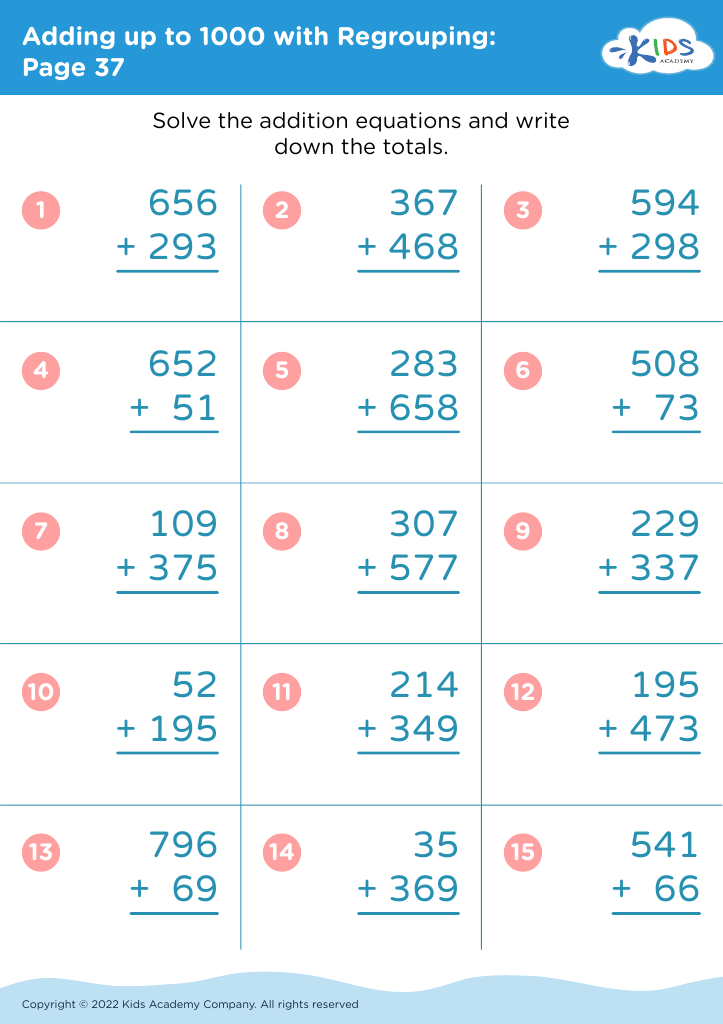
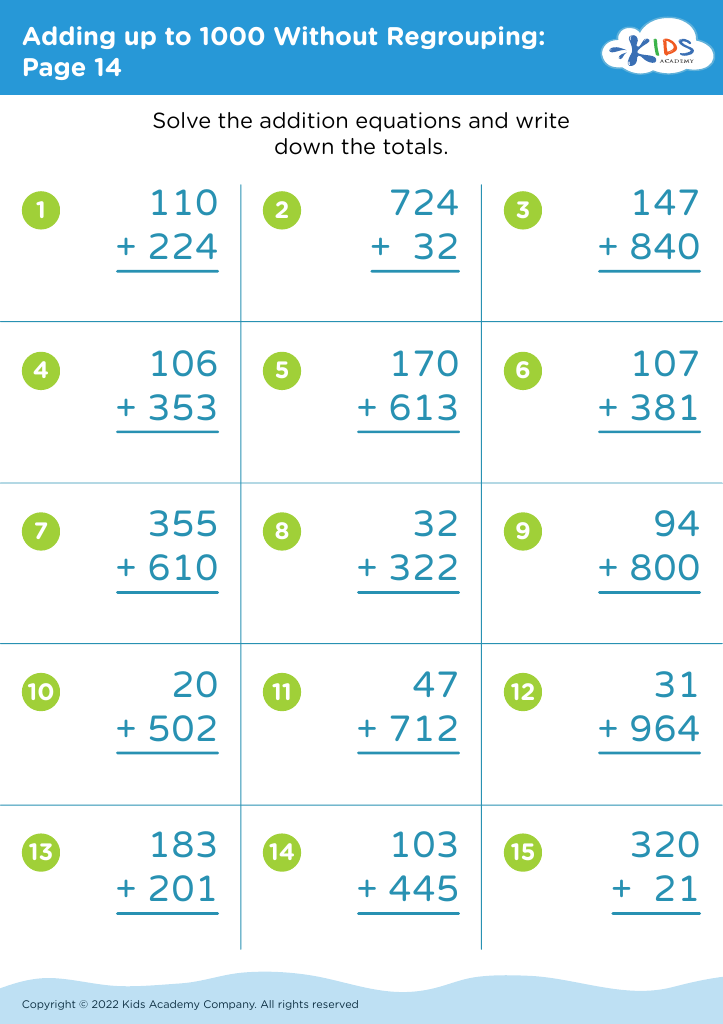
Fine motor skills development Addition Worksheets for Ages 3-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's fine motor skills while they learn addition with our engaging worksheets designed for ages 3-8. These printable activities not only promote early math proficiency but also foster the development of essential dexterity. Each worksheet features fun, interactive tasks that challenge young learners to trace numbers, manipulate objects, and complete exciting puzzles. As they practice addition, your child will strengthen their hand-eye coordination and grip, vital for future writing skills. Parents and educators alike will appreciate the balance of learning and play that our fine motor skills development addition worksheets provide. Start their journey to math mastery today!
Fine motor skills development is crucial for children aged 3-8, as these skills form the foundation for essential tasks in everyday life, such as writing, buttoning clothes, and using utensils. Parents and teachers should care about this aspect of development because fine motor skills significantly influence academic success and self-confidence.
Strengthening fine motor skills through engaging activities—like cutting, drawing, and manipulating small objects—helps improve hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and grip strength. These activities also promote cognitive growth, enhancing problem-solving and concentration abilities. As children develop these skills, they gain greater control over their movements, setting the stage for more complex tasks in the future.
Moreover, fine motor skills are closely linked to emotional and social development. Children who can successfully complete tasks like drawing or assembling puzzles often experience increased self-esteem and a sense of accomplishment. This boosts their willingness to participate in group activities and enhances cooperative play.
Ultimately, supporting fine motor skills development helps children build a variety of skills necessary for school readiness and lifelong learning, making it a vital focus for parents and teachers during these formative years.