Improve concentration Worksheets for Ages 3-6
9 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Improve Concentration Worksheets for Ages 3-6" are designed to enhance focus and attention in young learners through engaging activities. Tailored for preschool and early elementary kids, these worksheets use fun puzzles, matching games, and picture comprehension exercises to develop critical concentration skills. Brightly colored illustrations and age-appropriate challenges ensure children remain interested and motivated. By integrating play-based learning, these resources help build a strong foundation for academic success and lifelong attention management. Perfect for use at home or in the classroom, our worksheets support busy parents and educators in nurturing focused, confident, and motivated young learners.


Picnic Basket Sorting Worksheet
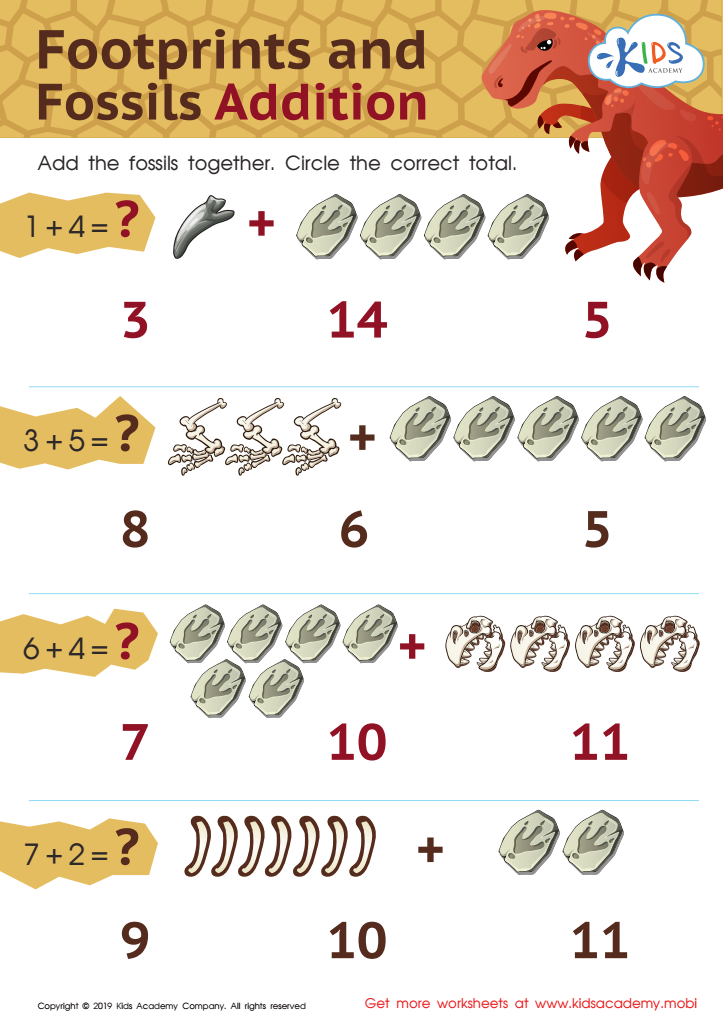

Footprints and Fossils Addition Worksheet
Improving concentration in children aged 3-6 is essential for numerous reasons, impacting their immediate and long-term development. At this young age, children are rapidly growing cognitively, emotionally, and socially. Enhancing concentration helps them absorb foundational skills crucial for their educational journey, such as basic literacy and numeracy. It also fosters better listening skills, enabling them to follow instructions and actively participate in classroom activities and at home.
Effective concentration aids in self-regulation, which is the ability to manage one's emotions and behaviors. When children learn to focus on tasks without frequent distractions, they build patience and perseverance—traits essential for tackling challenges throughout life. Strong focus allows them to explore their creativity deeply, prompting imaginative play and innovative thinking.
Moreover, establishing good concentration early sets the stage for lifelong learning habits. Children who practice focusing are more likely to cultivate an intrinsic motivation for learning, which can lead to better academic performance over time. It also equips them with the skills they need to develop fulfilling hobbies and interests outside formal education.
In conclusion, strengthening concentration in young children benefits their current academic engagement, emotional regulation, and imaginative processes, laying a robust foundation for future learning and personal development.






 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students






.jpg)









