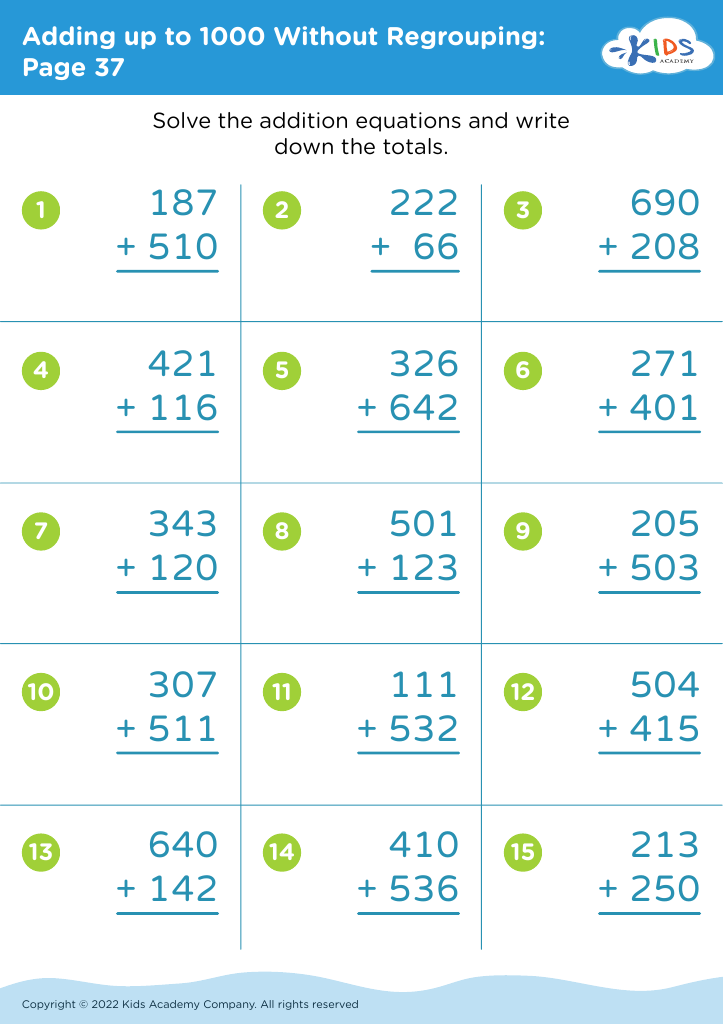
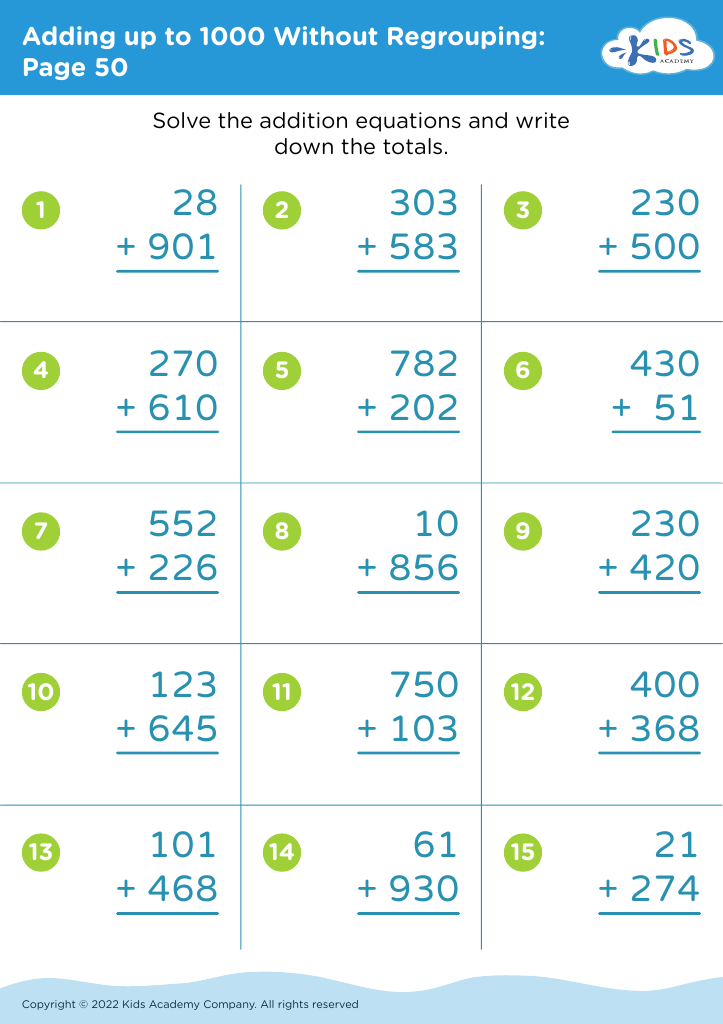
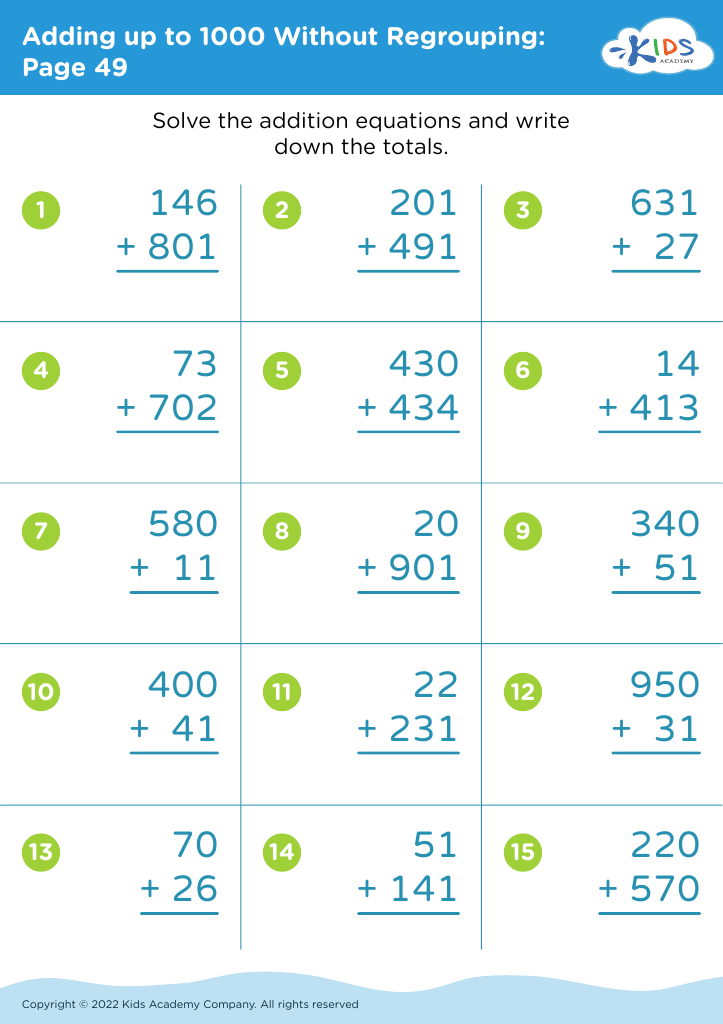
Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 3-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging "Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Without Regrouping Worksheets" designed specifically for children ages 3-7! These worksheets seamlessly combine essential mathematical concepts with fine motor skill development, making learning fun and interactive. Each activity is crafted to help young learners practice addition without regrouping while enhancing their hand-eye coordination and dexterity. From tracing numbers to colorful visuals, our worksheets provide a creative and effective way for children to build their confidence in math. Perfect for classroom or home use, these resources support early childhood education and foster a love for learning. Start your child’s educational journey today!
Fine motor skills are crucial for children aged 3-7 as they form the foundation for various academic and everyday tasks. These skills facilitate hand-eye coordination and dexterity, which are essential for writing, drawing, and other educational activities. The ability to manipulate small objects, like pencils and scissors, directly impacts a child's readiness for school.
When children focus on activities that strengthen fine motor skills and practice tasks such as adding up to 1000 without regrouping, they engage in cognitive exercises that enhance problem-solving and critical thinking abilities. Mastering addition helps build a strong numerical foundation, promoting confidence in mathematics. Reliable fine motor control allows children to approach these tasks with assurance rather than frustration, ultimately fostering a positive attitude toward learning.
Moreover, parental and teacher support enhances a child's learning experience. Engaged adults can provide guidance, encouragement, and opportunities for skill development, creating a nurturing environment where children can thrive. Advocating for activities that combine fine motor skills and mathematical concepts serves to develop well-rounded learners who are better prepared for future academic challenges. Thus, focusing on fine motor skills and basic math is vital for cultivating competent, confident, and capable children ready to explore the world academically and socially.