Visual perception Math Worksheets for Ages 3-8 - Page 3
57 filtered results
-
From - To


Bugs Counting Worksheet


Which Wagons Have 1 Less? Worksheet


Enrichment: Castle Counting Worksheet
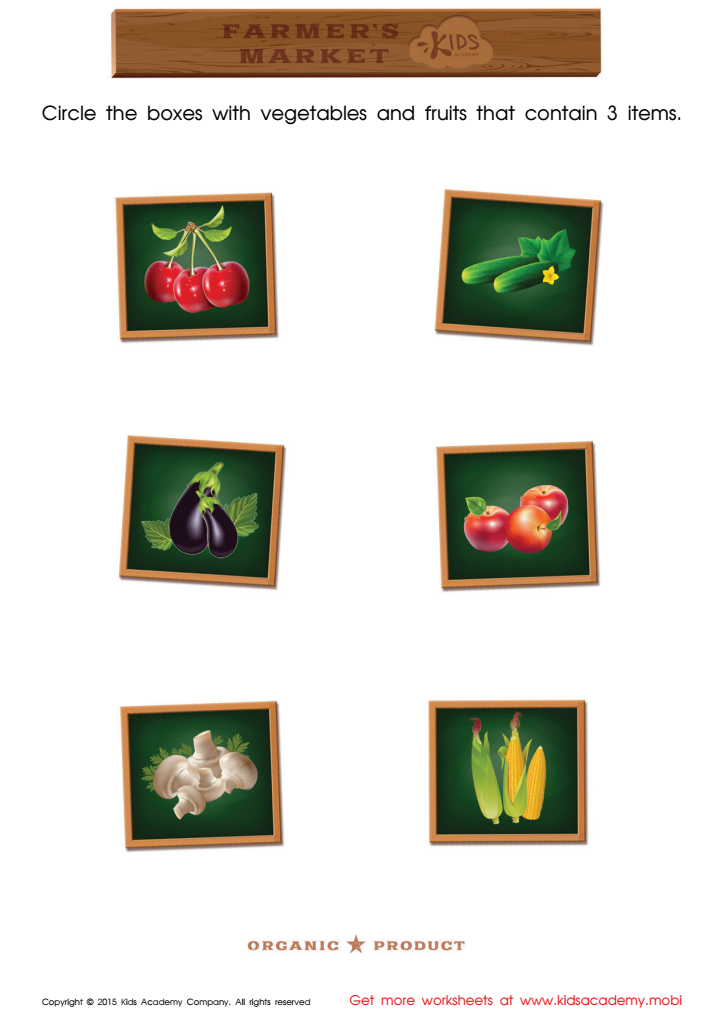


Count and Match Vegetables 1 – 5 Math Worksheet


Classifying by Size Sorting Worksheet
Visual perception math is foundational for children ages 3-8 and plays a crucial role in their overall cognitive development. Parents and teachers should care about this because it assists children in recognizing and understanding patterns, shapes, and spatial relationships, which are essential building blocks for math skills.
At these early ages, children are highly receptive to visual stimuli. Engaging them in visual perception activities helps improve their ability to discern differences and similarities among shapes and symbols, an ability vital for number recognition and later complex math operations. Visual perception skills also enhance children's visual memory, aiding their capacity to remember and reproduce sequences, another critical component in mathematical reasoning.
Moreover, strengthening visual perception paves the way for improved hand-eye coordination and fine motor skills. Activities that involve puzzles, matching games, and drawing can boost a child's dexterity and focus, foster critical thinking, and engage them more deeply in their learning environment.
On a broader scale, visual perception math skills help children develop problem-solving strategies that extend beyond academics, such as navigating spaces and understanding abstract concepts. This comprehensive growth reduces future learning obstacles and sets a strong foundation for lifelong learning and problem-solving abilities. Therefore, investing in visual perception activities safeguards a child's academic and holistic development.


 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students