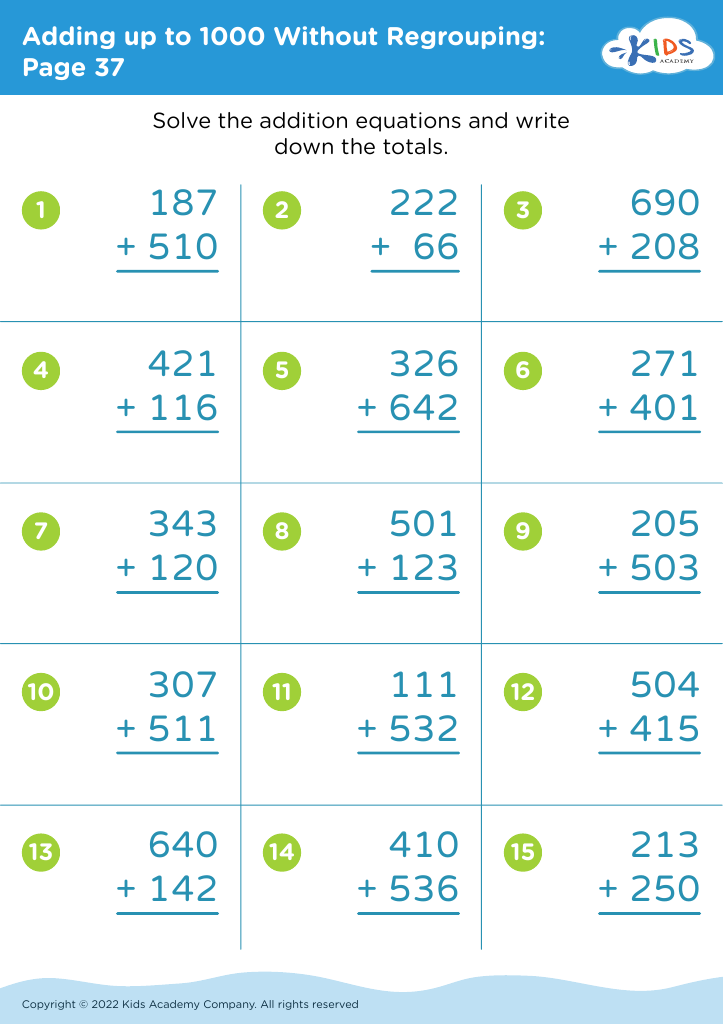
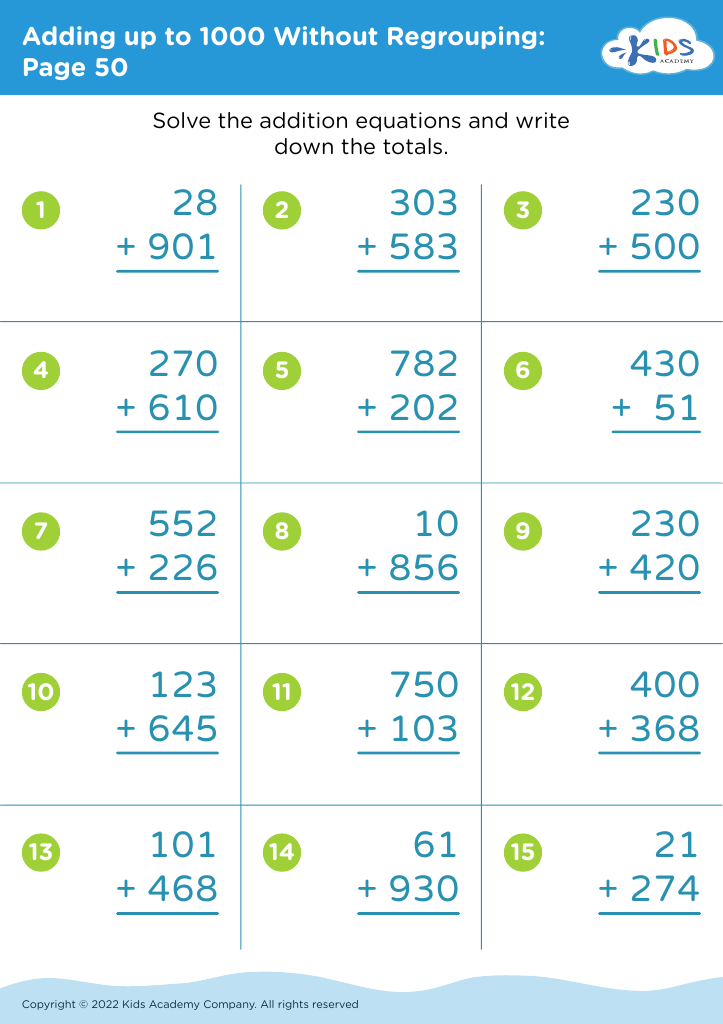
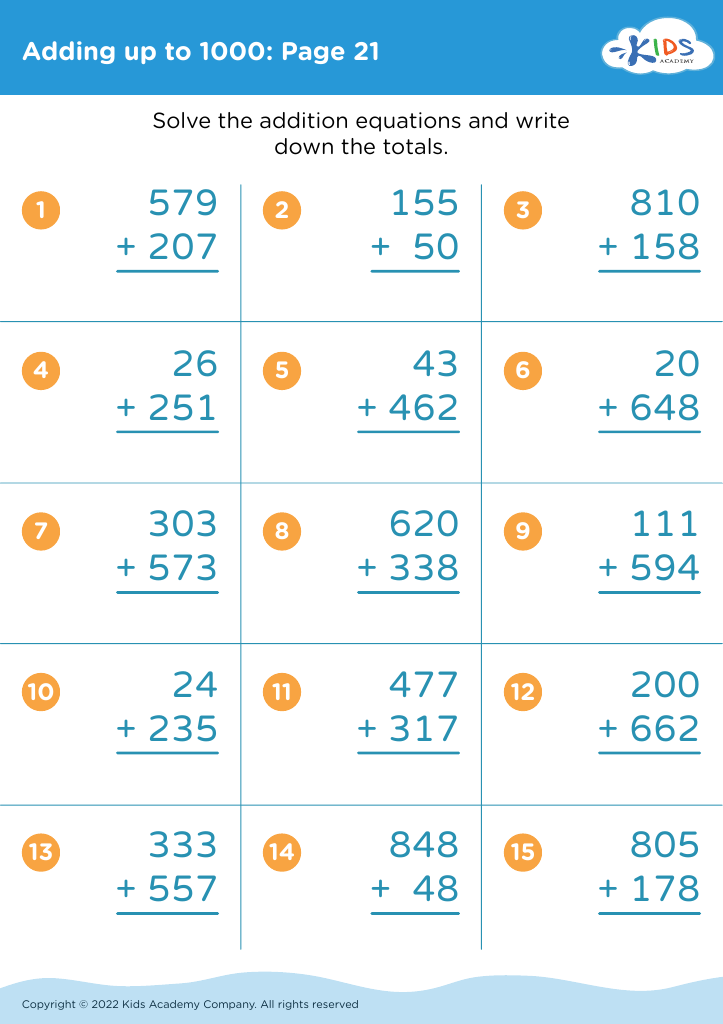
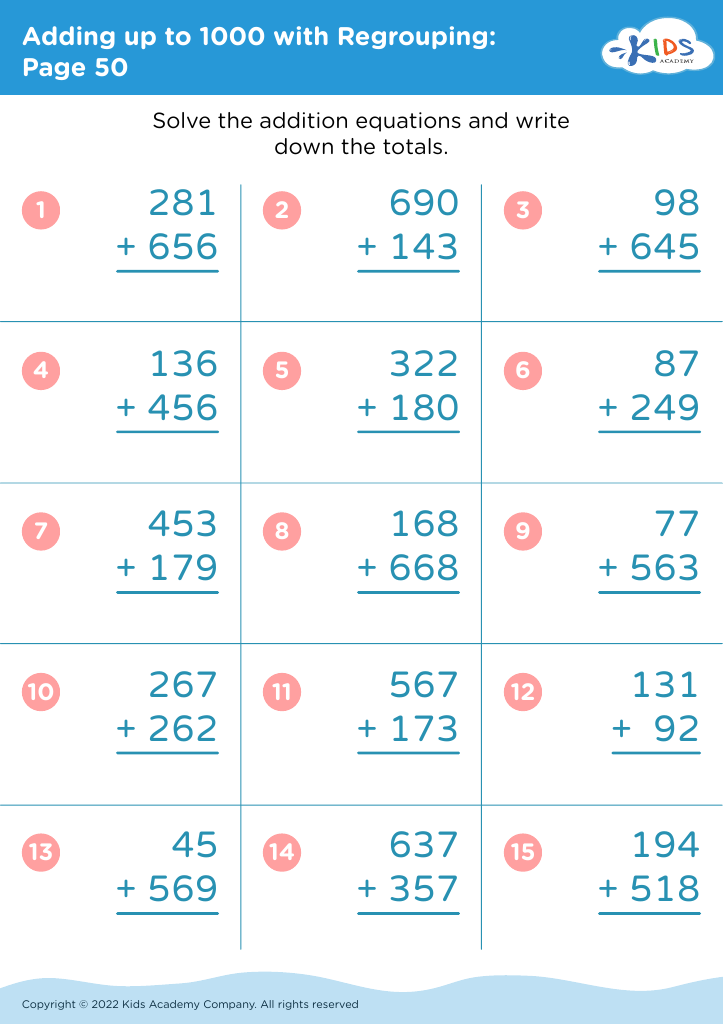
Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Worksheets for Ages 3-7
12 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging "Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 1000 Worksheets for Ages 3-7" designed to boost your child's math abilities and fine motor skills. These educational worksheets offer a fun way to practice addition up to 1000 while enhancing important skills like hand-eye coordination, pencil grip, and control. Suitable for preschool to early elementary kids, each worksheet is thoughtfully crafted to provide both challenge and excitement, fostering a love for learning and building a strong math foundation. Help your child develop these essential skills with engaging activities catered specifically for young learners.
Developing fine motor skills is crucial for children between the ages of 3-7 as these skills lay the foundational groundwork for a multitude of essential daily tasks and academic activities. Fine motor skills refer to the ability to control and coordinate small muscles, especially in the hands and fingers, which are necessary for tasks such as writing, cutting with scissors, tying shoelaces, and even manipulating small objects. Improving these skills can directly impact a child’s ability to perform academically later on, particularly in the realms of reading and writing, where precise hand-eye coordination is required.
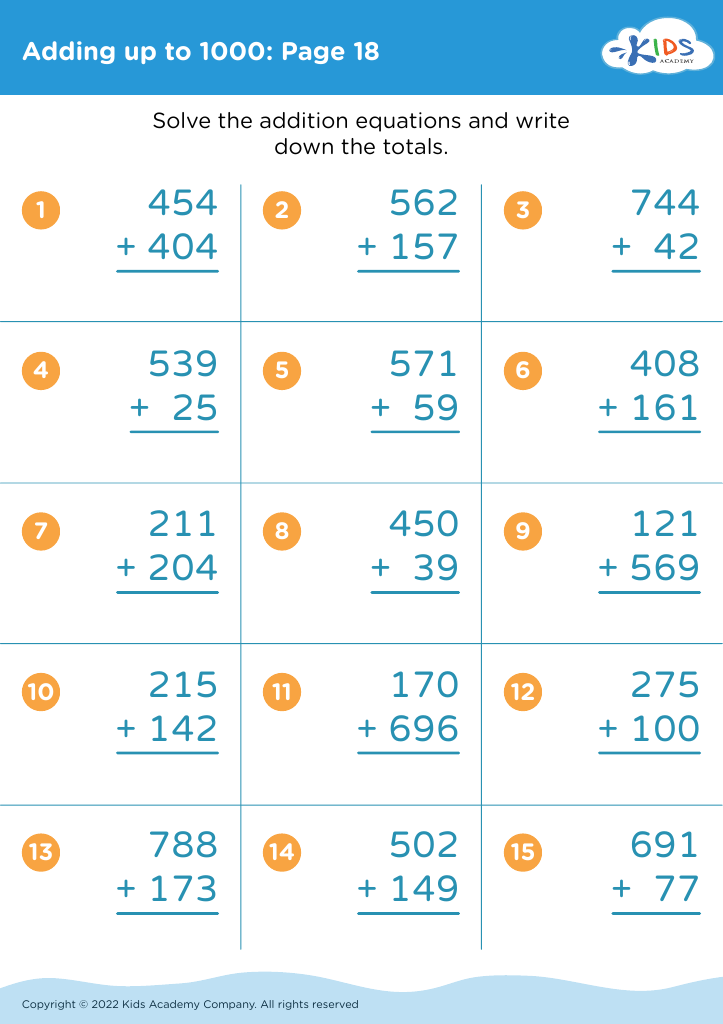
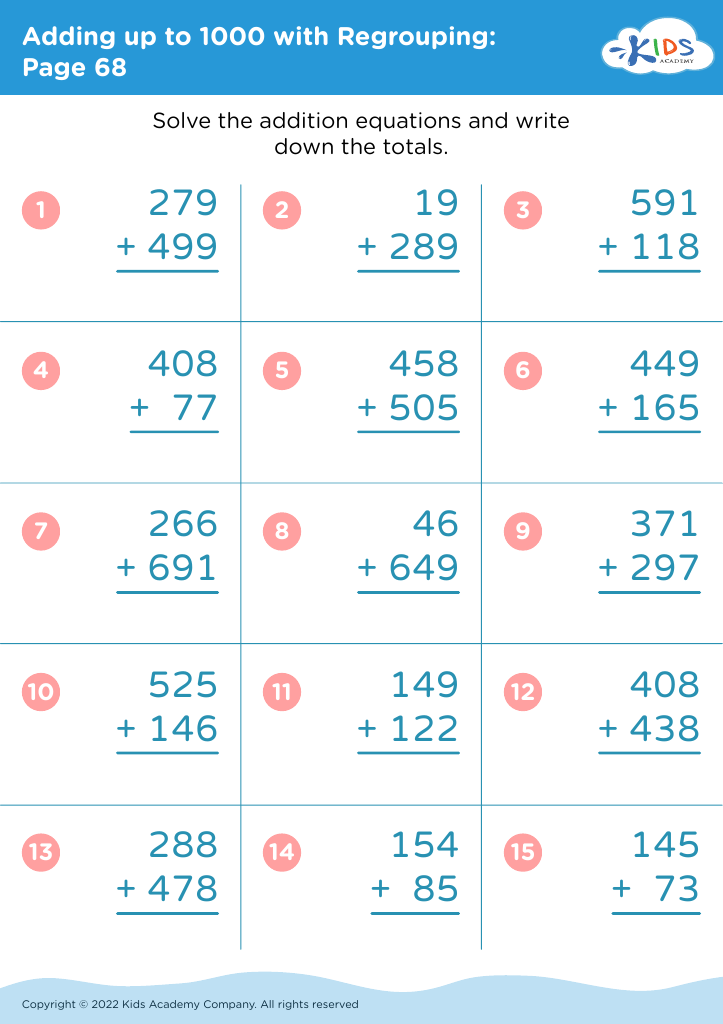
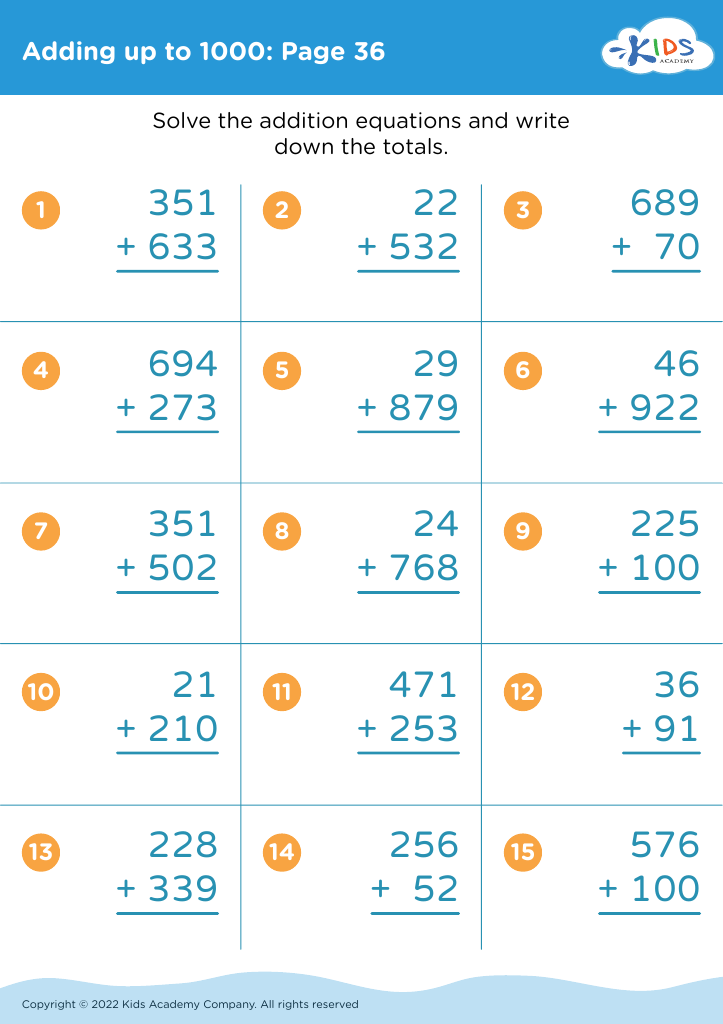
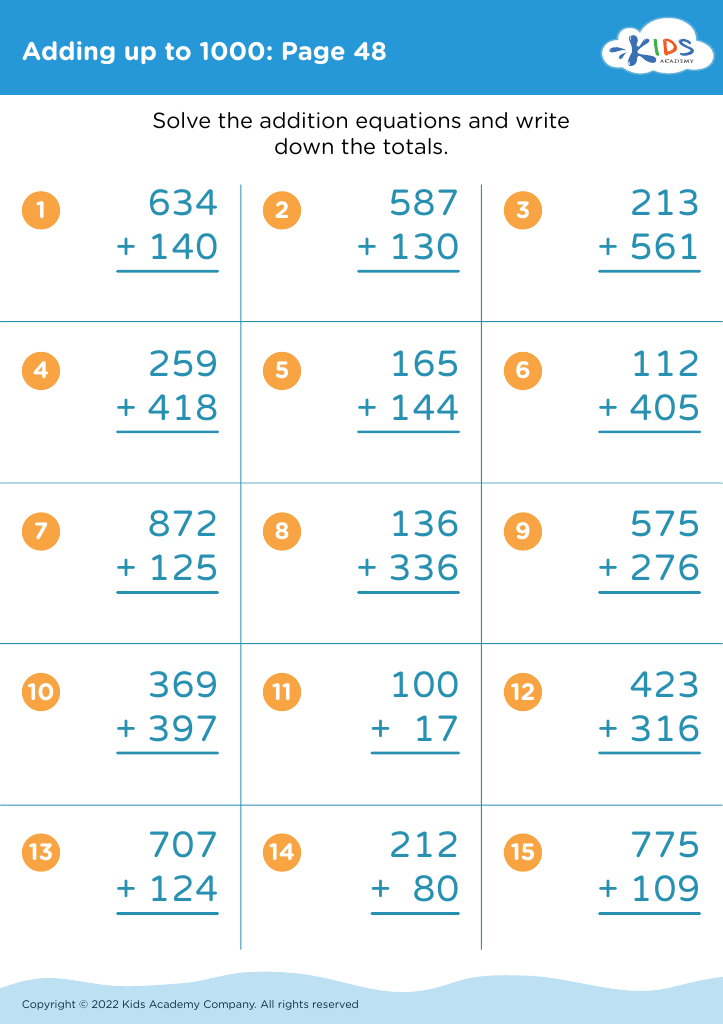
Adding up to 1000 may seem ambitious for ages 3-7, but incorporating early numeracy-focused fine motor tasks, such as sorting small objects, stacking blocks, or tracing numbers, strengthens cognitive abilities and aids in understanding numerical concepts. These activities blend counting with physical dexterity, creating a powerful dual-impact learning experience. As children experiment with these tasks, their problem-solving skills, concentration, and perseverance start to flourish.
For parents and teachers, prioritizing fine motor skill development does more than just support academic success—it boosts self-esteem, fosters independence, and promotes critical brain development. As children gain confidence in their tiny achievements, they build a robust foundation for more complex skills and concepts, setting the stage for lifelong learning and success.