Handwriting practice ABC Letters Worksheets for Ages 3-8 - Page 2
26 filtered results
-
From - To


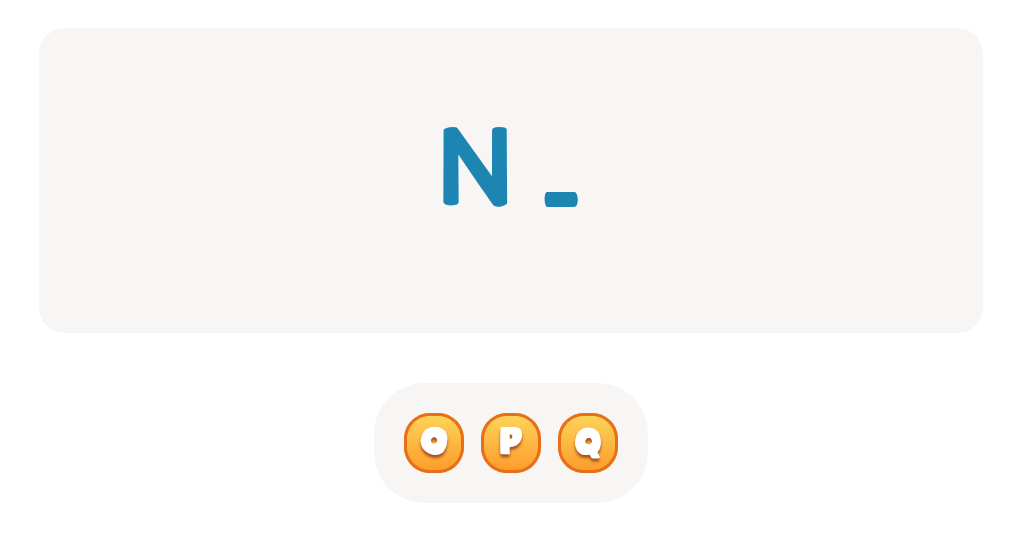
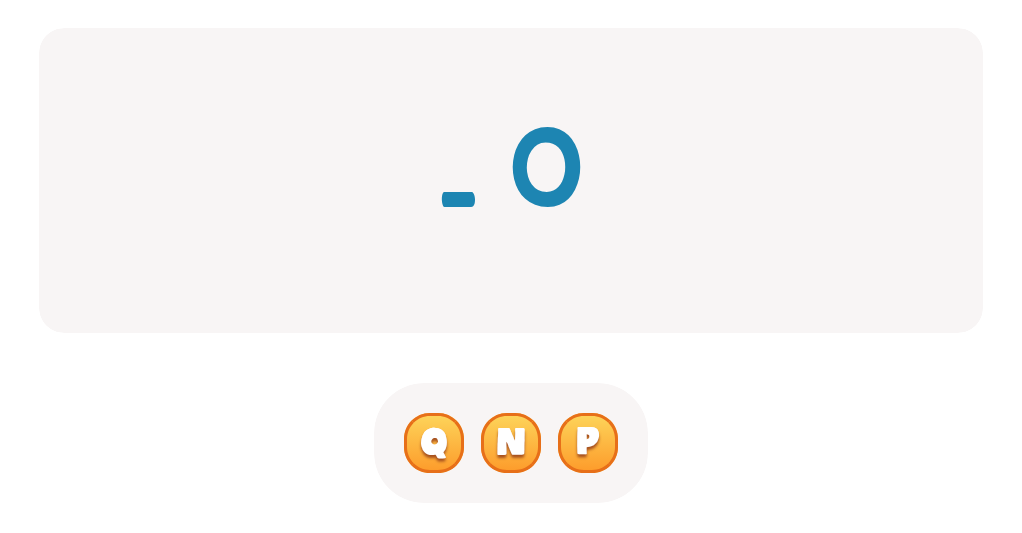
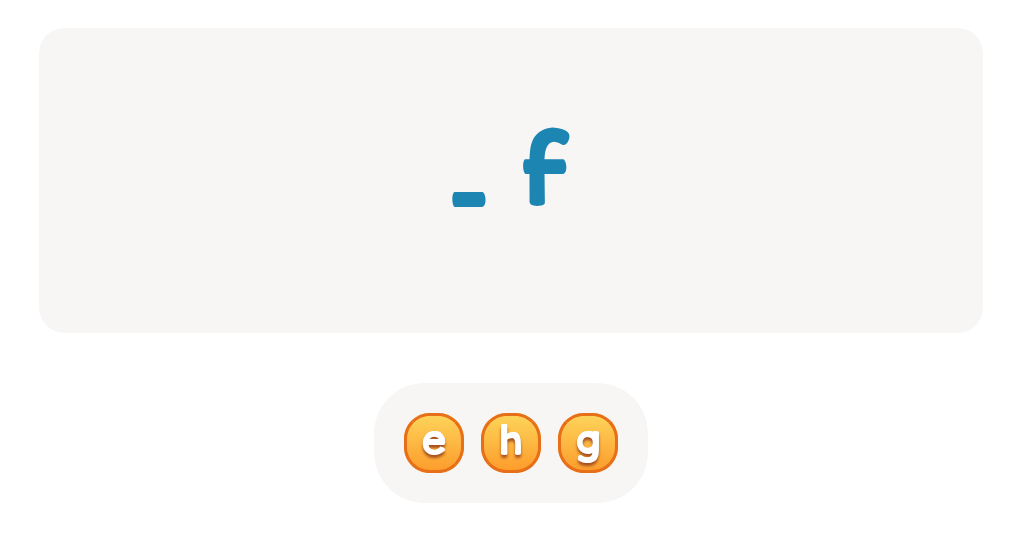
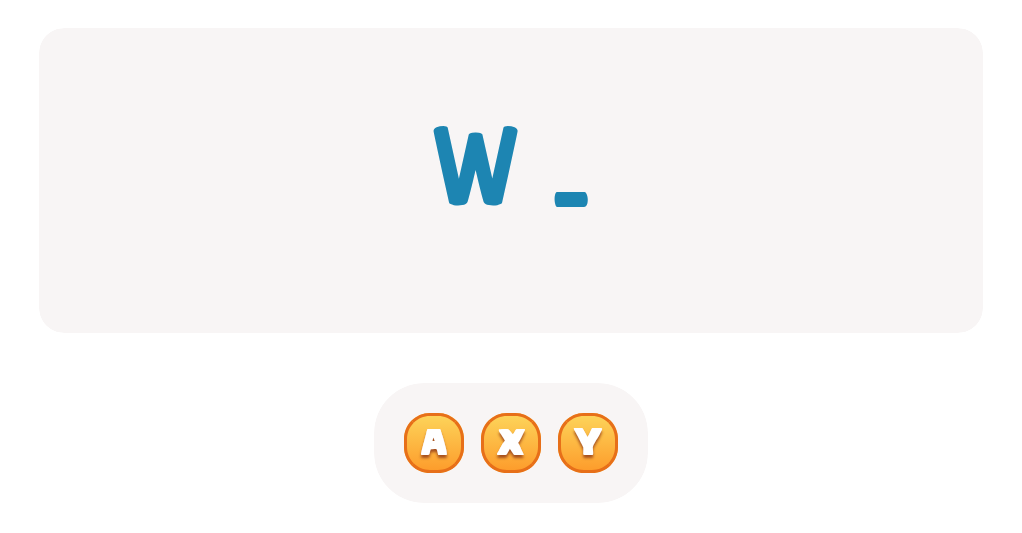
Letter N Coloring Sheet


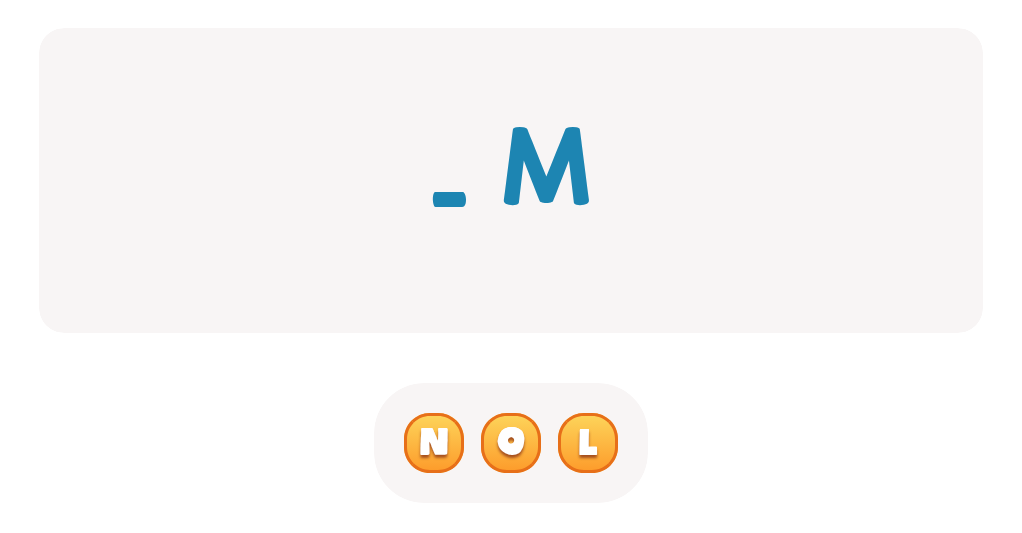
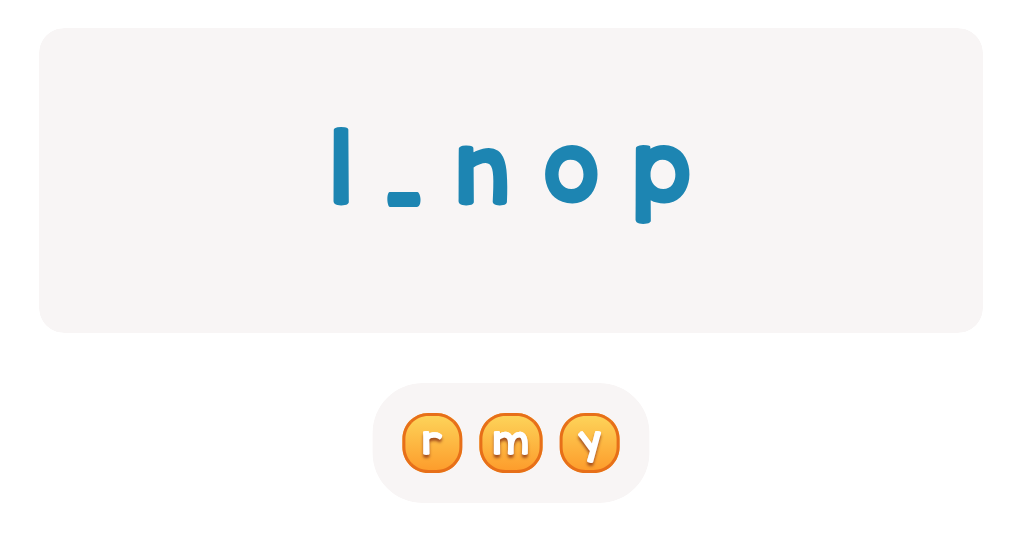
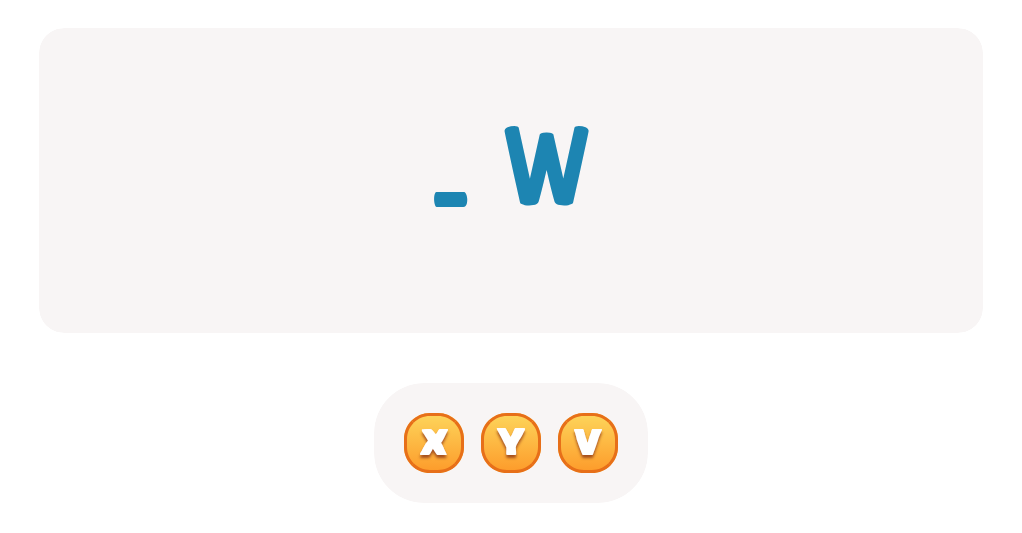
My Name: Cheerful Balloons Worksheet
Handwriting practice is essential for children aged 3-8 as it significantly impacts their overall academic development and fine motor skills. During these formative years, children are not only mastering the shapes of letters but also developing the muscular control needed for writing. Engaging in handwriting practice enhances their hand-eye coordination, which is crucial for tasks beyond writing, such as drawing and later using tools like scissors.
Furthermore, handwriting supports cognitive development. The process of forming letters helps children understand the connection between sounds and symbols, aiding their literacy skills. As they practice, they improve their spelling, vocabulary, and reading comprehension, laying a solid foundation for future learning.
Additionally, consistent handwriting practice fosters discipline and perseverance. It encourages children to take pride in their work as they see improvements over time. This sense of achievement can boost their confidence and encourage a lifelong love for learning.
Finally, with the advent of digital devices, emphasis on handwriting may wane, but it remains a vital skill in configuring personal expression and communication. Parents and teachers should prioritize handwriting practice in children’s education, ensuring they develop the necessary skills for effective communication and academic success.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students