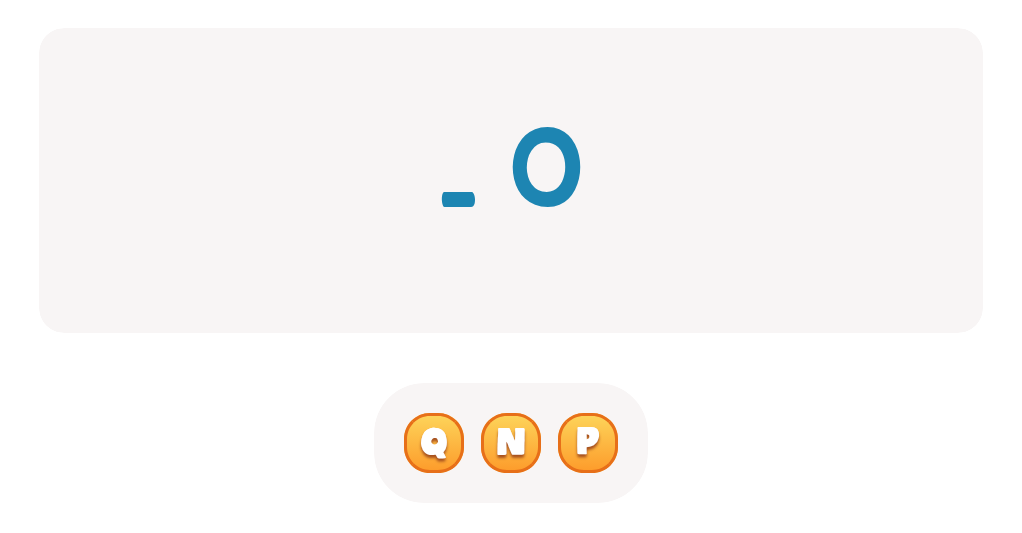
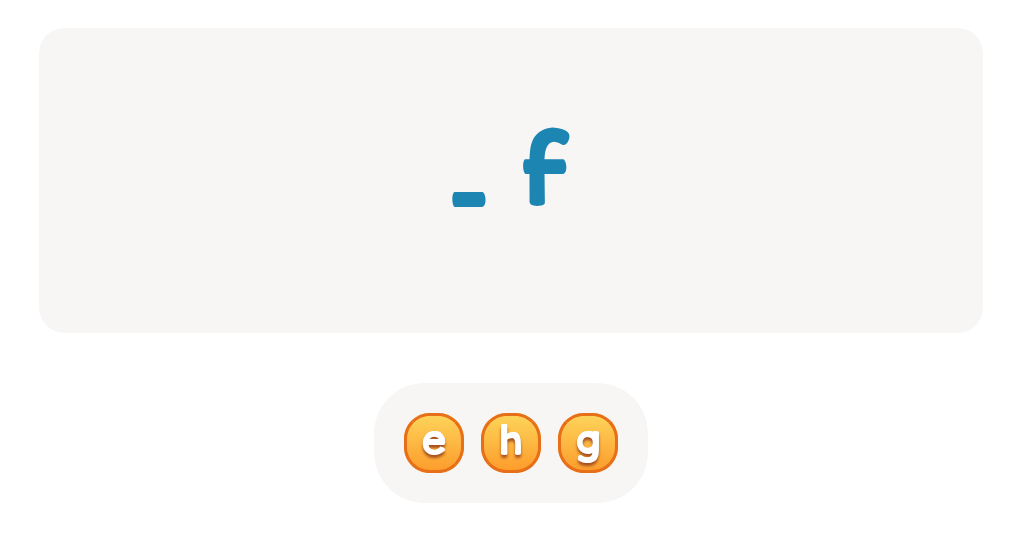
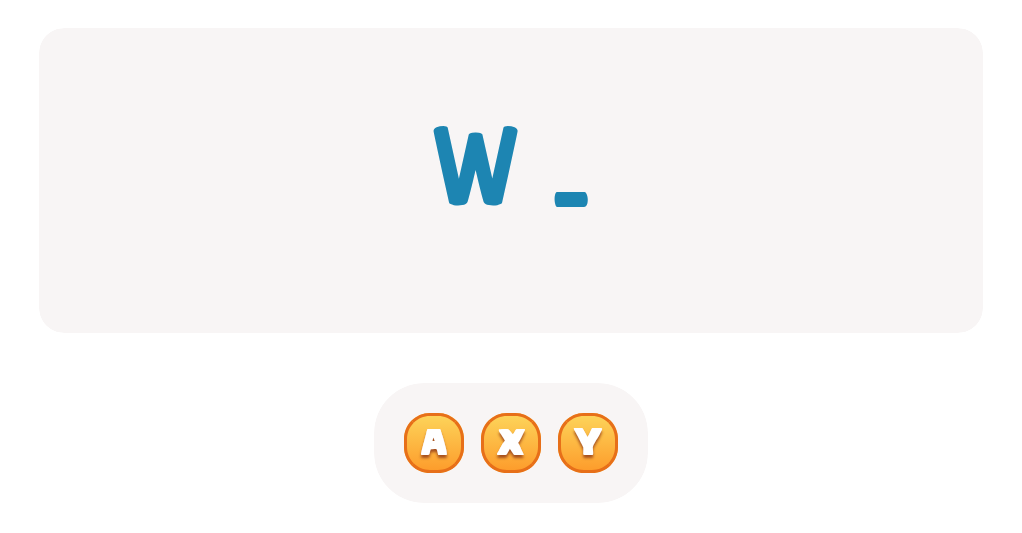
Handwriting practice ABC Letters Worksheets for Ages 3-4 - Page 2
26 filtered results
-
From - To


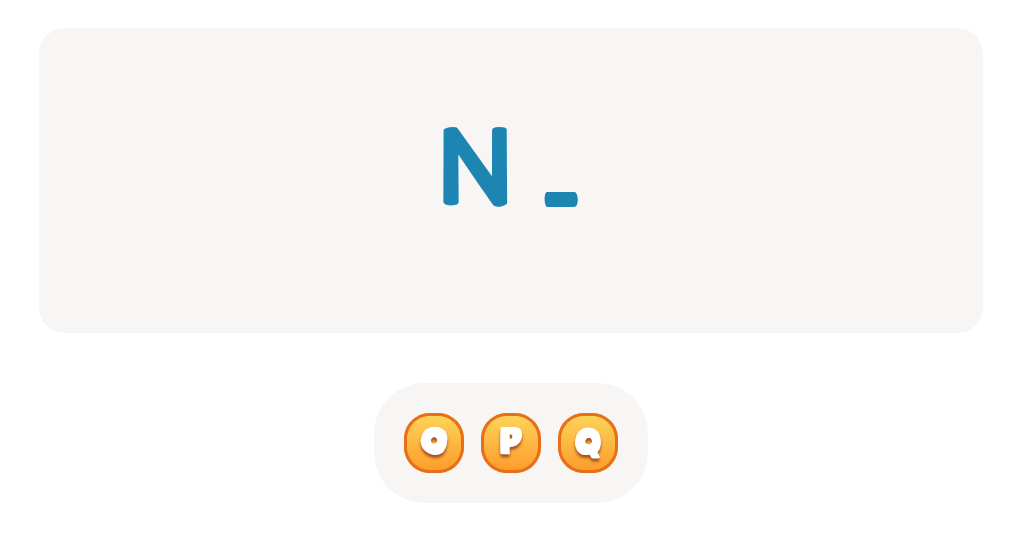
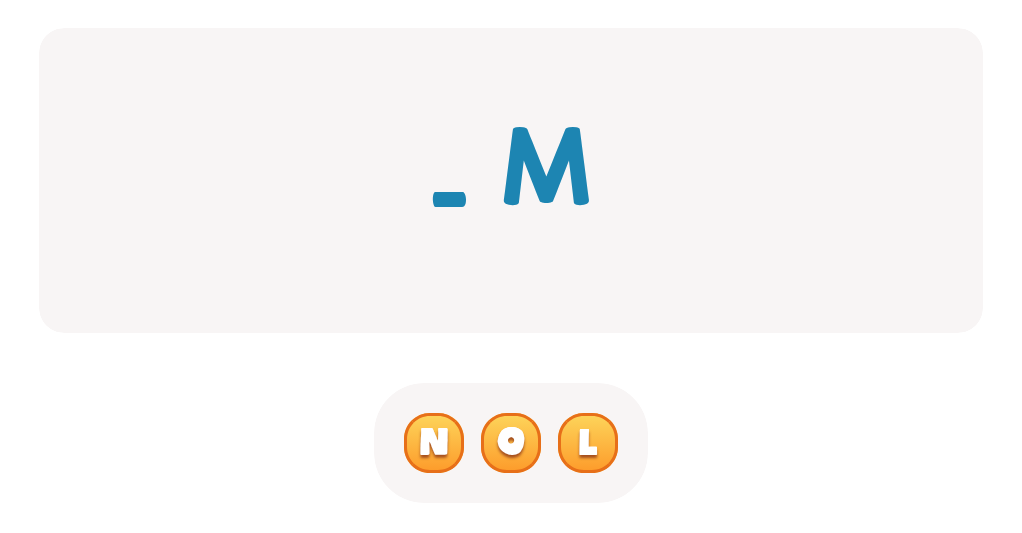
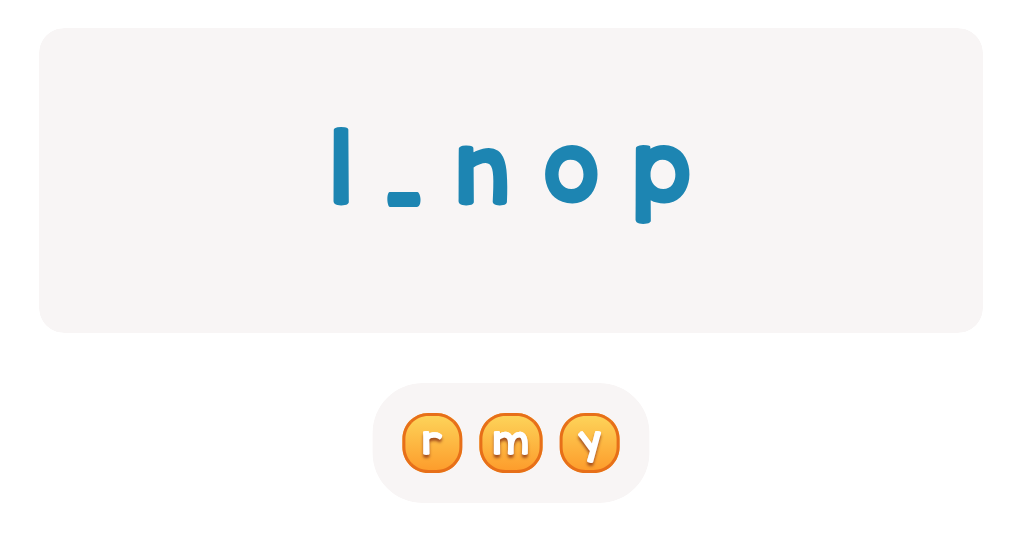
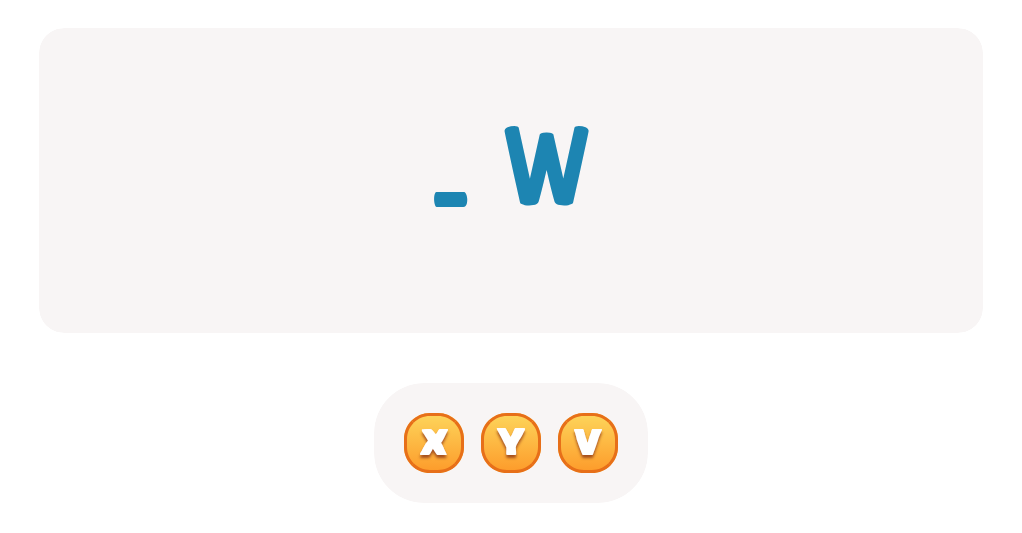
Letter N Coloring Sheet


My Name: Cheerful Balloons Worksheet
Handwriting practice for children ages 3-4 is crucial for several reasons. First, at this developmental stage, fine motor skills are rapidly developing. Engaging in handwriting activities helps strengthen the muscles in their hands and fingers, which is essential for tasks such as using scissors, buttoning clothes, and eventually typing.
Second, learning letter formation lays the foundation for effective literacy and communication skills. Familiarizing young children with the shapes and sounds of letters helps them decode language and recognize words, which will greatly enhance their reading abilities later on.
Additionally, handwriting practice fosters cognitive development. When children practice writing, they not only learn letters but also understand the connection between sounds and symbols. This early exposure is critical for phonemic awareness, a key predictor of future reading success.
Moreover, handwriting activities can enhance focus and concentration, skills that are important across all areas of learning. Engaging in these practices also promotes creativity and self-expression, important components in a child's holistic growth.
Ultimately, investing time in handwriting practice ensures that children build a strong foundation for literacy, motor skills, and cognitive development, preparing them for future academic success. Parents and teachers play a pivotal role in nurturing this vital early learning experience.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students