Handwriting improvement Addition Worksheets for Ages 3-8
4 filtered results
-
From - To
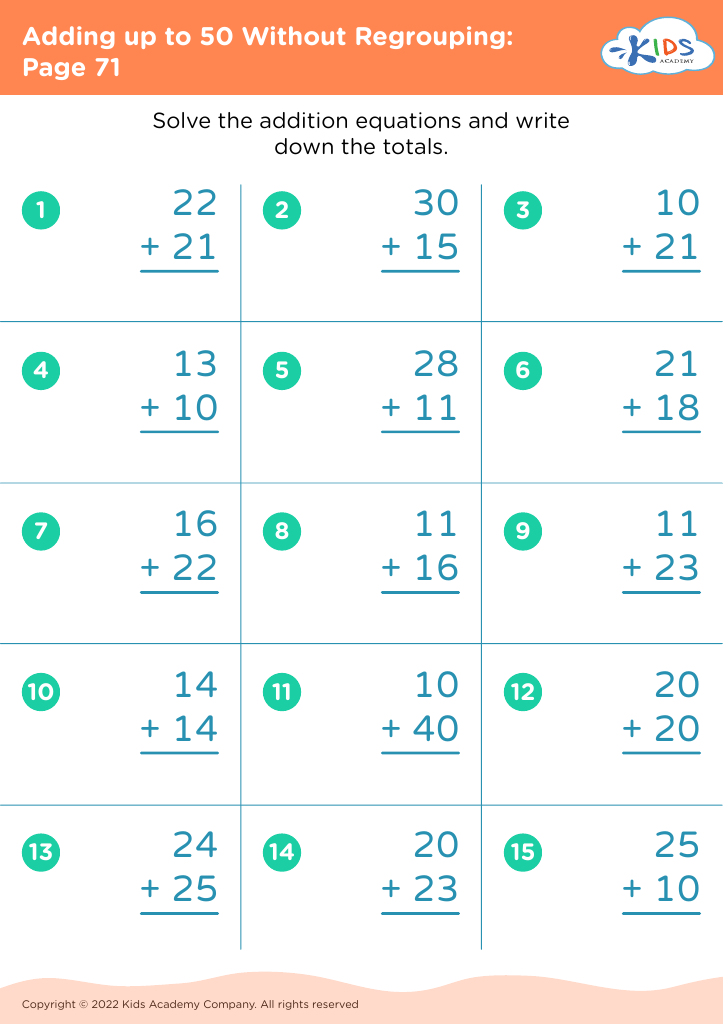
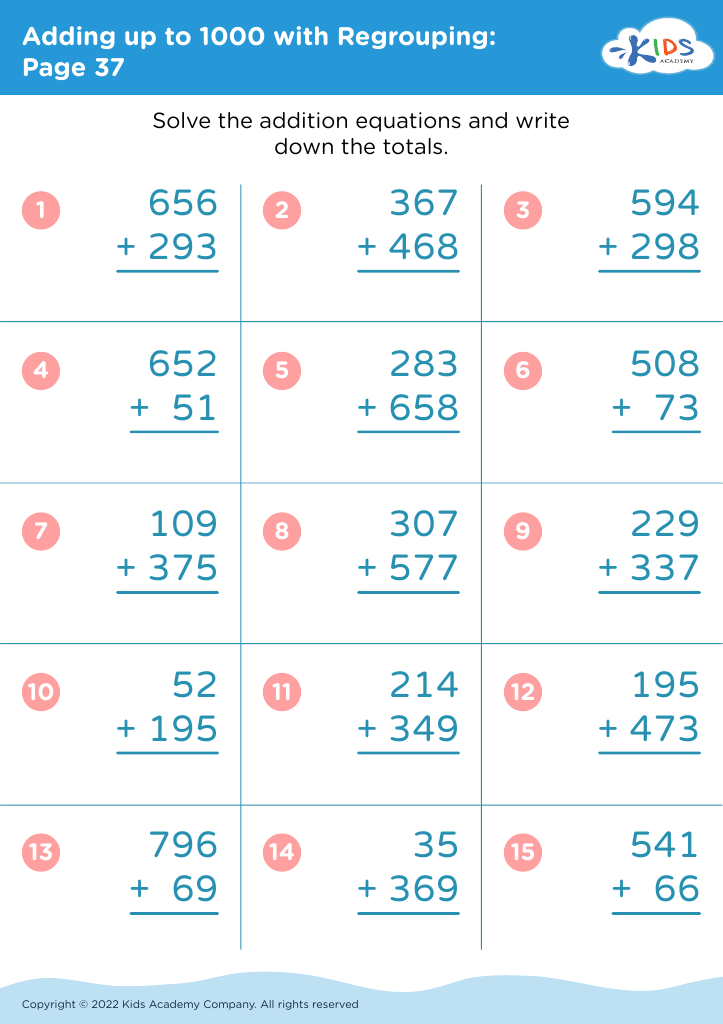
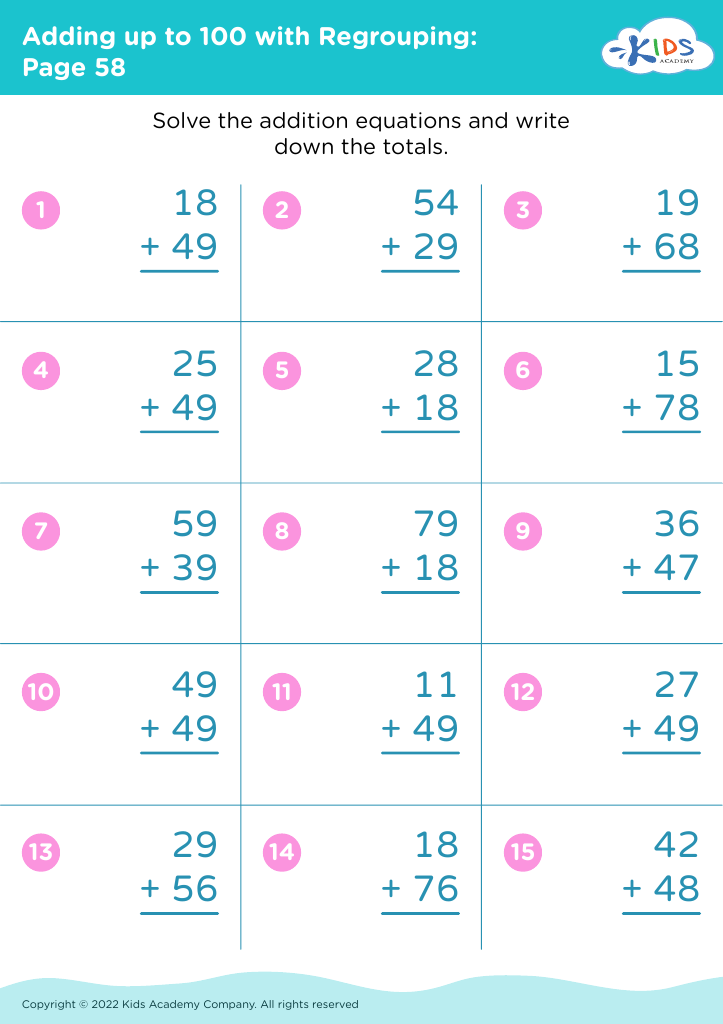
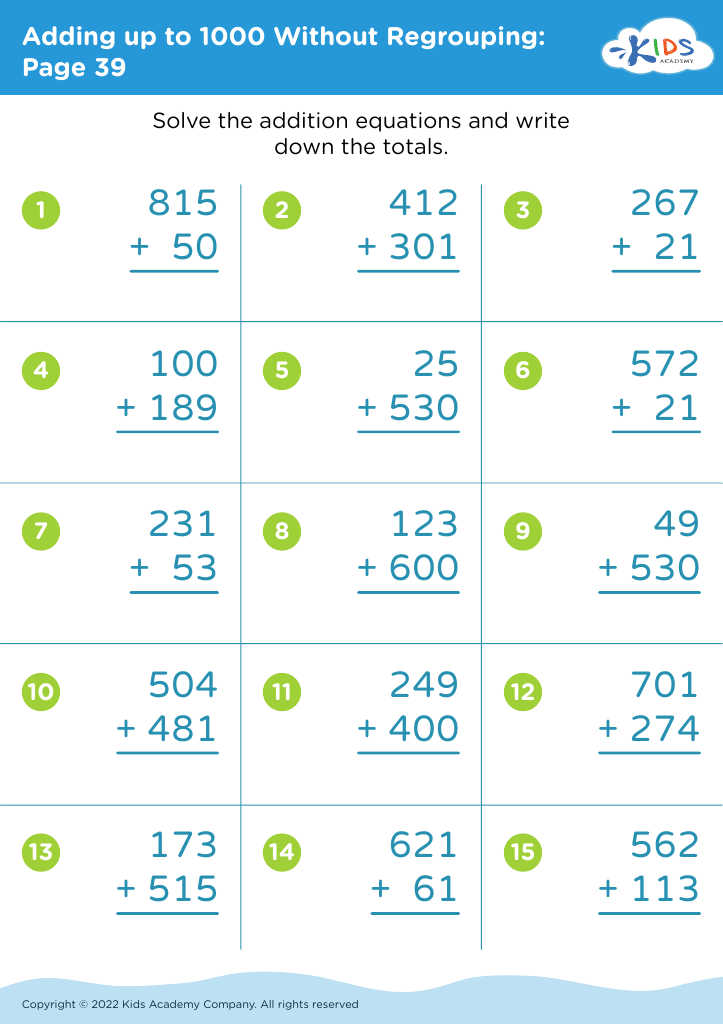
Welcome to our Handwriting Improvement Addition Worksheets designed specifically for children aged 3-8! These engaging, printable worksheets combine essential math skills with handwriting practice, making learning both fun and effective. Our carefully crafted activities focus on enhancing letter formation and pencil grip while promoting early addition concepts. With colorful illustrations and age-appropriate exercises, kids will develop their writing and math abilities simultaneously. Ideal for homeschool or classroom use, these worksheets encourage confidence and skill mastery in young learners. Explore our collection to help your child enjoy the journey of learning through playful practice and vibrant exercises!
Handwriting improvement in early childhood, particularly for children ages 3-8, is crucial for several reasons. First, developing strong handwriting skills lays the foundation for effective communication. As children learn to express themselves through writing, they gain confidence in their literacy abilities, enhancing their overall academic performance.
Fine motor skills, which are critical for handwriting, also contribute to other essential developmental areas. By practicing handwriting, children strengthen their hand-eye coordination and dexterity, skills that are beneficial in tasks beyond writing, such as drawing, using utensils, and participating in sports.
Furthermore, the process of writing itself fosters cognitive development. As children learn letter formation and practice writing, they engage in problem-solving and enhance their understanding of letters, sounds, and vocabulary. Improved handwriting also translates to better organization and clarity in their work, making it easier for teachers to assess their understanding and provide feedback.
Parents and educators should be proactive in supporting handwriting improvement, as it not only impacts literacy and academic success but also contributes to self-esteem and overall cognitive and motor development. Investing in good handwriting practices during these formative years sets children on a path toward lifelong learning and communication skills.