Basic Arithmetic Adding Up to 5 Worksheets for Ages 3-6 - Page 2
Parents and teachers should emphasize basic arithmetic adding up to 5 for children aged 3-6 because it's a crucial foundational skill in early mathematics education. During these formative years, children's cognitive abilities are highly receptive to learning fundamental concepts. Basic arithmetic encourages numerical literacy, enhancing essential brain development associated with recognizing patterns, logical thinking, and problem-solving.
Introducing concepts of addition strengthens children's understanding of quantities and their relationships. This foundational competence fortifies their readiness for more complex mathematical challenges encountered in later grades. Moreover, it yields a sense of achievement and confidence, motivating them to approach future learning experiences with enthusiasm.
Additionally, engaging in early arithmetic activities promotes fine motor skills through actions like counting on fingers or placing objects. It fosters the development of concentration and promotes persistence as children learn to tackle small challenges. The supportive involvement of parents or teachers in these activities enriches the learning environment, making it enjoyable and embedded in day-to-day routines, thus demystifying mathematics.
Therefore, engaging young learners in basic arithmetic up to 5 nurtures crucial developmental skills and lays a strong academic foundation. This early investment in math education benefits their overall learning trajectory, ultimately contributing to their long-term academic and personal growth.

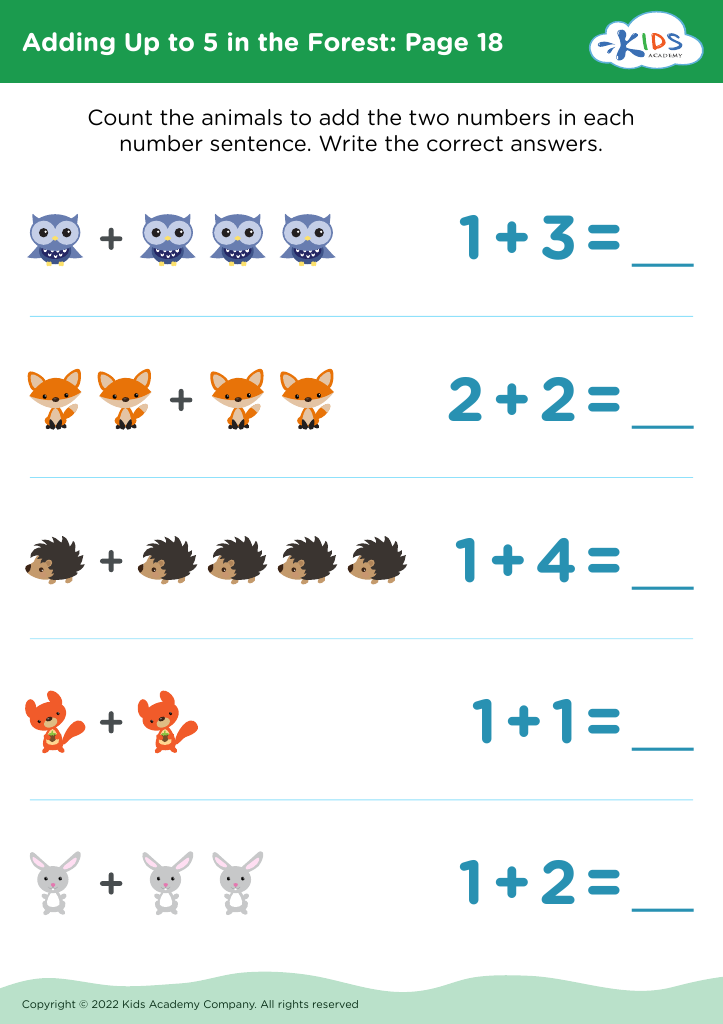












.jpg)











