Fine Motor Skills Grade 2 Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your second grader's fine motor skills while mastering the art of addition with our "Adding Up to 1000 Without Regrouping" worksheets! These engaging activities are designed to reinforce foundational math concepts, allowing students to practice adding two and three-digit numbers seamlessly. Our worksheets encourage precision and control, fostering the dexterity necessary for effective writing and calculation. Each exercise provides a fun and interactive way to boost both math proficiency and fine motor development. Ideal for classroom or home use, these worksheets help young learners build confidence and competence in their math skills while refining their hand coordination. Dive into learning today!
Fine motor skills are essential for children, especially in Grade 2, as they significantly impact academic success and everyday activities. For tasks like writing, drawing, and manipulating objects, these skills enable children to create and express themselves effectively. At this stage, children often engage in activities that require precision, such as tying shoelaces or holding scissors.
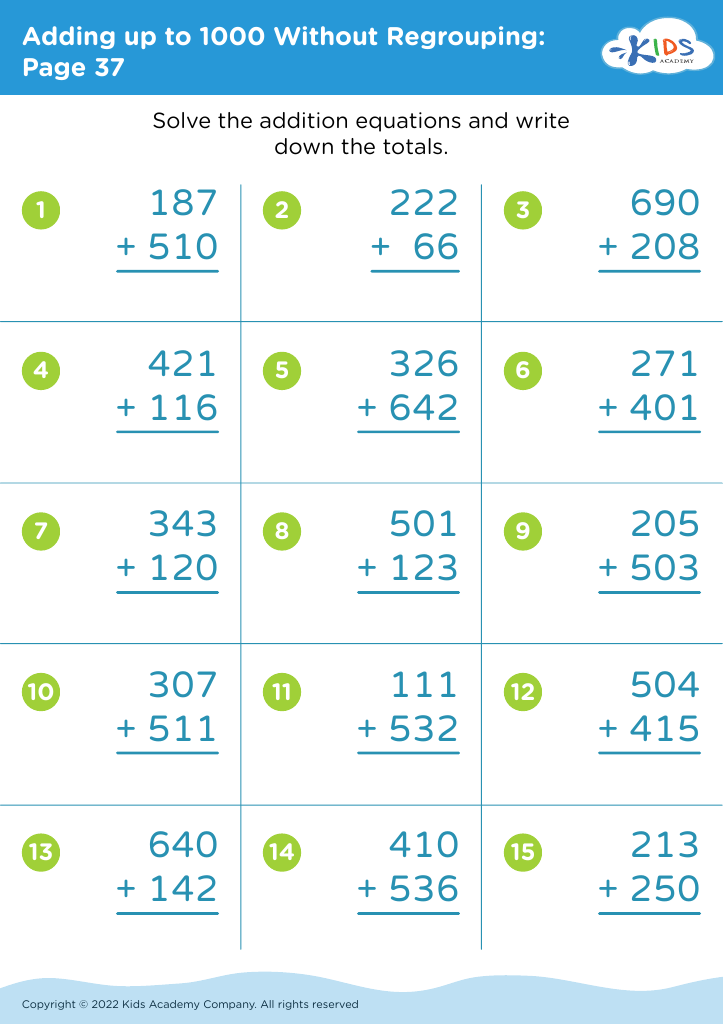
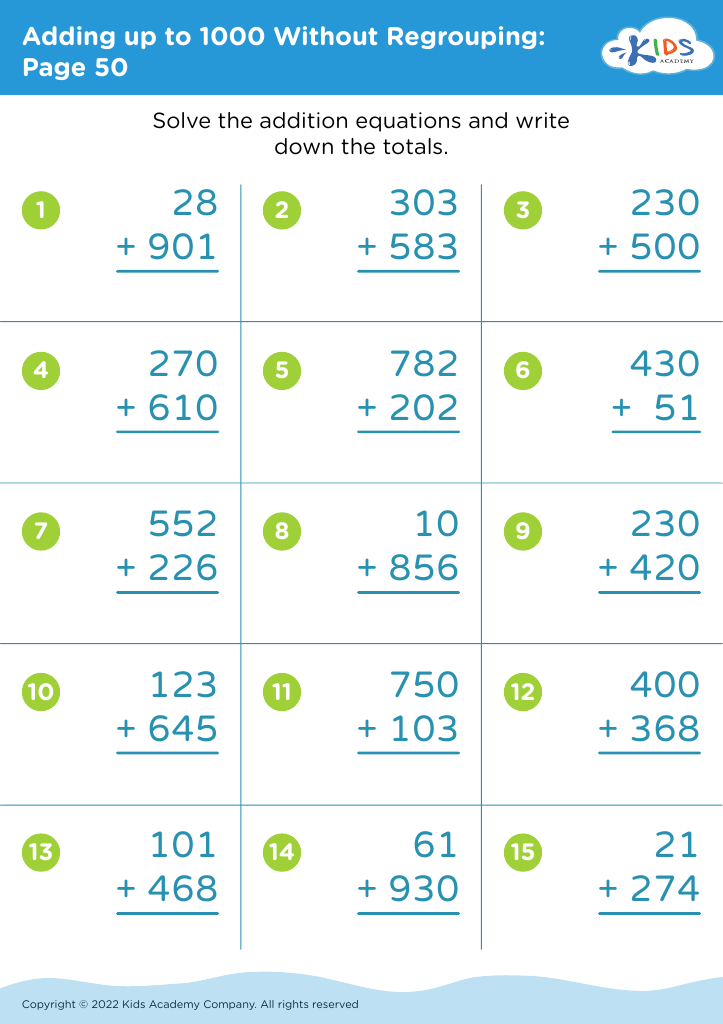
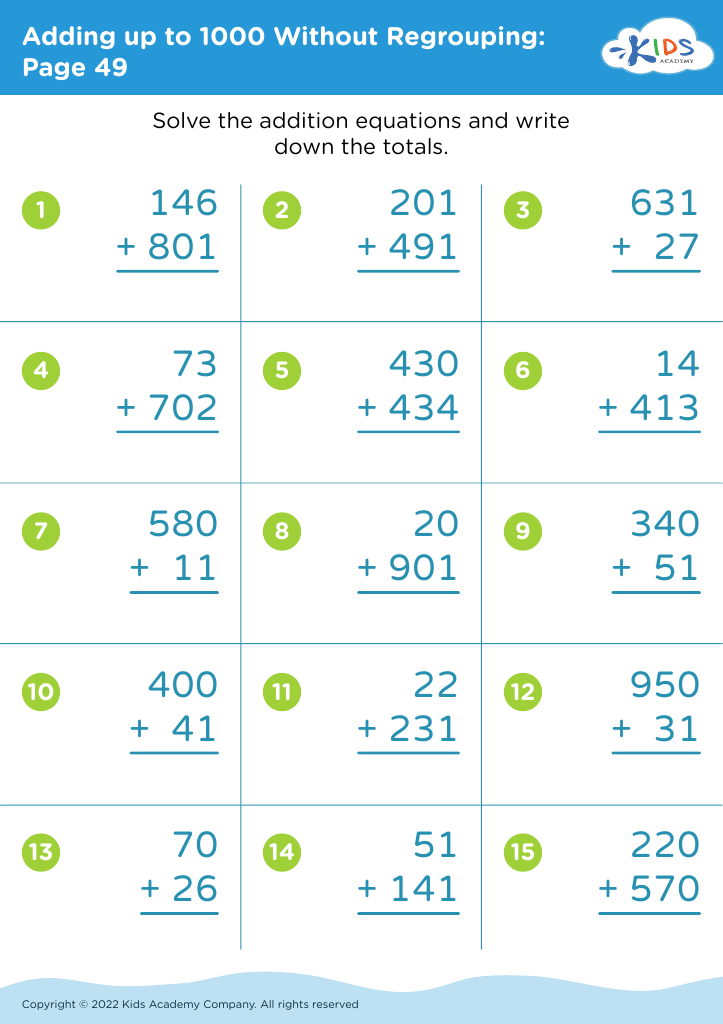
When teaching math concepts like adding numbers that total 1000 without regrouping, fine motor skills become crucial, as they influence a child's ability to organize and manipulate numerical data effectively. For example, students must be able to align numbers accurately, draw number lines, and use manipulatives like counters or blocks. The dexterity involved not only supports their understanding of addition but also builds confidence as they interact with math materials.
Teachers and parents who recognize the importance of honing fine motor skills through engaging activities—such as crafts, puzzles, and manipulatives—will enhance children’s overall learning experience. Focused development of these skills during foundational years contributes to smoother transitions into more complex academic challenges, fostering a lifelong love for learning and increasing the likelihood of future success in both academic and personal endeavors.