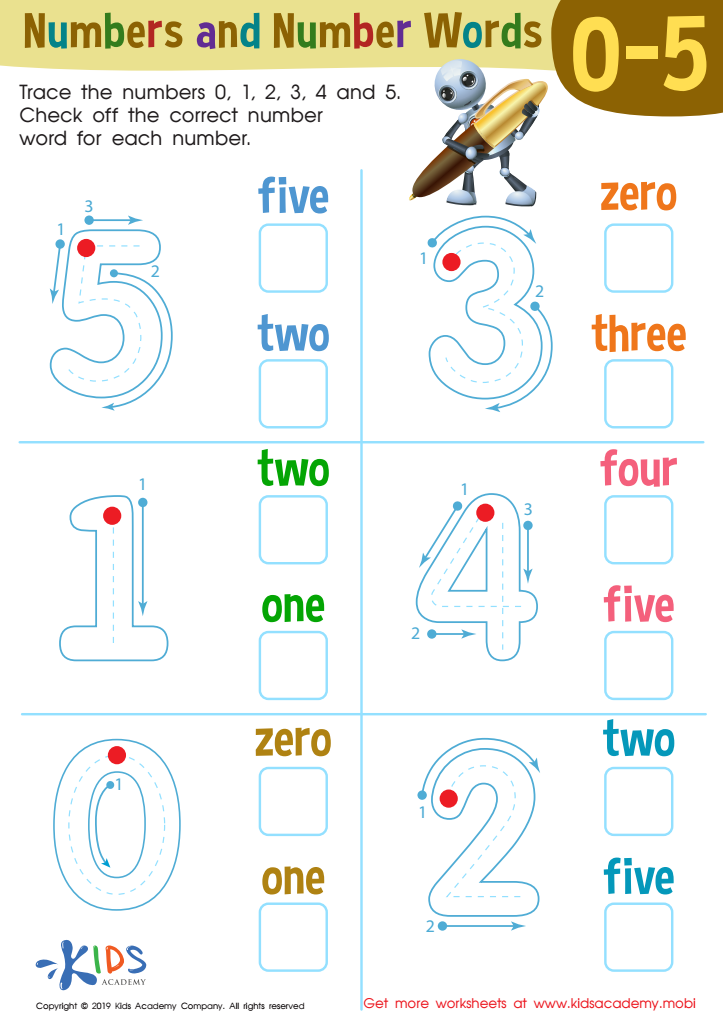

Numbers and Number Words Worksheet


Count and Trace 1 – 3 Worksheet


Write 0 Worksheet
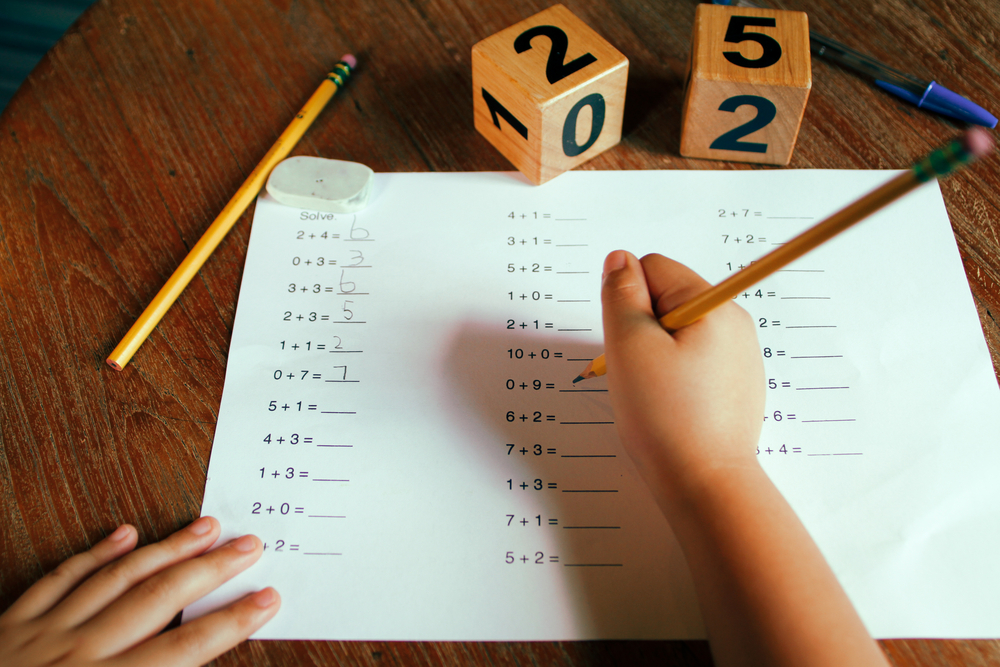
Writing practice for young children aged 3-6, particularly through engaging activities like Easy Numbers, is essential for several reasons. First, writing at this age helps develop fine motor skills, which are crucial for later handwriting and everyday tasks. By practicing simple number formation, children learn to control their hand movements and build the necessary muscle strength.
Additionally, writing numbers introduces children to early mathematical concepts. It aids in number recognition, counting, and basic arithmetic, laying a foundation for more complex mathematical skills in later years. This early writing practice enhances cognitive development, encouraging children to think critically as they learn the associations between numbers and their representations.
Moreover, writing activities can foster creativity and self-expression. Integrating numbers into drawings or stories allows children to explore their imaginations while solidifying their understanding of numbers.
Finally, consistent writing practice nurtures a positive attitude toward learning. Engaging in fun, supportive writing exercises helps build confidence and a love for learning that lasts a lifetime. Parents and teachers should prioritize these practices to ensure a well-rounded educational experience that supports both academic and personal growth in young children.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students