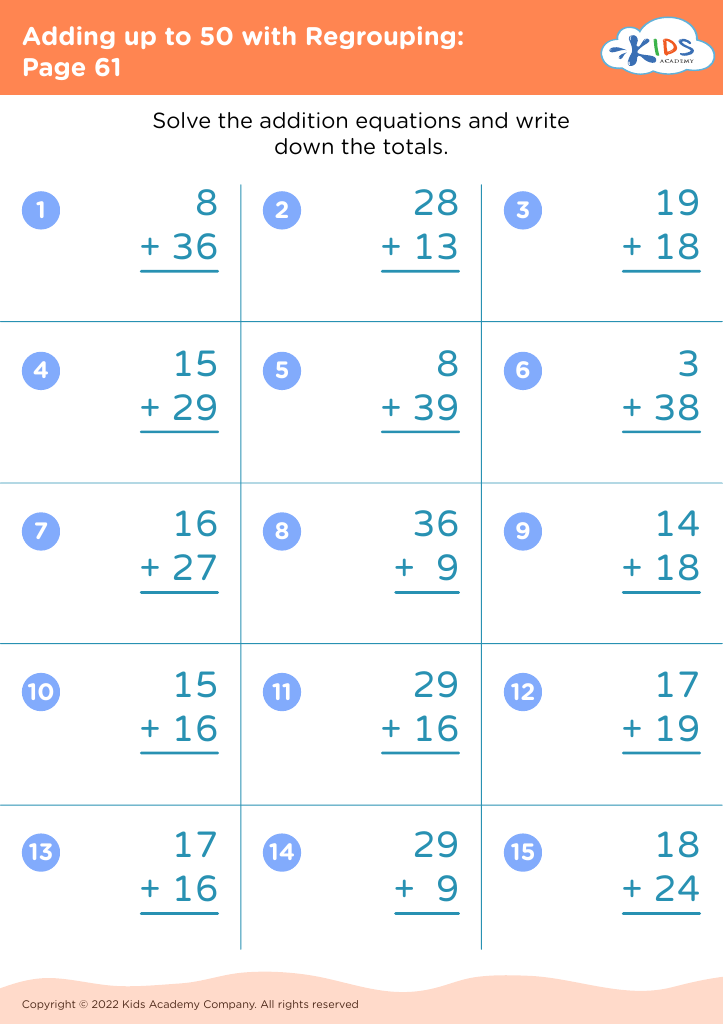
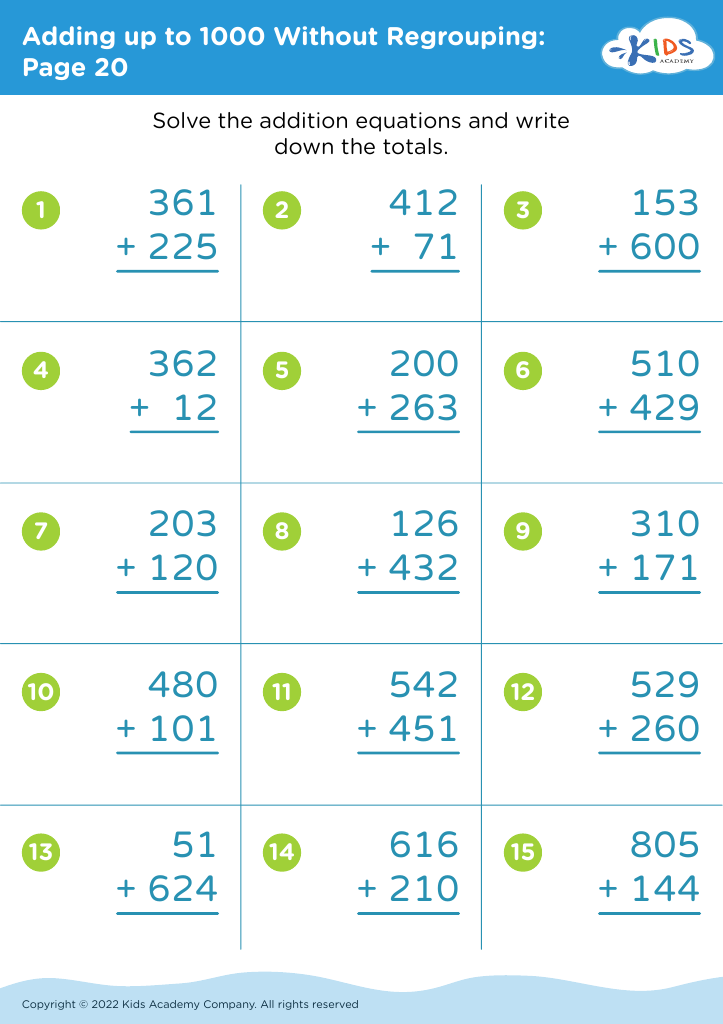
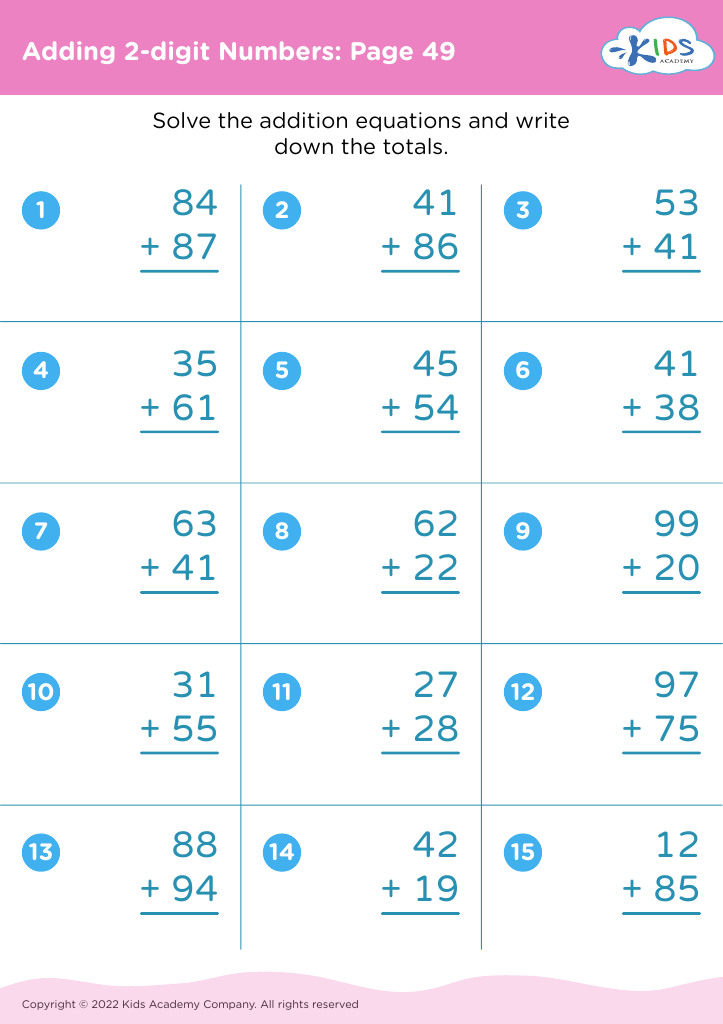
Practice inference skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Practice Inference Skills" addition and subtraction worksheets are designed for children ages 3-8 and help to build essential math skills. These engaging and educational worksheets provide fun problems that enhance children's abilities to infer, analyze, and solve simple arithmetic problems. By integrating these worksheets into daily learning routines, kids can make better logical connections, boosting both confidence and academic performance. Aligned with early education standards, our worksheets support parents and teachers in developing critical thinking and foundational math skills in young learners. Make math enjoyable and effective with our professionally designed practice sheets!
Parents and teachers should care about practicing inference skills in addition and subtraction for children ages 3-8 because these skills form the foundation of early mathematical understanding and literacy. At this young age, children are developing critical cognitive abilities that influence their overall learning trajectory. Inference skills help children read between the lines, understand context, and apply logic to solve problems, which are crucial for both math and general comprehension.
Practice with addition and subtraction aids in building number sense, which is the ability to understand, relate, and connect numbers. This is essential for higher-level math concepts they will encounter later in their academic journey. By integrating inference skills, children learn to approach problems analytically and develop strategies for finding solutions rather than just memorizing processes.
Early exposure to these skills promotes critical thinking and boosts confidence in mathematical abilities. Children learn pattern recognition, the concept of grouping, and the importance of accuracy. Engaging in these activities captures their natural curiosity and fosters a love for learning. Overall, consistent practice in these areas ensures that children gain a strong, intuitive grasp of basic math operations, setting the stage for future academic success and making everyday tasks more manageable.