Fine Motor Skills Normal Numbers up to 100 Worksheets for 4-Year-Olds
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Explore our engaging "Fine Motor Skills Normal Numbers Up to 100 Worksheets" designed specifically for 4-year-olds! These worksheets seamlessly blend early math practice with crucial fine motor skill development. Kids will enjoy a variety of activities, from number tracing to coloring, which not only enhance their counting abilities but also promote hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Our user-friendly format encourages young learners to practice writing numbers in a fun, interactive way, making math enjoyable. Perfect for preschool and home learning, these worksheets will foster both academic growth and essential motor skills, laying a solid foundation for future learning adventures!


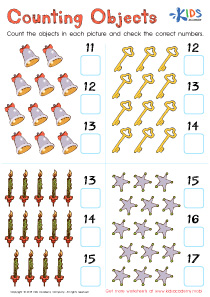
Holiday Counting Worksheet

Counting with Mittens Worksheet

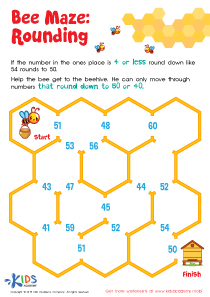
Number Puzzles Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial for children’s development, particularly for those around 4 years old. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles in hands and fingers, which are essential for various daily activities and academic tasks. As children learn to manipulate objects, cut with scissors, or write, their fine motor skills support their ability to engage in play, self-care, and learning experiences effectively.
Understanding normal numbers up to 100 is equally important at this age as it lays the foundation for mathematical understanding. When children are comfortable with counting, sorting, and recognizing numbers up to 100, they build confidence in their ability to engage with math concepts throughout their education.
Parents and teachers should care about both finite motor skills and number recognition for 4-year-olds because they promote not only academic success but also independence and self-esteem. Fine motor development supports task completion and encourages participation in age-appropriate activities that require dexterity.
By focusing on these skills, adults can provide activities and materials that enhance children's learning experiences, making them more creative and effective problem solvers. This holistic developmental approach paves the way for future learning and academic achievements.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students