Visual discrimination Upper & Lowercase Letters Worksheets for Ages 3-4
4 filtered results
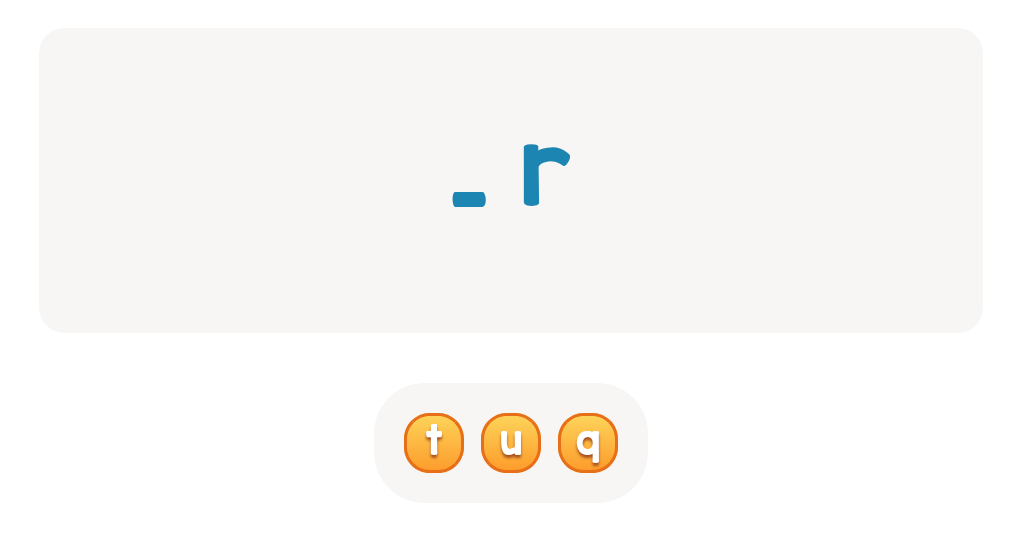
-
From - To
Enhance your child's early learning with our expertly designed Visual Discrimination Upper & Lowercase Letters Worksheets for ages 3-4. These engaging worksheets help young learners distinguish between upper and lowercase letters, fostering critical pre-reading skills. Perfect for both classroom and home use, each activity is crafted to support visual discrimination and letter recognition through fun, interactive exercises. Watch as your child gains confidence and mastery in recognizing letter shapes and sizes, setting a strong foundation for future literacy success. Ideal for preschoolers, these worksheets make learning an enjoyable and educational experience. Start strengthening your child's alphabet skills today!


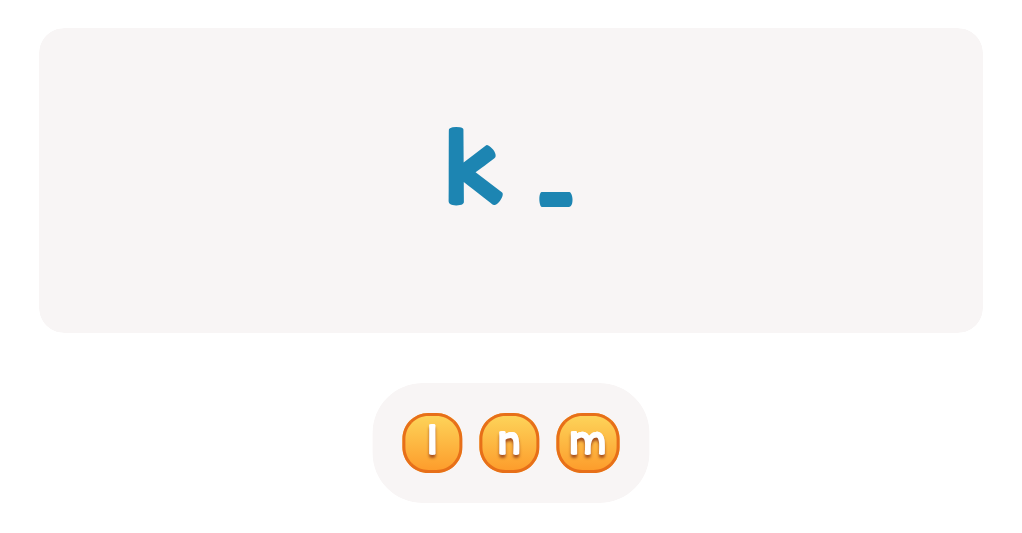
Find Lowercase Letters g h i Worksheet


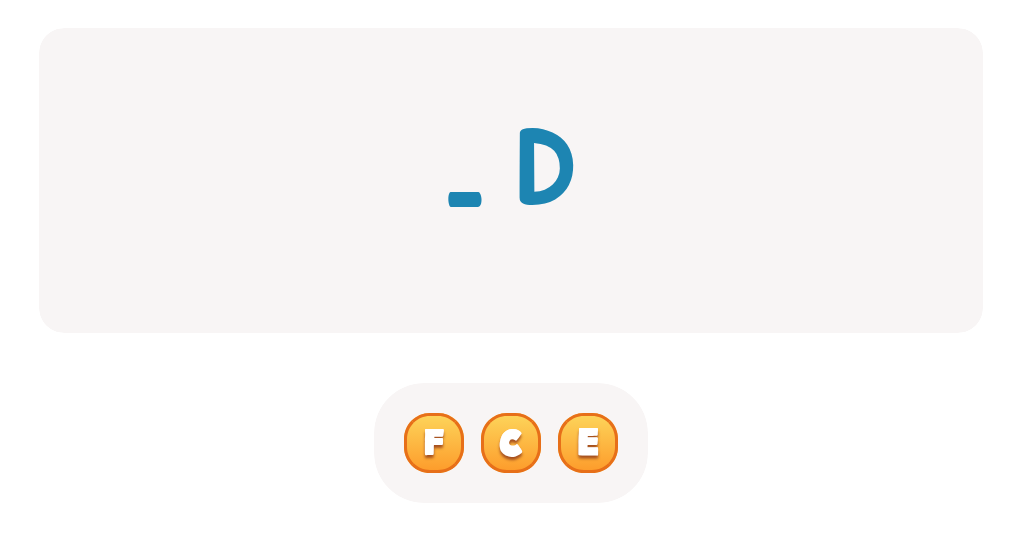
Find Uppercase Letters G, H, and I Worksheet


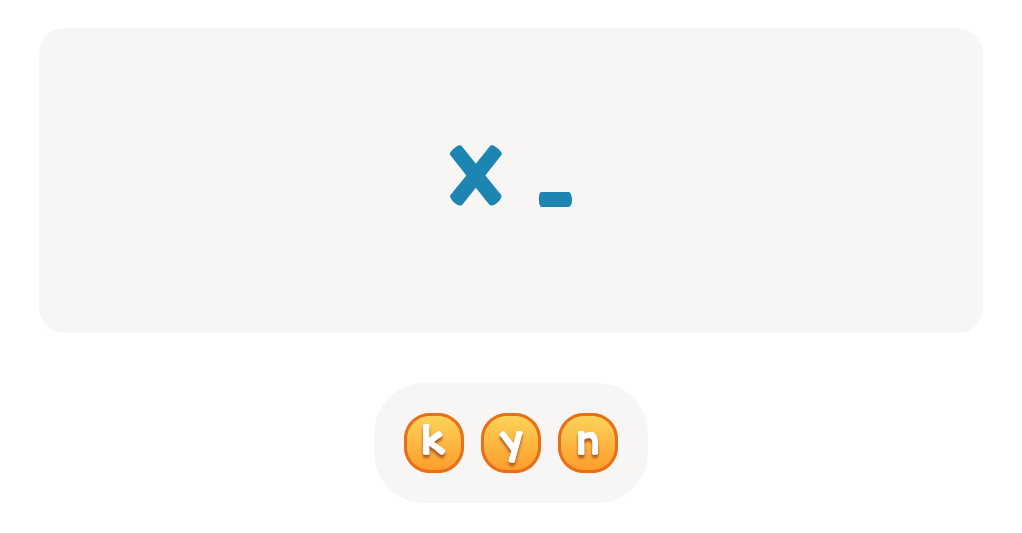
Find Lowercase Letters y z Worksheet


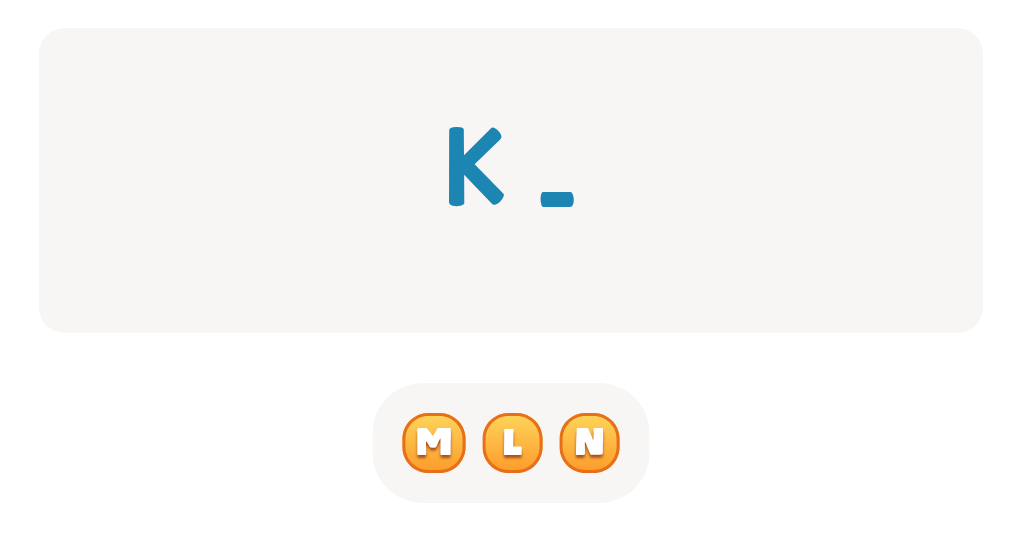
Find Uppercase Letters V, W, X Worksheet
Visual discrimination, especially in recognizing upper and lowercase letters, is critical for young children because it lays the foundation for reading and writing. At the ages of 3 to 4, children’s brains are like sponges, absorbing new information rapidly. During this pivotal time, understanding the differences between similar-looking letters, such as 'b' and 'd' or 'p' and 'q', begins the journey of literacy early and effectively.
Parents and teachers who focus on visual discrimination skills help children recognize letter shapes and forms, which is crucial for letter recognition. When kids can distinguish these "visual" differences, they are better equipped for future spelling and reading tasks. For instance, knowing that 'P' and 'p' sound the same, but look different, fosters an understanding of the alphabet's versatility and consistency in written language.
Consistent practice in visual differentiation aids in cognitive development. Skills honed include attention to detail, memory, and concentration—key components in a child's academic life. Moreover, attuned attention can help spot vision or learning difficulties early, allowing for timely and effective interventions.
Ultimately, caring about visual discrimination prepares kids for more complex reading and writing activities, enabling smoother transitions to formal schooling. Building these essential skills fosters confidence, leading to more enthusiastic and engaged young learners.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students