Fine Motor Skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-6 - Page 2
47 filtered results
-
From - To
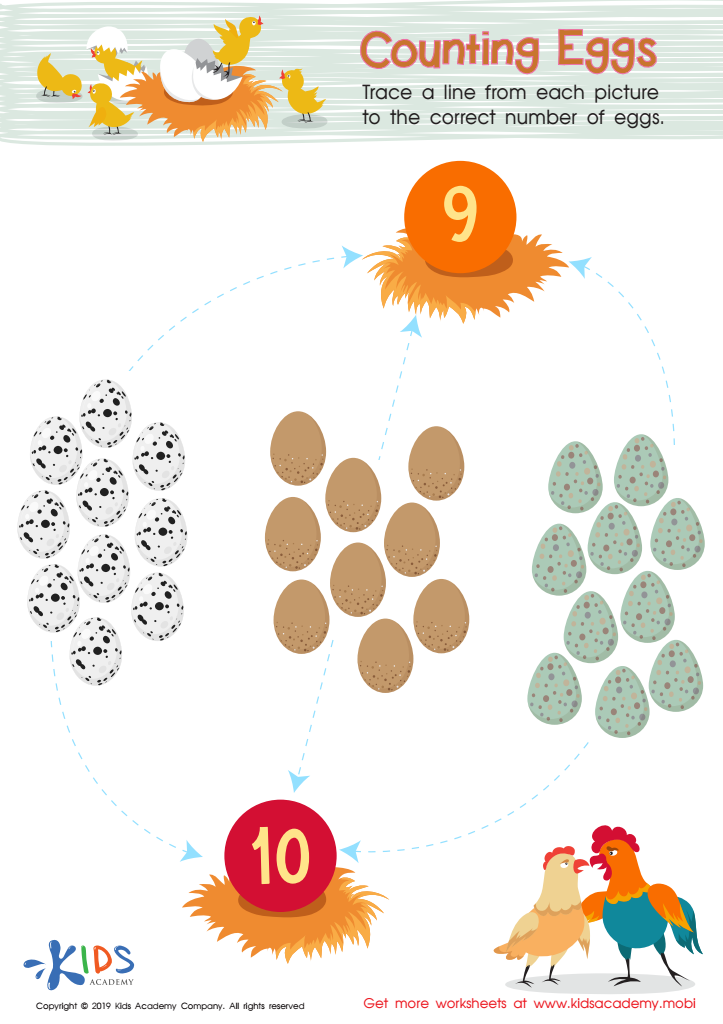

Counting Eggs Worksheet
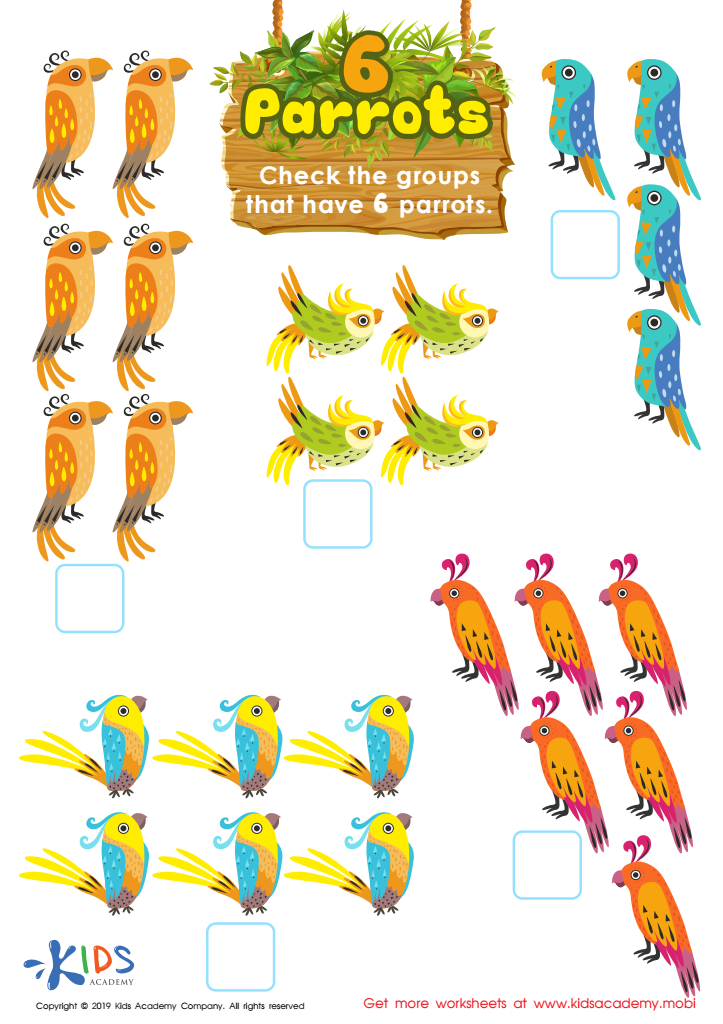

6 Parrots Worksheet

Rapunzel Addition Maze Worksheet
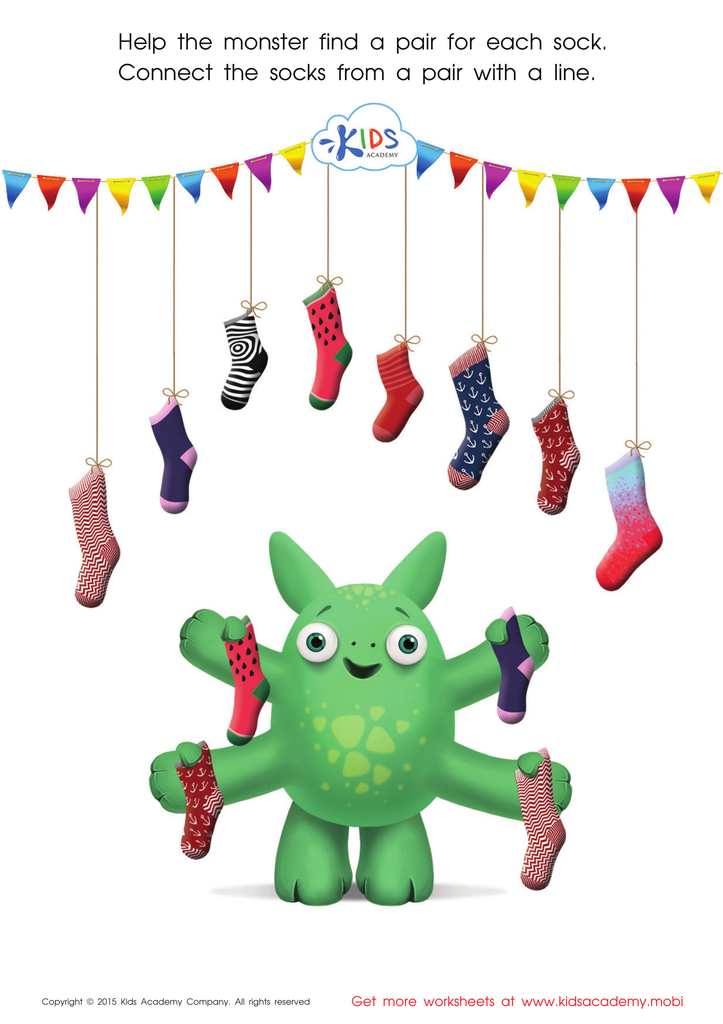


Math Matching Game: Monsterв's Socks Worksheet

Line up the Tigers Worksheet


Help the Bee Find 16 Flowers Worksheet


Planting Seeds for 11 Worksheet


Addition Robot Sorter Worksheet


Adding in the Arctic Worksheet


Math Matching Pairs Game: Monsterв's Socks Worksheet
Fine motor skills involve using the small muscles in the hands and fingers to perform tasks with precision and coordination. For children ages 3-6, these skills are crucial as they lay the foundation for more complex activities required in academic and everyday scenarios.
Fostering fine motor skills through addition and subtraction exercises is particularly significant because it integrates multiple domains of development. Firstly, handling manipulatives like counting beads, drawing numbers, or using worksheets that require tracing or coloring helps children develop dexterity and control in their fingers. These activities also strengthen hand-eye coordination, which is essential for tasks like writing and using scissors.
Moreover, combining fine motor skills with basic math concepts enriches cognitive development. When children physically manipulate objects to add or subtract, they are not only learning foundational mathematical principles but also improving their problem-solving skills and spatial awareness. Engaging with concrete materials to solve abstract problems helps solidify their understanding, making abstract math concepts more tangible.
Parents and teachers should prioritize these activities because they establish essential groundwork for academic success. Children with well-developed fine motor skills tend to excel in early writing, cutting, buttoning clothes, and other intricate tasks. Therefore, integrating fine motor skill activities with math learning equips children with a comprehensive toolkit for their future educational journey.


 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students