Alphabet tracing Normal Letter Recognition Worksheets for Ages 4-7
5 filtered results
-
From - To
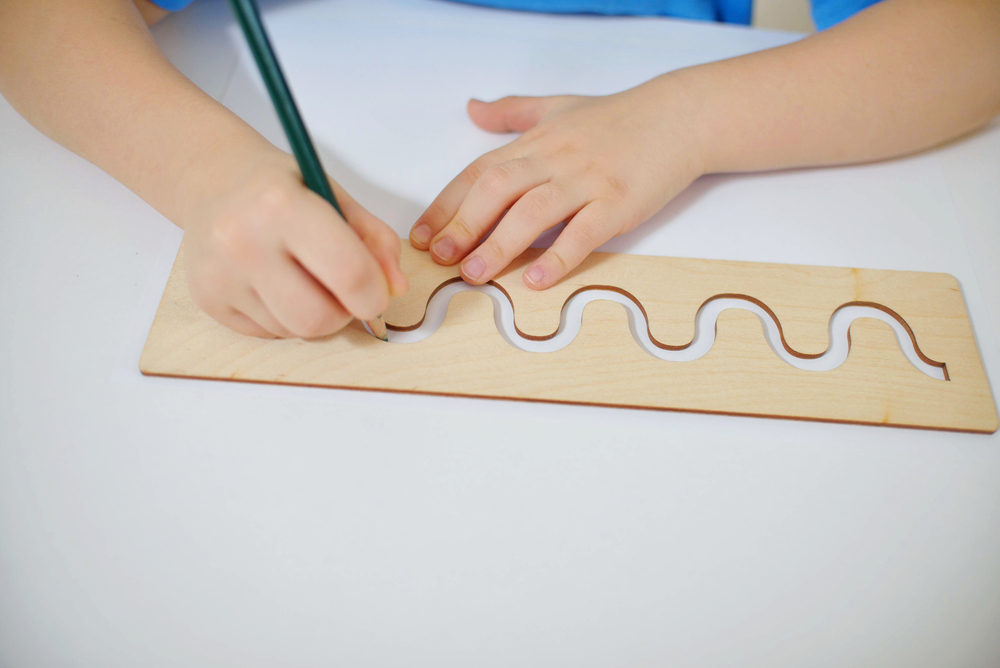
Enhance your child’s early literacy skills with our "Alphabet Tracing Normal Letter Recognition Worksheets," designed specifically for ages 4-7. These engaging worksheets help children recognize both uppercase and lowercase letters through fun tracing activities. By tracing the letters, kids improve their fine motor skills while reinforcing their understanding of the alphabet. Our resources are tailored to encourage learning through play, fostering a love for reading and writing. Ideal for homeschooling or classroom use, these printable worksheets not only support letter recognition but also build confidence in young learners. Start your child's educational journey today with our stimulating alphabet tracing worksheets!

Letter P Tracing Page


Letter Q Tracing Page

Letter H Tracing Page


Letter A Tracing Worksheet


Letter D Tracing Page
Alphabet tracing and normal letter recognition are crucial components of early literacy for children aged 4-7. During these formative years, children's brains are primed for language acquisition and fine motor skill development. Tracing letters engages their fine motor skills, enhances hand-eye coordination, and aids in developing the muscle memory necessary for writing. When children trace letters, they learn to recognize the shapes and structures of each character, laying the foundation for reading and writing.
Moreover, letter recognition is a precursor to reading fluency. Understanding letters' sounds and names helps children decode words, boosting their confidence and enthusiasm for literacy. Early familiarity with the alphabet also facilitates vocabulary expansion, leading to better communication skills.
For parents and teachers, supporting alphabet tracing and recognition fosters a love of learning and lays a solid academic foundation. Engaging in these activities can be fun and interactive, promoting positive learning experiences and strengthening parent-child or teacher-student bonds. As children gain confidence in their literacy skills, they become more eager learners, better prepared for future educational challenges. By prioritizing these skills, educators and parents can significantly impact children's long-term success in reading and communication.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















