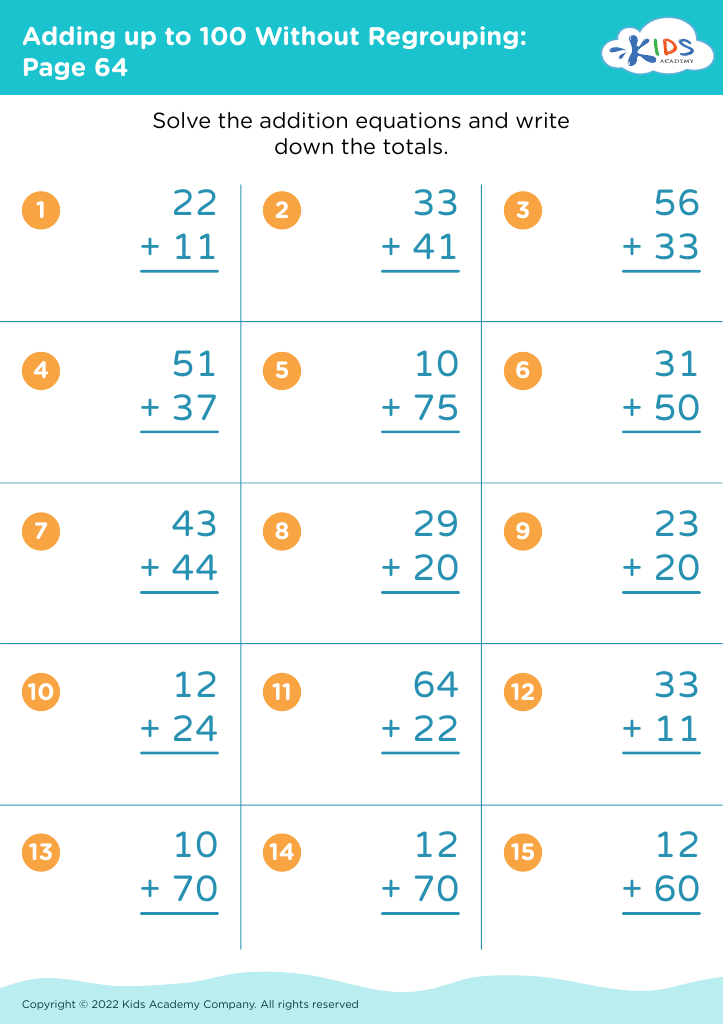
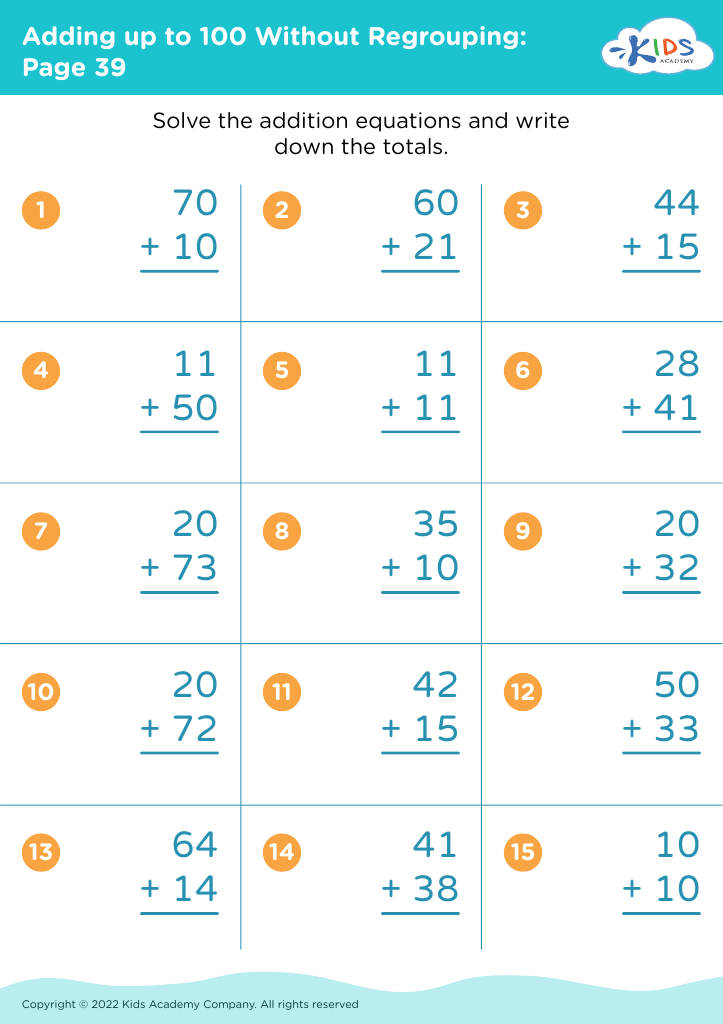
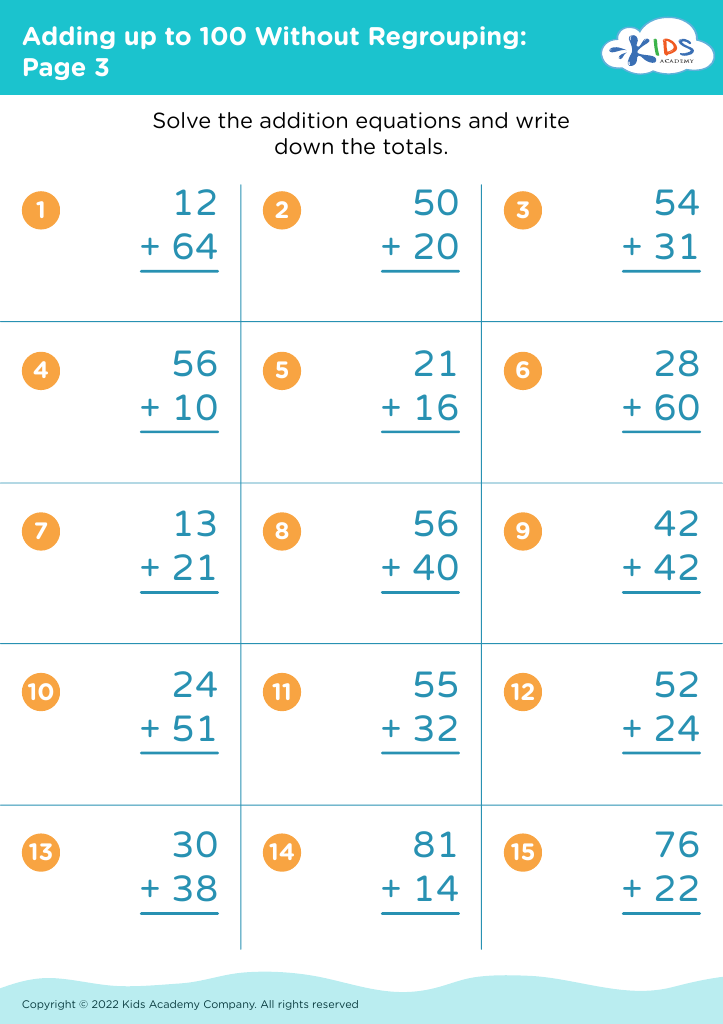
Improve counting skills Adding up to 100 Without Regrouping Worksheets for Ages 3-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child’s counting skills with our "Adding Up to 100 Without Regrouping Worksheets," specially designed for ages 3-8. These engaging worksheets provide a fun, interactive approach to learning basic addition concepts without the complexities of regrouping. Children will build confidence as they practice adding numbers to reach sums up to 100, reinforcing critical early math skills. Aligned with educational standards, our worksheets cater to different learning styles, making math enjoyable and accessible. Foster a solid foundation in arithmetic while encouraging a love for learning with these carefully crafted resources. Start your child's mathematical journey today!
Improving counting skills, especially for adding up to 100 without regrouping, is crucial for children aged 3-8 for several reasons. First, foundational math skills foster confidence in young learners. Mastering counting and basic addition provides a strong base for more complex mathematical concepts in later grades. It helps children develop number sense, which is the ability to understand and manipulate numbers effectively.
Moreover, counting and addition skills impact daily life. Children often encounter situations where they need to count, such as during snack time, games, or shopping. Proficient counting enables them to engage in these activities independently and enhances their problem-solving skills.
Besides cognitive development, working on counting skills can also improve fine motor skills during hands-on activities like using counting beads or manipulatives. It can become a fun, engaging experience if parents and teachers incorporate games and interactive methods into their teaching, nurturing a positive attitude towards math.
Lastly, early mastery of counting creates a solid framework for lifelong learning. As children advance in skills, they will find more complex mathematics easier to comprehend, thereby increasing their chances of academic success. Investing time in these basic skills today pays dividends as they grow and learn.