Hand-eye Coordination Normal Phonics Worksheets for Ages 4-6
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Boost your child's learning journey with our Hand-eye Coordination Normal Phonics Worksheets for Ages 4-6! These engaging worksheets are designed to enhance the essential skill of hand-eye coordination while reinforcing phonics knowledge. Perfect for preschool and kindergarten learners, each activity combines fun and education, allowing children to practice letter recognition, sounds, and writing while improving their fine motor skills. Our worksheets provide a variety of interactive exercises that keep young minds captivated and eager to learn. Download these valuable resources today and watch your child develop a stronger foundation in reading and writing, all while having fun!
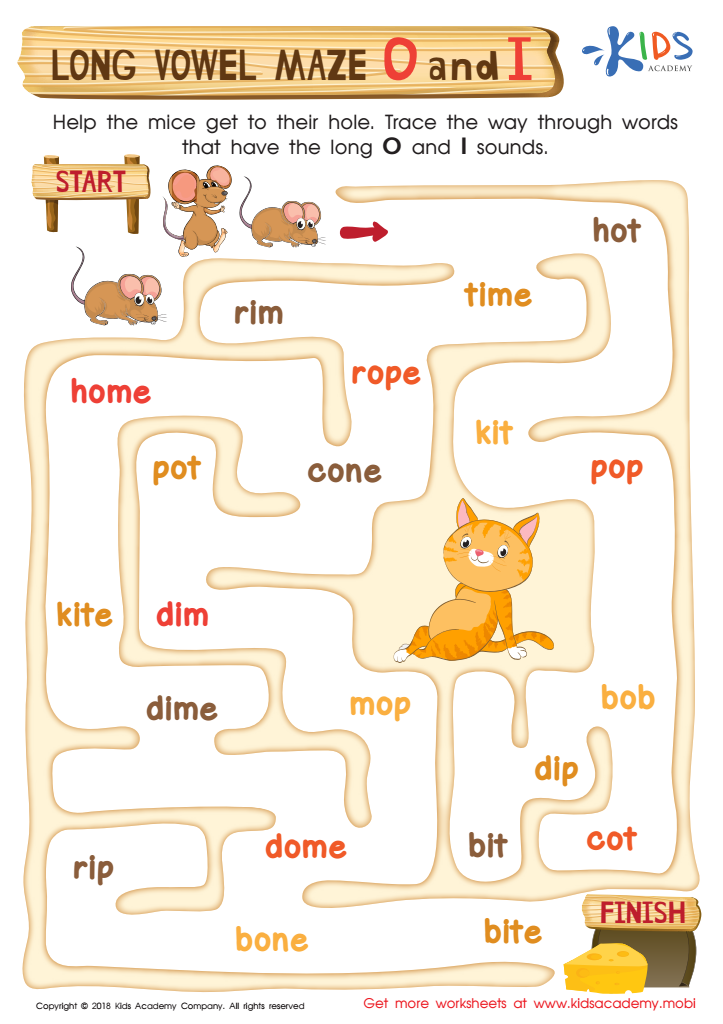

Long Vowel Maze /o/ and /i/ Worksheet
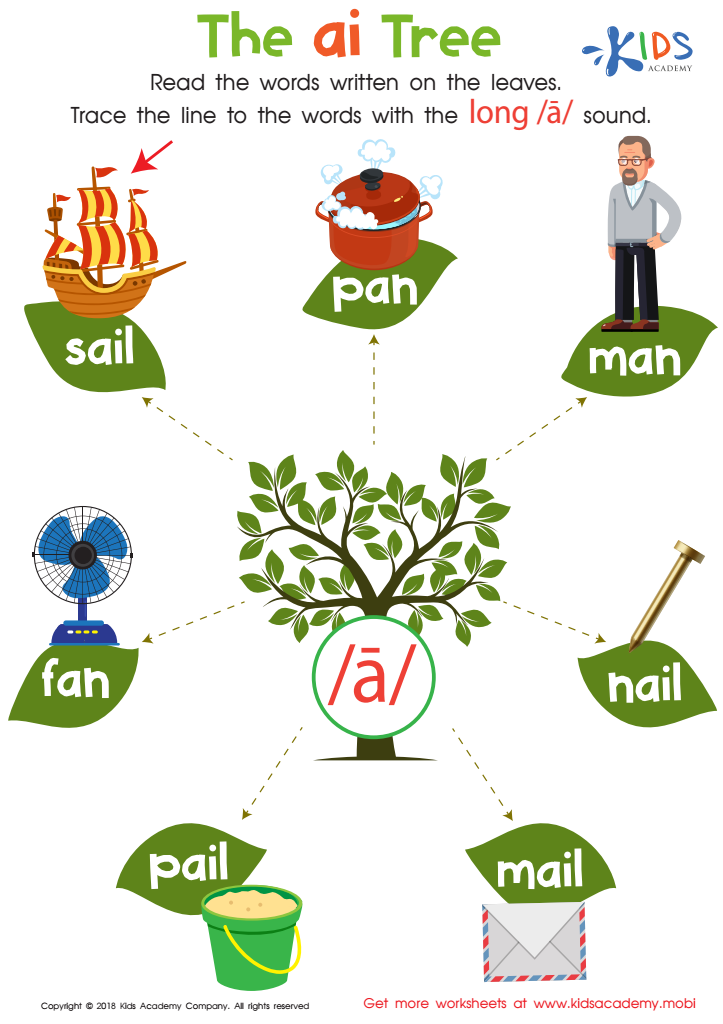

The AI Tree Worksheet
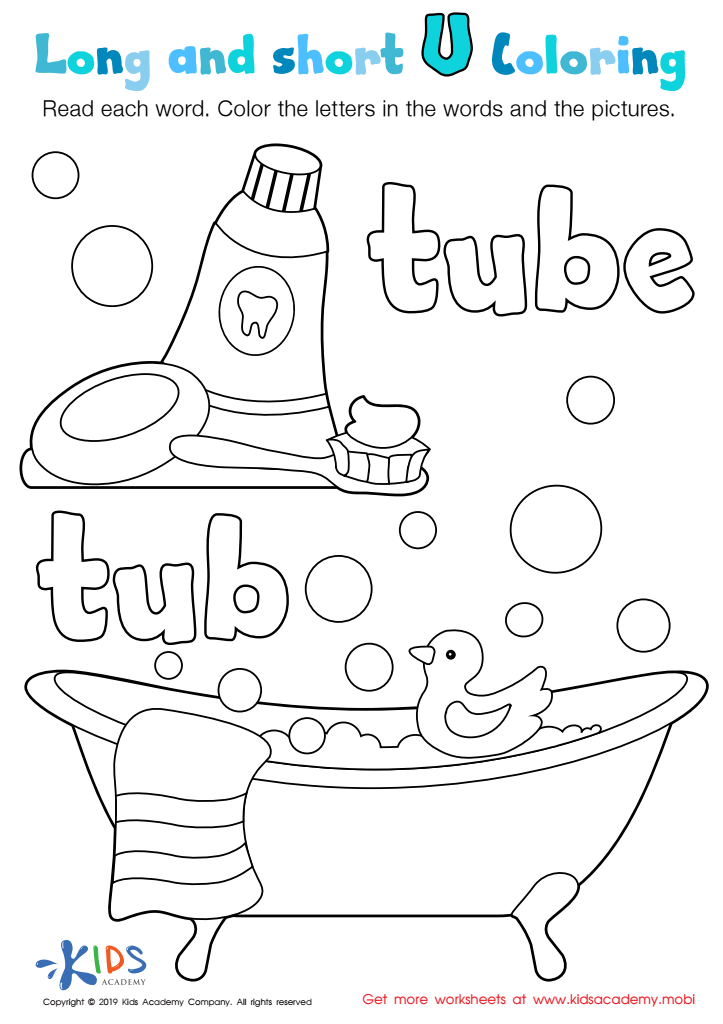

Long and Short U Worksheet


Feed the Whale Worksheet


Long and Short E Worksheet
Hand-eye coordination is a crucial skill that lays the foundation for various developmental milestones in young children, particularly in the context of learning phonics. For ages 4-6, effective phonics instruction involves recognizing letters, sounds, and eventually blending these to form words. Children with well-developed hand-eye coordination can easily engage in activities such as tracing letters, using manipulative tools, and participating in interactive games that reinforce these skills.
When parents and teachers prioritize hand-eye coordination alongside phonics, it significantly enhances learning outcomes. Children with strong coordination skills are better equipped to hold writing instruments, follow visual prompts, and manage phonetic games that reinforce sound-letter association. This physical competence boosts their confidence as they navigate more complex reading tasks.
Moreover, fostering hand-eye coordination through fun, play-based activities can increase engagement and motivation in young learners. When coordination is developed in tandem with phonics skills, it not only supports literacy acquisition but also promotes overall fine motor skills and cognitive development. Thus, focusing on hand-eye coordination during these formative years holds considerable importance for fostering lifelong learning and academic success in young children. Ultimately, it can be a decisive element in a child’s literacy journey.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students















